About SAML v2
OpenSSO Enterprise delivers a solution that allows businesses to establish a framework for sharing trusted information across a distributed network of partners using the standards-based SAML v2. Towards this end, HTTP(S)-based service endpoints and SOAP service endpoints are supplied as well as assertion and protocol object manipulating classes. A web browser can access all HTTP(S)-based service endpoints and an application can make use of the SOAP endpoints and API as long as metadata for each participating business on BOTH sides of the SAML v2 interaction is exchanged beforehand.
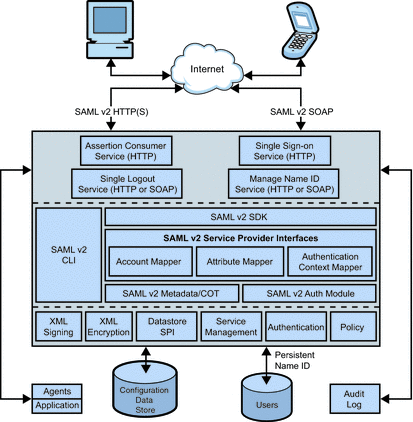
Figure 11–3 illustrates the SAML v2 framework which consists of web-based services [using SOAP, XML over HTTP(S) or HTML over HTTP(S)], and Java™-based application provider interfaces (API) and service provider interfaces (SPI). Additionally, the figure shows an agent embedded into a web container in which a service provider application is deployed. This agent enables the service provider to participate in the SAML v1.x or Liberty ID-FF protocols.
Figure 11–3 SAML v2 Architecture
The following sections contain more information about the SAML v2 framework.
Key Features
The key features of SAML v2 in OpenSSO Enterprise include:
-
Single sign-on using the POST profile, the Artifact binding (also referred to as HTTP redirect), and unsolicited responses (initiated by the identity provider)
-
Single logout using HTTP redirect and SOAP binding
-
Federation termination using HTTP redirect and SOAP binding
-
Auto-federation (automatic linking of service provider and identity provider user accounts based on a common attribute)
-
Bulk federation
-
Dynamic creation of user accounts
-
One time federation (transient NameID format for SSO)
-
Basic Authentication, SSL and SSL with client authentication for SOAP binding security
-
SAML v2 authentication
-
Identity provider discovery
-
XML verification, signing, encryption and decryption
-
Profile initiation and processing using included JavaServer Pages™ (JSP™)
-
Load balancing support
-
IDP Proxy
-
Assertion failover
-
Enhanced Client or Proxy (ECP) support in SP and IDP
-
Assertion queries and requests
-
Attribute queries
-
New Name Identifier
-
Affiliation
-
Name Identifier Mapping
-
XACML profile for authorization
Note –See XACML Service for more information.
-
Protocol coexistence with the SAML v1.x and the Liberty ID-FF
Additionally, OpenSSO Enterprise has received high scores and passed the Liberty Alliance Project interoperability tests for SAML v2. For more information, see the SAMLv2 support matrix on the Liberty Alliance Project web site.
Administration
In order to communicate using the SAML v2 profiles you need, at least, two instances of OpenSSO Enterprise. One instance will act for the identity provider and the other will act for the service provider. Name identifiers are used to communicate regarding a user.
Note –
SAML v2 single sign-on interactions support both persistent and transient identifiers. A persistent identifier is saved to a particular user entry as the value of two attributes. A transient identifier is temporary and no data will be written to the user's data store entry.
To prepare your instances for SAML v2 interactions, you need to exchange a particular provider's configuration information or metadata between all participating identity and service providers, and assemble the providers into a circle of trust. Utility APIs can then be used to communicate with the data store, reading, writing, and managing the relevant properties and property values. For more information see the Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Administration Guide.
Application Programming Interfaces
The SAML v2 framework contains API that can be used to construct and process assertions, requests, and responses. The SAML v2 Java API packages include:
-
The com.sun.identity.saml2.assertion package provides interfaces to construct and process SAML v2 assertions. It also contains the AssertionFactory, a factory class used to obtain instances of the objects defined in the assertion schema.
-
The com.sun.identity.saml2.common package provides interfaces and classes used to define common SAML v2 utilities and constants.
-
The com.sun.identity.saml2.protocol package provides interfaces used to construct and process the SAML v2 requests and responses. It also contains the ProtocolFactory, a factory class used to obtain object instances for concrete elements in the protocol schema.
More information can be found in Using the SAML v2 SDK in Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Developer’s Guide and the Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Java API Reference.
Service Provider Interfaces
The com.sun.identity.saml2.plugins package provides pluggable interfaces to implement SAML v2 functionality into your application. Default implementations are provided, but a customized implementation can be plugged in by modifying the corresponding attribute in the provider's extended metadata configuration file. The interfaces include mappers for:
-
Account mapping (map between the account referred to in the incoming request and the local user account)
-
Attribute mapping (specifies which set of user attributes in an identity provider user account needs to be included in an assertion, and maps the included attributes to attributes in the user account defined by the service provider)
-
Authentication context mapping (map between Authentication Contexts defined in the SAML v2 specifications and authentication framework schemes defined in OpenSSO Enterprise (user/module/service/role/level based authentication)
-
Service provider adapter (allows user to plug-in application specific logic before and/or after single sign-on, single logout, termination and new name identifier process.
More information can be found in Service Provider Interfaces in Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Developer’s Guide and the Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Java API Reference.
JavaServer Pages
The SAML v2 framework provides JSP that can be used to initiate single sign-on, single logout and termination requests from either the identity provider or the service provider using a web browser. The JSP accept query parameters to allow flexibility in constructing SAML v2 requests; they can be modified for your deployment. More information can be found in JavaServer Pages in Sun OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 Developer’s Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
