Installing and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue
This chapter describes the procedures to install and configure the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue.
This chapter contains the following sections.
-
Planning the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
-
Installing and Configuring the Sun Java System Message Queue
-
Verifying the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
-
Planning the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
-
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Packages
-
Registering and Configuring the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue
-
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
-
Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Fault Monitor
Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Overview
Use the information in this section to understand how the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue enables the Sun Java System Message Queue for high availability.
The Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue is a data service with appropriate extension properties to configure a failover messaging service.
Configure the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue as a failover data service to enable the Sun Java System Message Queue for high availability. See Chapter 1, Planning for Sun Cluster Data Services, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for general information about data services.
The Sun Java System Message Queue is an integral part of the application server. The Sun Java System Message Queue is a robust Java Messaging Service (JMS) provider for JMS clients. The Sun Java System Message Queue is packaged with the Sun Java System Application Server installation. Refer to Sun Java System Message Queue documentation for information about the Sun Java System Message Queue. Implementation of the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue does not assume the existence of programs on which your architecture depends. Programs on which your architecture depends such as databases and web servers should be configured to be highly available, but might run on a different cluster.
Overview of the Installation and Configuration Process for Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue
The following table lists the sections that describe the installation and configuration tasks. Perform these tasks in the order that they are listed.
Table 1 Task Map: Installing and Configuring the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue|
Task |
For Instructions |
|---|---|
|
Plan the Sun Java System Message Queue installation and configuration |
Planning the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration |
|
Configure and activate network resources | |
|
Install and configure the Sun Java System Message Queue | |
|
Verify the Sun Java System Message Queue installation |
How to Verify the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration |
|
Plan the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue installation and configuration |
Planning the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration |
|
Install the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue package |
How to Install the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Packages |
|
Register and Configure the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue as a failover data service | |
|
Configure the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type | |
|
Verify the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue installation and configuration |
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration |
|
Tune the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue fault monitor |
Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Fault Monitor |
Note –
If you run multiple data services in your Sun Cluster configuration, you can set up the data services in any order, with the following exception. If the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue depends on the Sun Cluster HA for DNS, you must set up DNS first. For details, see Sun Cluster Data Service for DNS Guide for Solaris OS for details. DNS software is included in the Solaris operating environment. If the cluster is to obtain the DNS service from another server, configure the cluster to be a DNS client first.
Planning the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
To install and configure the Sun Java System Message Queue, use this section as a checklist in conjunction with the worksheets in the Configuration Worksheets in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
Consider the following before you start your installation. Store static files and data on the local file system of each cluster node. Dynamic data should reside on the cluster file system so that you can view or update the data from any cluster node. The Sun Java System Message Queue binaries and configuration files must be highly available and accessible to application-server instances that are running on all nodes.
Note –
The Sun Java System Message Queue can be configured to run in a whole root non-global zone, if required. The Sun Java System Message Queue is not supported in a sparse root non-global zone.
Configuring and Activating Network Resources
Before you install and configure the Sun Java System Message Queue, set up the network resources that the service uses after installation and configuration. To configure and activate the network resources, use the following command-line procedure.
 How to Configure and Activate Network Resources
How to Configure and Activate Network Resources
To perform this procedure, you need the following information about your configuration.
-
The names of the cluster nodes that can master the data service.
-
The network resource that clients use to access the Sun Java System Message Queue. Normally, you set up this hostname when you install the cluster. See the Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS for details on network resources.
-
On a cluster member, become superuser or assume a role that provides solaris.cluster.modify and solaris.cluster.modify RBAC authorization.
-
Verify that all of the network addresses that you use have been added to your name service database.
You should have performed this verification during the Sun Cluster installation.
Note –To avoid name service look-up failures, ensure that all of the logical hostnames are present in the /etc/inet/hosts file on all the cluster nodes. Configure name service mapping in the /etc/nsswitch.conf file on the servers to check the local files before trying to access NIS, NIS+, or DNS.
-
Create a failover resource group to contain the network and application resources.
# clresourcegroup create [-n node-zone-list] resource-group
- resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the resource group. This name can be your choice.
- [-n node-zone-list]
-
Specifies a comma-separated, ordered list of zones that can master this resource group. The format of each entry in the list is node. In this format, node specifies the node name and zone specifies the name of a non-global Solaris zone. To specify the global zone, or to specify a node without non-global zones, specify only node.
