Processes and System Performance
The following table describes terms related to processes.
Table 22–1 Process Terminology|
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Process |
Any system activity or job. Each time you boot a system, execute a command, or start an application, the system activates one or more processes. |
|
Lightweight process (LWP) |
A virtual CPU or execution resource. LWPs are scheduled by the kernel to use available CPU resources based on their scheduling class and priority. LWPs include a kernel thread and an LWP. A kernel thread contains information that has to be in memory all the time. An LWP contains information that is swappable. |
|
Application thread |
A series of instructions with a separate stack that can execute independently in a user's address space. They can be multiplexed on top of LWPs. |
A process can consist of multiple LWPs and multiple application threads. The kernel schedules a kernel-thread structure, which is the scheduling entity in the SunOS environment. Various process structures are described in the following table.
Table 22–2 Process Structures|
Structure |
Description |
|---|---|
|
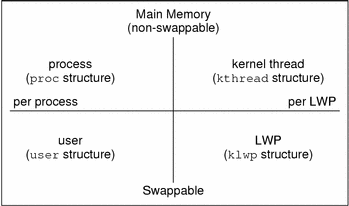
proc |
Contains information that pertains to the whole process and must be in main memory all the time. |
|
kthread |
Contains information that pertains to one LWP and must be in main memory all the time. |
|
user |
Contains the “per process” information that is swappable. |
|
klwp |
Contains the “per LWP process” information that is swappable. |
The following figure illustrates the relationship of these process structures.
Figure 22–1 Process Structures
Most process resources are accessible to all the threads in the process. Almost all process virtual memory is shared. A change in shared data by one thread is available to the other threads in the process.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
