Example—Configuration Using PAP Authentication
The tasks in Configuring PAP Authentication show how to set up PAP authentication over the PPP link. The procedures use as an example a PAP scenario that was created for the fictitious “Big Company” that was introduced in Example— Configuration for Dial-up PPP.
Big Company wants to enable its users to work from home. The system administrators want a secure solution for the serial lines to the dial-in server. UNIX-style login that uses the NIS password databases has served BigCompany's network well in the past. The system administrators want a UNIX-like authentication scheme for calls that come in to the network over the PPP link. So they implement the following scenario that uses PAP authentication.
Figure 30–3 Example—PAP Authentication Scenario (Working From Home)
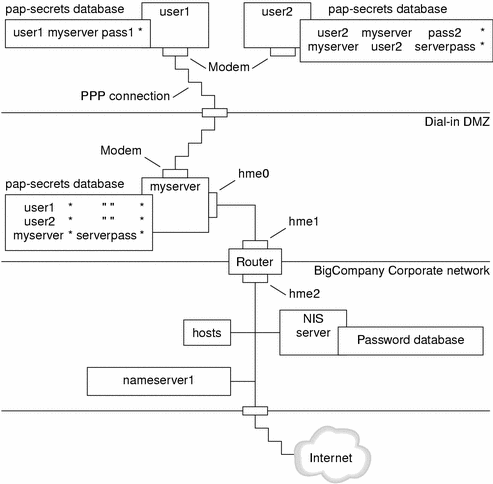
The system administrators create a dedicated dial-in DMZ that is separated from the rest of the corporate network by a router. The term DMZ comes from the military term demilitarized zone. The DMZ is an isolated network that is set up for security purposes. The DMZ typically contains resources that a company offers to the public, such as web servers, anonymous FTP servers, databases, and modem servers. Network designers often place the DMZ between a firewall and a company's Internet connection.
The only occupants of the DMZ that is pictured in Figure 30–3 are the dial-in server myserver and the router. The dial-in server requires callers to provide PAP credentials (including user names and passwords) when setting up the link. Furthermore, the dial-in server uses the login option of PAP. Therefore, the callers' PAP user names and passwords must correspond exactly to their UNIX user names and passwords that already are in the dial-in server's password database.
After the PPP link is established, the caller's packets are forwarded to the router. The router forwards the transmission to its destination on the corporate network or Internet.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
