Preface
This tutorial is a guide to developing enterprise applications for the JavaTM Platform, Enterprise Edition 5 (Java EE 5).
This preface contains information about and conventions for the entire Sun Java System Application Server documentation set.
Before You Read This Book
Before proceeding with this tutorial, you should have a good knowledge of the Java programming language. A good way to get to that point is to work through The Java Tutorial, Fourth Edition, Sharon Zakhour et al. (Addison-Wesley, 2006). You should also be familiar with the Java DataBase Connectivity (JDBCTM) and relational database features described in JDBC API Tutorial and Reference, Third Edition, Maydene Fisher et al. (Addison-Wesley, 2003).
How This Book Is Organized
The Java EE 5 platform is quite large, and this tutorial reflects this. However, you don’t have to digest everything in it at once. The tutorial has been divided into parts to help you navigate the content more easily.
This tutorial opens with an introductory chapter, which you should read before proceeding to any specific technology area. Chapter 1, Overview covers the Java EE 5 platform architecture and APIs, the Sun Java System Application Server 9.1, and how to use the this tutorial's examples.
When you have digested the basics, you can delve into one or more of the five main technology areas listed next. Because there are dependencies between some of the chapters, Figure P–1 contains a roadmap for navigating through the tutorial.
-
The web-tier technology chapters in Part II, The Web Tier cover the components used in developing the presentation layer of a Java EE 5 or stand-alone web application:
-
Java Servlet
-
JavaServer PagesTM (JSPTM)
-
JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL)
-
JavaServerTM Faces
-
Web application internationalization and localization
-
-
The web services technology chapters in Part III, Web Services cover the APIs used in developing standard web services:
-
The Java API for XML-based Web Services (JAX-WS)
-
The Java API for XML Binding (JAXB)
-
The Streaming API for XML (StAX)
-
The SOAP with Attachments API for JavaTM (SAAJ)
-
-
The Enterprise JavaBeansTM (EJBTM) technology chapters in Part IV, Enterprise Beans cover the components used in developing the business logic of a Java EE 5 application:
-
Session beans
-
Message-driven beans
-
-
The persistence technology chapters in Part V, Persistence cover the Java Persistence API, which is used for accessing databases from Java EE applications:
-
Introduction to the Java Persistence API
-
Persistence in the Web Tier
-
Persistence in the EJB Tier
-
The Java Persistence Query Language
-
-
The platform services chapters in Part VI, Services cover the system services used by all the Java EE 5 component technologies:
-
Security
-
Java Message Service
-
Transactions
-
Resource connections
-
The Java EE Connector Architecture
-
Figure P–1 Roadmap to This Tutorial
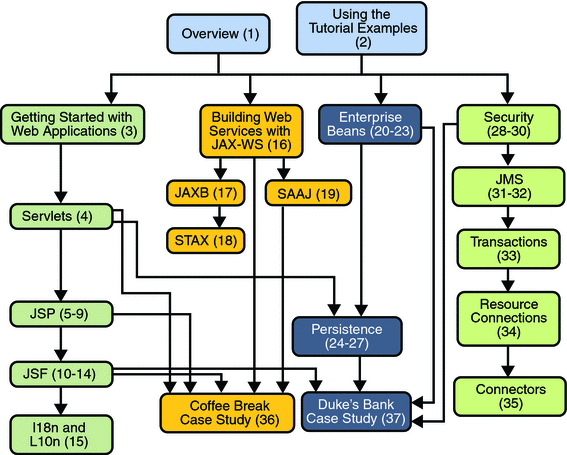
After you have become familiar with some of the technology areas, you are ready to tackle the case studies in Part VII, Case Studies, which tie together several of the technologies discussed in the tutorial. The Coffee Break Application describes an application that uses the web application and web services APIs. The Duke’s Bank Application describes an application that employs web application technologies, enterprise beans, and the Java Persistence API.
Finally, Part VIII, Appendixes contains information about Java encoding schemes and Java EE certification that may be helpful to the Java EE 5 application developer, and information about the tutorial's authors.