This list is optional. If you omit this list, the global zone of each cluster node can master the resource group.
-
Add network resources to the resource group.
Use the following command to add a logical hostname to a resource group.
# clreslogicalhostname create -g resource-group [-h hostname, …] [-N netiflist] lhresource
- -g resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the resource group.
- -h hostname, …
-
Specifies a comma-separated list of network resources.
- -N netiflist
-
Specifies an optional, comma-separated list that identifies the IP Networking Multipathing groups that are on each node or zone. The format of each entry in the list is netif@node. The replaceable items in this format are as follows:
- netif
-
Specifies an IPMP group name, such as sc_ipmp0, or a public network interface card (NIC). If you specify a public NIC, Sun Cluster attempts to create the required IPMP groups.
- node
-
Specifies the name or ID of a node. To specify the global zone, or to specify a node without non-global zones, specify only node.
Note –If you require a fully qualified hostname, you must specify the fully qualified name with the -h option and you cannot use the fully qualified form in the resource name.
Note –Sun Cluster does not currently support the use of the adapter name for netif.
-
Run the clresourcegroup command to enable the resource group and bring the resource group online.
# clresourcegroup online resource-group
- resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the resource group.
Installing and Configuring the Sun Java System Message Queue
The Sun Java System Message Queue is a Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE™) 1.3 compliant messaging service. This queue is designed to meet the needs of enterprise customers and run under the control of Sun Cluster software. This section describes the steps to install and enable the Sun Java System Message Queue to run as the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue.
Note –
If you run the Sun Java System Message Queue and another messaging service server and they use the same network resources, configure them to listen on different ports. Otherwise, a port conflict might occur between the two services.
Use the following procedure to install the Sun Java System Message Queue.
 How to Install the Sun Java System Message Queue
How to Install the Sun Java System Message Queue
Use the following procedure to install the Sun Java System Message Queue. Only the sections that are specific to the Sun Java System Message Queue are included here. See the Sun Java System Message Queue for Solaris OS documentation for details.
Note –
Do not set the AUTOSTART property to YES in the /etc/imq/imqbrokerd.conf file. The AUTOSTART property is set to NO by default because Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue starts and stops the application after you have configured the data service.
-
Install the Sun Java System Message Queue package on all the nodes of the cluster if they are not already installed.
-
Identify a location on a global file system where you intend to keep your message queue (for example, /global/s1mq).
You can create a separate directory for this file system.
-
On any node set IMQ_VARHOME and run the imqbrokerd command to create the configuration directory and files.
# IMQ_VARHOME=/global/s1mq # export IMQ_VARHOME # imqbrokerd -name hamq1
-
Set the imq.portmapper.hostname property to the logical hostname by editing $IMQ_VARHOME/instances/hamq1/props/config.properties.
Verifying the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
This section describes how to verify the Sun Java System Message Queue installation and configuration.
 How to Verify the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
How to Verify the Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
Use this procedure to verify the Sun Java System Message Queue installation and configuration. This procedure does not verify that your application is highly available.
-
Ensure that the logical hostname is running.
-
Set IMQ_VARHOME and start the message broker manually:
# IMQ_VARHOME=/global/s1mq # export IMQ_VARHOME # imqbrokerd -name hamq1
-
# /usr/bin/imqcmd shutdown bkr -b hostname:port
-
Repeat Step 2 on all the potential primaries of the Sun Java System Message Queue resource group.
Planning the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
This section contains the information that you need to plan your Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue installation and configuration.
Standard Data Service Configurations
Use the standard configurations in this section to plan the installation and configuration of the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue. The Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue might support additional configurations. However, you must contact your Enterprise Services representative for information on additional configurations.
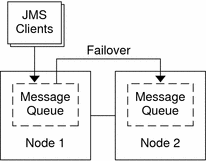
The following figure illustrates a standard failover configuration for the Sun Java System Message Queue.
Figure 1 Two-Node Cluster with Failover Data Service Configuration
Configuration Considerations
If you choose to use your message service with another highly available application, resource dependencies might exist. See Appendix B, Standard Properties, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for a description of the Resource_dependencies property.
