About the Administration Console
The console is divided into three frames: Header, Navigation and Data. The Header frame displays corporate branding information as well as the first and last name of the currently logged-in user as defined in their profile. It also contains a set of tabs to allow the user to switch between the management modules, a hyperlink to the Access Manager Help system, a Search function and a Logout link. The Navigation frame on the left displays the object hierarchy of the chosen management module, and the Data frame on the right displays the attributes of the object selected in the Navigation frame.
Figure 2–1 Legacy Mode Administration Console
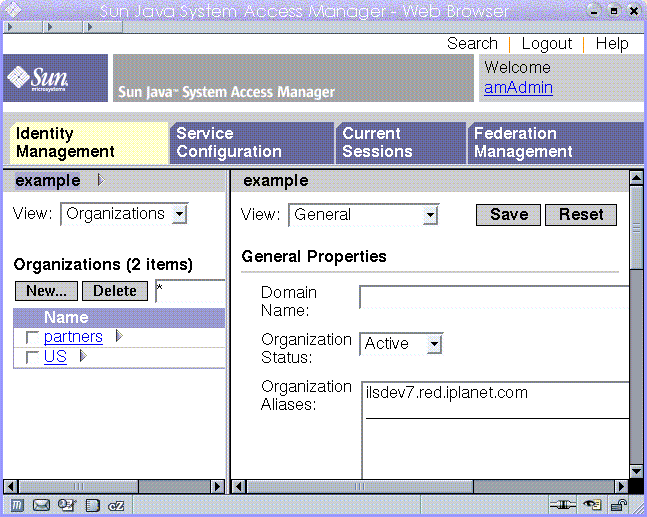
For information about what the Console does and about the differences between the Realm mode and Legacy mode console interfaces, see Chapter 4, The Access Manager Console, in Sun Java System Access Manager 7 2005Q4 Administration Guide.
Generating The Console Interface
When the Access Manager console receives an HTTP(S) request, it first determines whether the requesting user has been authenticated. If not, the user is redirected to the Access Manager login page supplied by the Authentication Service. After successful authentication, the user is redirected back to the console which reads all of the user’s available roles, and extracts the applicable permissions and behaviors. The console is then dynamically constructed for the user based on this information. For example, users with one or more administrative roles will see the administration console view while those without any administrative roles will see the end user console view. Roles also control the actions a user can perform and the identity objects that a user sees. Pertaining to the former, the organization administrator role allows the user read and write access to all objects within that organization while a help desk administrator role only permits write access to the users’ passwords. With regards to the latter, a person with a people container administrator role will only see users in the relevant people container while the organization administrator will see all identity objects. Roles also control read and write permissions for service attributes as well as the services the user can access.
Plug-In Modules
An external application can be plugged-in to the console as a module, gaining complete control of the Navigation and Data frames for its specific functionality. In this case, a tab with the name of the custom application needs to be added to the Header frame. The application developer would create the JSPs for both left and right frames, and all view beans, and models associated with them.
Accessing the Console
The Naming Service defines URLs used to access the internal services of Access Manager. The URL used to access the Administration Console web application is:
http://AcceessManager-HostName.domain_name:port/ amconsole
The first time Administration Console (amconsole) is accessed, it brings the user to the Authentication web application (amserver) for authentication and authorization purposes. After login, amserver redirects the user to the configured success login URL. The default successful login URL is:
http(s)://AcceessManager-HostName.domain_name:port/ amconsole/base/AMAdminFrame
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
