x86: N+1 (Star) Topology
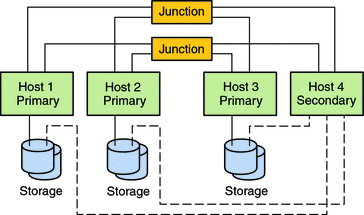
An N+1 topology includes some number of primary Solaris hosts and one secondary host. You do not have to configure the primary hosts and secondary host identically. The primary hosts actively provide application services. The secondary host need not be idle while waiting for a primary host to fail.
The secondary host is the only host in the configuration that is physically connected to all the multihost storage.
If a failure occurs on a primary host, Sun Cluster fails over the resources to the secondary host. The secondary host is where the resources function until they are switched back (either automatically or manually) to the primary host.
The secondary host must always have enough excess CPU capacity to handle the load if one of the primary hosts fails.
The following figure illustrates an N+1 configuration.
Figure 2–11 x86: N+1 Topology
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