Configuration Planning Questions
Use the questions in this section to plan the installation and configuration of the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue. See Considerations for Installing and Configuring a Data Service in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for information that might apply to these questions.
-
What resource groups will you use for network addresses and application resources and the dependencies between them?
-
What is the logical hostname (for failover services) for clients that will access the data service?
-
Where will the system configuration files reside?
Installing the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Packages
If you did not install the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue packages during your initial Sun Cluster installation, perform this procedure to install the packages. To install the packages, use the Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer.
 How to Install the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Packages
How to Install the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Packages
Perform this procedure on each cluster node where you are installing the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue packages.
You can run the Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer with a command-line interface (CLI) or with a graphical user interface (GUI). The content and sequence of instructions in the CLI and the GUI are similar.
Note –
Even if you plan to configure this data service to run in non-global zones, install the packages for this data service in the global zone. The packages are propagated to any existing non-global zones and to any non-global zones that are created after you install the packages.
Before You Begin
Ensure that you have the Sun JavaTM Availability Suite DVD-ROM.
If you intend to run the Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer with a GUI, ensure that your DISPLAY environment variable is set.
-
On the cluster node where you are installing the data service packages, become superuser.
-
Load the Sun Java Availability Suite DVD-ROM into the DVD-ROM drive.
If the Volume Management daemon vold(1M) is running and configured to manage DVD-ROM devices, the daemon automatically mounts the DVD-ROM on the /cdrom directory.
-
Change to the Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer directory of the DVD-ROM.
-
Start the Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer.
# ./installer
-
When you are prompted, accept the license agreement.
If any Sun Java Enterprise System components are installed, you are prompted to select whether to upgrade the components or install new software.
-
From the list of Sun Cluster agents under Availability Services, select the data service for Sun Java System Message Queue.
-
If you require support for languages other than English, select the option to install multilingual packages.
English language support is always installed.
-
When prompted whether to configure the data service now or later, choose Configure Later.
Choose Configure Later to perform the configuration after the installation.
-
Follow the instructions on the screen to install the data service packages on the node.
The Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer displays the status of the installation. When the installation is complete, the wizard displays an installation summary and the installation logs.
-
(GUI only) If you do not want to register the product and receive product updates, deselect the Product Registration option.
The Product Registration option is not available with the CLI. If you are running the Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer with the CLI, omit this step
-
Exit the Sun Java Enterprise System Common Installer.
-
Unload the Sun Java Availability Suite DVD-ROM from the DVD-ROM drive.
Next Steps
See Registering and Configuring the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue to register Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue and to configure the cluster for the data service.
Registering and Configuring the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue
This procedure describes how to use the Sun Cluster maintenance commands to register and configure the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue.
Note –
See Tools for Data Service Resource Administration in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for details about additional options that enable you to register and configure the data service.
To perform this procedure, you need the following information about your configuration.
-
The name of the resource type for the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue is SUNW.s1mq.
-
The names of the cluster nodes that can master the data service.
-
The network resource that clients use to access the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue.
-
The port where the Sun Java System Message Queue listens.
Setting Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Extension Properties
The section that follows contains instructions for registering and configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue resources. For information about the extension properties, see Appendix A, Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Extension Properties. The Tunable entry indicates when you can update a property.
See Appendix B, Standard Properties, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for details on all the Sun Cluster properties.
To set an extension property of a resource, include the following option in the clresource(1CL) command that creates or modifies the resource:
-p property=value |
- -p property
-
Identifies the extension property that you are setting.
- value
-
Specifies the value to which you are setting the extension property.
You can also use the procedures in Chapter 2, Administering Data Service Resources, in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS to configure resources after the resources are created.
 How to Register and Configure the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue as a Failover Data Service
How to Register and Configure the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue as a Failover Data Service
Perform the following steps to complete your configuration.
-
On a cluster member, become superuser or assume a role that provides solaris.cluster.modify and solaris.cluster.adminRBAC authorization.
-
Add the resource group for the Sun Java System Message Queue if you have not performed the steps in Configuring and Activating Network Resources.
# clresourcegroup create [-n node-zone-list] resource-group
-
Add the logical hostname resource to the resource group if you have not performed the steps in Configuring and Activating Network Resources.
# clreslogicalhostname create -g resource group -h logical-hostname logical-hostname
Note –If you require a fully qualified hostname, you must specify the fully qualified name with the -h option and you cannot use the fully qualified form in the resource name.
