| Exit Print View | |
Sun OpenDS Standard Edition 2.0 Administration Guide |

|
Configuring the Directory Server
Configuring Security in the Directory Server
Managing Root User, Global Administrator, and Administrator Accounts
Working With Multiple Root Users
Root Users and the Privilege Subsystem
Managing Root Users With dsconfig
To View the Default Root User Privileges
To Edit the Default Root User Privileges
To Change a Root User's Password
To Change a Root User's Privileges
Setting Root User Resource Limits
Managing Global Administrators
Password Policies in a Replicated Environment
To View the List of Password Policies
Properties of the Default Password Policy
To View the Properties of the Default Password Policy
To Create a New Password Policy
To Create a First Login Password Policy
To Assign a Password Policy to an Individual Account
To Prevent Password Policy Modifications
To Assign a Password Policy to a Group of Users
To Change the Directory Manager's Password
To Reset and Generate a New Password for a User
Managing a User's Account Information
To View a User's Account Information
To View Account Status Information
Setting Resource Limits on a User Account
To Set Resource Limits on an Account
To Create a Static Group With groupOfNames
To Create a Static Group With groupOfUniqueNames
To Create a Static Group With groupOfEntries
To List All Members of a Static Group
To List All Static Groups of Which a User Is a Member
To Determine Whether a User is a Member of a Group
To List All Members of a Dynamic Group
To List All Dynamic Groups of Which a User Is a Member
To Determine Whether a User Is a Member of a Dynamic Group
Defining Virtual Static Groups
To Create a Virtual Static Group
To List All Members of a Virtual Static Group
To List All Virtual-Static Groups of Which a User Is a Member
To Determine Whether a User is a Member of a Virtual Static Group
Maintaining Referential Integrity
Overview of the Referential Integrity Plug-In
To Enable the Referential Integrity Plug-In
Simulating DSEE Roles in an OpenDS Directory Server
To Determine Whether a User is a Member of a Role
A virtual static group, efficiently manages scalability for clients that can only support static groups. In a virtual static group, each entry behaves like a static group entry by using virtual attributes. The virtual attributes are dynamically determined when invoked, and the operations that determine group membership are passed to another group, such as a dynamic group, as shown in the following diagram.
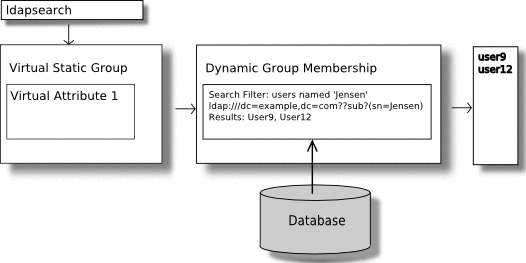
Virtual static groups should include either the groupOfNames or groupOfUniqueNames object class but should not include the member or uniqueMember attribute. Virtual static groups should also contain the ds-virtual-static-group auxiliary object class and the ds-target-group-dn attribute. The ds-target-group-dn attribute is used to reference the actual group to mirror as a virtual static group and is used in place of the member or uniquemember attribute. For example:
dn: cn=Example Virtual Static Group,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com objectClass: top objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames objectClass: ds-virtual-static-group cn: Example Virtual Static Group ds-target-group-dn: cn=Example Real Group,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com
Virtual static groups are most efficient when the application issues a search targeted at the membership attribute but does not actually retrieve the entire set of members. It is common for applications to use a filter such as the following to attempt to determine whether a user is a member of a given group:
(&(objectClass=groupOfUniqueNames)(uniqueMember=uid=john.doe,\ ou=People,dc=example,dc=com))
For applications that retrieve the set of members, virtual static groups might not be ideal because the process of constructing the entire member list can be expensive.
This sample file, virtual-static.ldif, specifies a virtual static group named cupertinoEmployees.
dn: cn=virtualStatic,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com cn: Virtual Static objectclass: top objectclass: groupOfUniqueNames objectclass: ds-virtual-static-group ou: Groups ds-target-group-dn: cn=cupertinoEmployees,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com
$ ldapmodify -h localhost -p 1389 -D "cn=Directory Manager" -w password \ --defaultAdd --filename virtual-static.ldif Processing ADD request for cn=virtualStatic,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com ADD operation successful for DN cn=virtualStatic,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com
Virtual static groups are best used in cases where the search is targeted at the membership attribute. This procedure is therefore not recommended but is included to show how to access the list.
This example procedure uses the dynamic group, cupertinoEmployees, created in the previous example.
$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1389 -D "cn=Directory Manager" -w password \
-b dc=example,dc=com "(isMemberOf=cn=virtualStatic,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com)"
dn: uid=abergin,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: person
objectClass: inetOrgPerson
objectClass: top
objectClass: organizationalPerson
ou: Product Testing
ou: People
sn: Bergin
facsimiletelephonenumber: +1 408 555 7472
roomnumber: 3472
userpassword: {SSHA}YcDl0pHLxkd/ouW2jslAk1XaT5SiY4ium5qh8w==
l: Cupertino
cn: Andy Bergin
telephonenumber: +1 408 555 8585
givenname: Andy
uid: abergin
mail: abergin@example.com
...(more entries)...$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1389 -D "cn=Directory Manager" -w password \ -b dc=example,dc=com "(uid=abergin)" isMemberOf dn: uid=abergin,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com isMemberOf: cn=QA Managers,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com isMemberOf: cn=cupertinoEmployees,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com isMemberOf: cn=virtualStatic,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com
$ ldapsearch -h localhost -p 1389 -D "cn=Directory Manager" -w password \ -b "cn=virtualStatic,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com" \ "(&(objectclass=groupOfUniqueNames) \ (uniquemember=uid=abergin,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com))" dn: cn=virtualStatic,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames objectClass: top objectClass: ds-virtual-static-group ou: Groups ds-target-group-dn: cn=cupertinoEmployees,ou=Groups,dc=example,dc=com cn: Virtual Static cn: virtualStatic