Configuring for Interoperation
The goal of the installation process is a system of interoperating component instances. When you install components and perform basic configuration, you supply configuration values that result in component instance interoperation.
The configuration values that result in interoperation include such values as the URLs or port numbers that one component instance uses to communicate with another component instance and the administrator account IDs and passwords that one component instance uses to authorize access to another component instance. For example, if your solution uses Access Manager, you must first install and configure an LDAP repository, such as a Directory Server instance. Then, when you install and configure an Access Manager instance, you must provide configuration values that tell the instance where to find the LDAP directory you prepared.
The Java ES installer does not know what components are installed on the other computers used in the solution. For example, when you install Access Manager, the installer does not know where the appropriate LDAP directory is located. To ensure the success of your installation and configuration process, you must plan in advance which components are installed on each computer. As you add a components to the solution, you configure them to interoperate with the components already installed on the other computers.
You might perform a sequence of installation and configuration tasks similar to the one illustrated in Figure 3–2.
Figure 3–2 Configuring Components to Interoperate
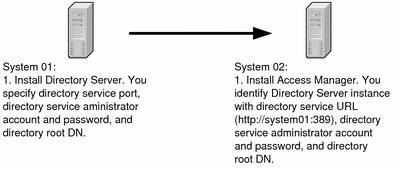
Whatever the architecture of your solution, you must develop an installation plan that includes all the configuration values needed to configure the components and achieve an interoperating, distributed solution.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