-
Register the SUNW.s1mq resource type for the data service.
# clresourcetype register SUNW.s1mq
-
If the Smooth_Shutdown extension property is set to TRUE, create a file named scs1mqconfig in the $IMQ_VARHOME/instances/broker/ directory. Add the following line to the file you created:
Password password
See Appendix A, Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Extension Properties for a description of the Smooth_Shutdown extension property.
-
Add the Sun Java System Message Queue resource instance to the failover resource group.
[If Smooth_Shutdown will be set to FALSE (the default):] # clresource create -g resource-group -t SUNW.s1mq \ -p Confdir_list=$IMQ_VARHOME/instances/broker \ -p Broker_Name=broker \ -p Network_Resources_Used=logical hostname \ -p Port_list=port/tcp[,port/tcp] resource
[If Smooth_Shutdown is set to TRUE:] # clresource create -g resource-group -t SUNW.s1mq \ -p Confdir_list=$IMQ_VARHOME/instances/broker \ -p Broker_Name=broker \ -p Broker_User=user \ -p Network_resources_used=logical hostname \ -p Port_list=port/tcp[,port/tcp] \ -p Smooth_Shutdown=TRUE resource
The resource is created in the enabled state.
The resource group that contains the application resources is the same resource group that you created for your network resources in How to Configure and Activate Network Resources.
- -t SUNW.s1mq
-
Specifies the type of resource to add.
- -p Confdir_list=$IMQ_VARHOME/instances/broker
-
Specifies a path for your Sun Java System Message Queue configuration directory. The Confdir_list extension property is required. The Confdir_list property must have exactly one entry.
- -p Broker_Name=broker
-
Specifies the name of the broker to monitor.
- -p Broker_User=user
-
Specifies the user name of the managed broker.
- -p Network_resources_used=network-resource
-
Specifies a comma-separated list of network resources (logical hostnames) in resource-group, which the Sun Java System Message Queue application resource must use.
- -p Port_list=port-number/protocol
-
Specifies a port number and the protocol to be used, for example, 80/tcp. The Port_list property must have one or two entries.
- -p Smooth_Shutdown=TRUE
-
Used to shutdown the broker. Use of the impcmd command exposes the broker password in the imqcmd command string.
- resource
-
Specifies the Sun Java System Message Queue application resource name.
-
Bring the resource group online.
# clresourcegroup online resource-group
- resource-group
-
Specifies the name of the application resource group that is being enabled.
-
Verify that the resource group and application-server resource are online.
# clresourcegroup status # ps -ef
Example 1 Registering and Configuring the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue
This example shows how to register the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue.
Cluster Information Node names: phys-schost-1, phys-schost-2 Logical hostname: schost-1 Resource group: resource-group-1 (for all resources) Resources: schost-1 (logical hostname), SUNW.s1mq (Sun Java System Message Queue application resource) (Create a failover resource group.) # clresourcegroup create -n phys-schost-1,phys-schost-2 s1mq-rg (Add a logical hostname resource to the resource group.) # clreslogicalhostname -g s1mq-rg -h schost-1 schost-1 (Register the SUNW.s1mq resource type.) # clresourcetype register SUNW.s1mq (Create a Sun Java System Message Queue resource and add it to the resource group.) # clresource create -g s1mq-rg \ -t SUNW.s1mq \ -p Confdir_list=$IMQ_VARHOME/instances/hamq1 \ -p Broker_Name=hamq1 \ -p Network_resources_used=schost-1 \ -p Port_list=7676/tcp s1mq-rs (Enable the application resource group.) # clresourcegroup online s1mq-rg |
Example 2 Registering and Configuring Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue With Smooth_Shutdown Enabled
This example shows how to register Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue with Smooth_Shutdown enabled.