Application Server Documentation Set
The Application Server documentation set describes deployment planning and system installation. The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) for Application Server documentation is http://docs.sun.com/coll/1343.4. For an introduction to Application Server, refer to the books in the order in which they are listed in the following table.
Table P–1 Books in the Application Server Documentation Set|
Book Title |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Documentation Center |
Application Server documentation topics organized by task and subject. |
|
Release Notes |
Late-breaking information about the software and the documentation. Includes a comprehensive, table-based summary of the supported hardware, operating system, Java Development Kit (JDKTM), and database drivers. |
|
Quick Start Guide |
How to get started with the Application Server product. |
|
Installation Guide |
Installing the software and its components. |
|
Deployment Planning Guide |
Evaluating your system needs and enterprise to ensure that you deploy the Application Server in a manner that best suits your site. General issues and concerns that you must be aware of when deploying the server are also discussed. |
|
Application Deployment Guide |
Deployment of applications and application components to the Application Server. Includes information about deployment descriptors. |
|
Developer’s Guide |
Creating and implementing Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE platform) applications intended to run on the Application Server that follow the open Java standards model for Java EE components and APIs. Includes information about developer tools, security, debugging, and creating lifecycle modules. |
|
Java EE 5 Tutorial |
Using Java EE 5 platform technologies and APIs to develop Java EE applications. |
|
Java WSIT Tutorial |
Developing web applications using the Web Service Interoperability Technologies (WSIT). Describes how, when, and why to use the WSIT technologies and the features and options that each technology supports. |
|
Administration Guide |
System administration for the Application Server, including configuration, monitoring, security, resource management, and web services management. |
|
High Availability Administration Guide |
Post-installation configuration and administration instructions for the high-availability database. |
|
Administration Reference |
Editing the Application Server configuration file, domain.xml. |
|
Upgrade and Migration Guide |
Upgrading from an older version of Application Server or migrating Java EE applications from competitive application servers. This guide also describes differences between adjacent product releases and configuration options that can result in incompatibility with the product specifications. |
|
Performance Tuning Guide |
Tuning the Application Server to improve performance. |
|
Troubleshooting Guide |
Solving Application Server problems. |
|
Error Message Reference |
Solving Application Server error messages. |
|
Reference Manual |
Utility commands available with the Application Server; written in man page style. Includes the asadmin command line interface. |
Related Documentation
Application Server can be purchased by itself or as a component of Sun Java Enterprise System (Java ES), a software infrastructure that supports enterprise applications distributed across a network or Internet environment. If you purchased Application Server as a component of Java ES, you should be familiar with the system documentation at http://docs.sun.com/coll/1286.3. The URL for all documentation about Java ES and its components is http://docs.sun.com/prod/entsys.5.
For documentation about other stand-alone Sun Java System server products, go to the following:
A JavadocTM tool reference for packages provided with the Application Server is located at http://glassfish.dev.java.net/nonav/javaee5/api/index.html. Additionally, the following resources might be useful:
For information on creating enterprise applications in the NetBeansTM Integrated Development Environment (IDE), see http://www.netbeans.org/kb/55/index.html.
For information about the Java DB database included with the Application Server, see http://developers.sun.com/javadb/.
The GlassFish Samples project is a collection of sample applications that demonstrate a broad range of Java EE technologies. The GlassFish Samples are bundled with the Java EE Software Development Kit (SDK), and are also available from the GlassFish Samples project page at https://glassfish-samples.dev.java.net/.
Default Paths and File Names
The following table describes the default paths and file names that are used in this book.
