Caching Web Pages (Reference)
The following sections cover the files and components that are needed to use NCA. Also, specifics about how NCA interacts with the web server are included.
NCA Files
You need several files to support the NCA feature. Many of these files are ASCII, but some of them are binary. The following table lists all of the files.
Table 2–1 NCA Files|
File Name |
Function |
|---|---|
|
File that lists all physical interfaces that are configured on the server. |
|
|
File that lists all host names that are associated with the server. Entries in this file must match entries in /etc/hostname.* files for NCA to function. |
|
|
Script that starts the NCA server. This script is run when a server is booted. |
|
|
Script that starts NCA logging. This script is run when a server is booted. |
|
|
File that lists the interfaces on which NCA is run. See the nca.if(4) man page for more information. |
|
|
File that lists configuration parameters for NCA. See the ncakmod.conf(4) man page for more information. |
|
|
File that lists configuration parameters for NCA logging. See the ncalogd.conf(4) man page for more information. |
|
|
Command that is used to convert data in the log file to the common log format. See the ncab2clf(1) man page for more information. |
|
|
Command that is used to configure NCA to run on multiple interfaces during boot. See the ncaconfd(1M) man page for more information. |
|
|
Library that uses AF_NCA sockets instead of AF_INET sockets. This library must be used on web servers that use AF_INET sockets. See the ncad_addr(4) man page for more information. |
|
|
File that holds the log file data. The file is in binary format, so do not edit it. |
NCA Architecture
The NCA feature includes the following components.
-
Kernel module, ncakmod
-
Web server, httpd
The kernel module ncakmod maintains the cache of web pages in system memory. The module communicates with a web server, httpd, through a sockets interface (family type PF_NCA).
The kernel module also provides a logging facility that logs all HTTP cache hits. NCA logging writes HTTP data to the disk in binary format. NCA provides a conversion utility for converting binary log files to common log format (CLF).
The following figure shows the flow of data for the conventional path and the path that is used when NCA is enabled.
Figure 2–1 Data Flow with the NCA Service
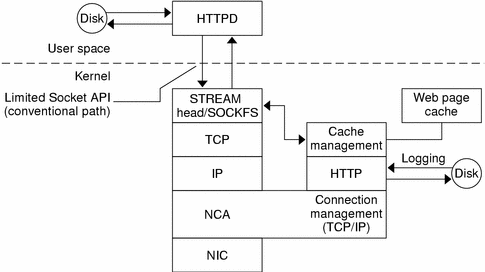
NCA to Httpd Request Flow
The following list shows the request flow between the client and the web server.
-
An HTTP request is made from the client to the web server.
-
If the page is in cache, the in-kernel cache web page is returned.
-
If the page is not in cache, the request goes to the web server to retrieve or update the page.
-
Depending on the HTTP protocol semantics that are used in the HTTP response, the page is cached or not and then it is returned to the client. If the Pragma: No-cache header is included in the HTTP request, the page is not cached.
Interpositioning Library for Door Server Daemon Support
Many web servers use AF_INET sockets. By default, NCA uses AF_NCA sockets. To correct this situation, an interpositioning library is provided. The new library is loaded in front of the standard socket library, libsocket.so. The library call bind() is interposed by the new library, ncad_addr.so. If the status is enabled in /etc/nca/ncakmod.conf, the version of Apache that is included with the Solaris 9 release is already set up to call this library. If you are using IWS or Netscape servers, see How to Load the NCA Socket Utility Library to use the new library.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