Cluster Information Node names: phys-schost-1, phys-schost-2 Logical hostname: schost-1 Resource group: resource-group-1 (for all resources) Resources: schost-1 (logical hostname), s1mq-1 (Sun Java System Message Queue application resource) (Create a failover resource group.) # clresourcegroup create -n phys-schost-1,phys-schost-2 s1mq-rg (Add a logical hostname resource to the resource group.) # clreslogicalhostname create -g s1mq-rg -h schost-1 schost-1 (Register the SUNW.s1mq resource type.) # clresourcetype register SUNW.s1mq (Create a Sun Java System Message Queue resource and add it to the resource group.) # clresource create -g s1mq-rg \ -t SUNW.s1mq \ -p Confdir_list=$IMQ_VARHOME/instances/hamq1 \ -p Broker_Name=hamq1 \ -p Broker_User=admin \ -p Network_resources_used=schost-1 \ -p Port_list=7676/tcp \ -p Smooth_Shutdown=TRUE s1mq-rs (Enable the application resource group.) # clresourcegroup online s1mq-rg |
Configuring the SUNW.HAStoragePlus Resource Type
The SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type was introduced in Sun Cluster 3.0 5/02. This new resource type performs the same functions as SUNW.HAStorage, and synchronizes actions between HA storage and the data service.
SUNW.HAStoragePlus also has an additional feature to make a local file system highly available. Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue is not disk intensive and not scalable, and therefore setting up the SUNW.HAStoragePlus resource type is optional.
See the SUNW.HAStoragePlus(5) man page and Relationship Between Resource Groups and Device Groups in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for background information. See Synchronizing the Startups Between Resource Groups and Device Groups in Sun Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide for Solaris OS for the procedure. If you are using a Sun Cluster 3.0 version prior to 5/02, you must set up SUNW.HAStorage instead of SUNW.HAStoragePlus.
Verifying the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
This section contains the procedure to verify that you installed and configured your data service correctly.
 How to Verify the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
How to Verify the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Installation and Configuration
Use this procedure to verify that you installed and configured the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue correctly.
-
Ensure that the Message Queue is started under the control of Sun Cluster software.
# clresourcegroup online resource group
-
Connect to the Sun Java System Message Queue from a web browser to verify that the Sun Java System Message Queue software functions correctly.
-
Run the clresourcegroup command to switch the resource group to another cluster node, such as node2.
# clresourcegroup online -n node2 resource-group
-
Verify that the resource group and message queue resource is online.
# clresourcegroup status # ps -ef
-
Repeat Step 2 through Step 4 on all the potential primaries of the Sun Java System Message Queue resource groups.
Tuning the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Fault Monitor
The Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue fault monitor is contained in the resource that represents Sun Java System Message Queue. You create this resource when you register and configure Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue. For more information, see Registering and Configuring the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue.
System properties and extension properties of this resource control the behavior of the fault monitor. The default values of these properties determine the preset behavior of the fault monitor. The preset behavior should be suitable for most Sun Cluster installations. Therefore, you should tune the Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue fault monitor only if you need to modify this preset behavior.
For more information, see the following sections.
Operations by the Fault Monitor During a Probe
The Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue fault monitor uses the Smooth_shutdown extension property. For instructions on setting this property, see Setting Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue Extension Properties.
The Sun Cluster HA for Sun Java System Message Queue probe sends a request to the server to query the health of the Sun Java System Message Queue server instance.
The probe connects to the IP address and port combinations defined by the network resource configuration and the Port_list setting for the resource group. If the connection succeeds, the probe reads the port mapper information. Finally the probe disconnects. If any part of the connection fails, a failure is recorded.
Heavy network traffic, heavy system load, and misconfiguration can cause the query to fail. Misconfiguration can occur if you did not configure the Sun Java System Message Queue server to listen on all the IP address and port combinations that are probed. The Sun Java System Message Queue server should service every port for every IP address that is specified for this resource.
When the probe fails to connect to the server, a complete probe failure occurs. The following error message is sent, where the %s indicates the hostname and %d indicates the port number.
Failed to connect to the host <%s> and port <%d>. |
The probe accumulates partial failures that happen within the resource property interval Retry_interval until they equal a complete failure that requires action.
The following are partial probe failures.
-
Failure to disconnect. The following error message is sent, where %d indicates the port number and %s indicates the resource name.
Failed to disconnect from port %d of resource %s.
-
Failure to complete all probe steps within Probe_timeout time.
-
Failure to read data from the server for other reasons. The following error message is sent, where the first %s indicates the hostname, %d indicates the port number, and the second %s indicates further details about the error.
Failed to communicate with server %s port %d: %s
Based on the history of failures, a failure can cause either a local restart or a failover of the data service.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