Table P–2 Default Paths and File Names|
Placeholder |
Description |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|
|
tut-install |
Represents the base installation directory for the Java EE Tutorial. |
None. Install the tutorial in a directory without spaces in the path. |
|
java-home |
Represents the base installation directory for the Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE platform). |
None. Same value as the JAVA_HOME environment variable. |
|
as-install |
Represents the base installation directory for the Application Server or the Software Development Kit (SDK) of which the Application Server is a part. |
Java ES installations on the SolarisTM operating system: /opt/SUNWappserver/appserver Java ES installations on the Linux operating system: /opt/sun/appserver/ Other Solaris and Linux non-SDK installations, non-root user: user’s-home-directory/SUNWappserver Other Solaris and Linux non-SDK installations, root user: /opt/SUNWappserver Solaris and Linux SDK installations: user’s-home-directory/SDK Windows, all non-SDK installations: SystemDrive:\Sun\AppServer Windows, all SDK installations: SystemDrive:\Sun\SDK |
|
domain-root-dir |
Represents the directory containing all Application Server domains. |
Java ES Solaris installations: /var/opt/SUNWappserver/domains/ Java ES Linux installations: /var/opt/sun/appserver/domains/ All other installations: as-install/domains/ |
|
domain-dir |
Represents the directory for a domain. In configuration files, you might see domain-dir represented as follows: ${com.sun.aas.instanceRoot} |
domain-root-dir/domain-dir |
|
instance-dir |
Represents the directory for a server instance. |
domain-dir/instance-dir |
Typographic Conventions
The following table describes the typographic changes that are used in this book.
Table P–3 Typographic Conventions|
Typeface |
Meaning |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
AaBbCc123 |
The names of commands, files, and directories, and onscreen computer output |
Edit your .login file. Use ls -a to list all files. machine_name% you have mail. |
|
AaBbCc123 |
What you type, contrasted with onscreen computer output |
machine_name% su Password: |
|
AaBbCc123 |
A placeholder to be replaced with a real name or value |
The command to remove a file is rm filename. |
|
AaBbCc123 |
Book titles, new terms, and terms to be emphasized (note that some emphasized items appear bold online) |
Read Chapter 6 in the User's Guide. A cache is a copy that is stored locally. Do not save the file. |
Symbol Conventions
The following table explains symbols that might be used in this book.
Table P–4 Symbol Conventions|
Symbol |
Description |
Example |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
|
[ ] |
Contains optional arguments and command options. |
ls [-l] |
The -l option is not required. |
|
{ | } |
Contains a set of choices for a required command option. |
-d {y|n} |
The -d option requires that you use either the y argument or the n argument. |
|
${ } |
Indicates a variable reference. |
${com.sun.javaRoot} |
References the value of the com.sun.javaRoot variable. |
|
- |
Joins simultaneous multiple keystrokes. |
Control-A |
Press the Control key while you press the A key. |
|
+ |
Joins consecutive multiple keystrokes. |
Ctrl+A+N |
Press the Control key, release it, and then press the subsequent keys. |
|
-> |
Indicates menu item selection in a graphical user interface. |
File -> New -> Templates |
From the File menu, choose New. From the New submenu, choose Templates. |
Documentation, Support, and Training
The Sun web site provides information about the following additional resources:
Searching Sun Product Documentation
Besides searching Sun product documentation from the docs.sun.comSM web site, you can use a search engine by typing the following syntax in the search field:
search-term site:docs.sun.com |
For example, to search for “broker,” type the following:
broker site:docs.sun.com |
To include other Sun web sites in your search (for example, java.sun.com, www.sun.com, and developers.sun.com), use sun.com in place of docs.sun.com in the search field.
Third-Party Web Site References
Third-party URLs are referenced in this document and provide additional, related information.
Note –
Sun is not responsible for the availability of third-party web sites mentioned in this document. Sun does not endorse and is not responsible or liable for any content, advertising, products, or other materials that are available on or through such sites or resources. Sun will not be responsible or liable for any actual or alleged damage or loss caused or alleged to be caused by or in connection with use of or reliance on any such content, goods, or services that are available on or through such sites or resources.
Sun Welcomes Your Comments
Sun is interested in improving its documentation and welcomes your comments and suggestions. To share your comments, go to http://docs.sun.com and click Send Comments. In the online form, provide the full document title and part number. The part number is a 7-digit or 9-digit number that can be found on the book's title page or in the document's URL. For example, the part number of this book is 819-3669.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
