The Administration Framework and Installation
This section highlights key aspects of the administration framework you must understand before installing server software in a production environment. This section does not address the developer and performance tuning tools provided with Directory Server Resource Kit. You can install such tools independently of the administration framework.
Before you read this section, read Directory Server Enterprise Edition Administration Model in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.2 Deployment Planning Guide. Consider the following figure which shows how the network traffic flows. The figure shows network traffic flows between the configuration management tools, DSCC, dsconf(1M), and dpconf(1M), the local administration agents, and servers. The figure also shows communication between the local agents, the local command line tools, dsadm(1M) and dpadm(1M), and the servers that you manage.
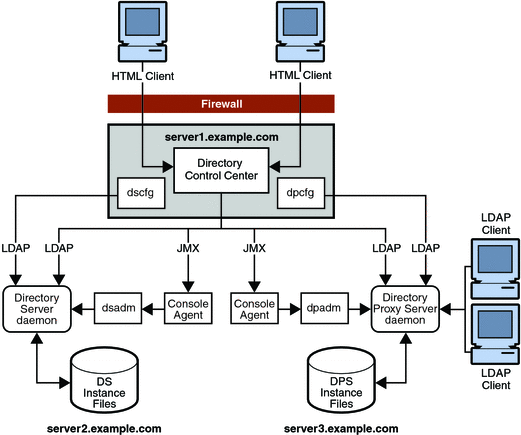
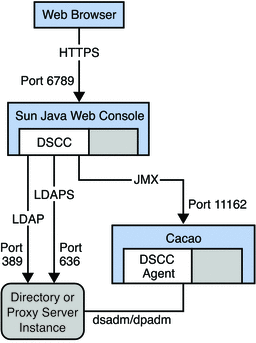
Notice the command line management and monitoring tools, dsconf(1M) and dpconf(1M), require only LDAP access to the servers that you manage. LDAP traffic typically flows through the default ports, 389 for LDAP and 636 for secure LDAP using SSL. When you create servers as a non-root user, the default ports are 1389 for LDAP, and 1636 for secure LDAP using SSL.
By convention, only root can install software using reserved port numbers less than 1024. Solaris systems allow the administrator to permit non-root users to use privileged ports, using role-based access control (RBAC).
DSCC is a web application that runs in the following modes:
-
Inside the Sun Java Web Console framework when installed using the native packages distribution.
-
Outside the Sun Java Web Console when installed using the zip distribution.
You typically install DSCC on only one system in your deployment. You then manage all your servers from that installation of DSCC. You access DSCC through a browser using the URL, https://hostname:6789, http://hostname:8080, or https://hostname:8181 based on the software distribution you use to install Directory Server Enterprise Edition and the configuration of the application server in case of installation using the zip distribution.
DSCC requires LDAP access to the servers for online management operations. DSCC also requires Java Management Extension (JMX) access to agents installed alongside the servers. The agents perform server process management operations on behalf of DSCC, that cannot be performed through LDAP on a running server. You can use DSCC to create and to start new servers.
As part of the normal installation process, you install the local DSCC agents alongside server software. DSCC contacts the agents over the network using a specific port number. You must therefore either accept the default port number, 11162, or specify a different port number.
The agents run inside a common agent container on the server system. This common agent container provides its agents with a single external port for management applications. The common agent container also consolidates resources to save resources on systems where multiple local agents share the container. The common agent container is the agent that listens for DSCC on the default port number, 11162, routing management traffic to other agents. DSCC communicates with local agents through the common agent container. For troubleshooting purposes, a common agent container can be managed independently using the cacaoadm command.
Figure 1–1 Ports and Protocols After Installation of Native Packages Distribution
Each time you install Directory Server Enterprise Edition software from the zip distribution, you also install an instance of the common agent container. Therefore, when you install multiple versions in parallel on the same host system, only one version can use the default port. You cannot install from the zip distribution where a common agent container instance already uses the default port. You must then specify a different port number for the additional common agent container instance.
-
Install configuration management software.
The configuration management tools are installed and DSCC is initialized.
As DSCC stores its configuration data in its own, private Directory Server instance, Directory Server is also installed from native packages during the DSCC installation.
-
Install server software on the systems where you plan to run server instances.
The server software, required libraries, local administration tools, and local agents are installed. All the software is installed to enable you to set up directory services but no servers are running at this point.
-
Create and configure server instances on the systems.
The Directory Server and Directory Proxy Server instances are created. Instances are created either using DSCC, or with the local administration tools that are installed alongside the server software. Server instances are then configured either through DSCC or through the configuration management command line tools.
Server software installation is a three stage process.
The first two stages are combined when you install everything on a single host system. DSCC uses the local agents to perform certain operations on the servers. Thus, the local agents must be installed in a local common agent container.
In the zip distribution, the Web Archive (WAR) file that is used to configure DSCC is copied to your system during the second stage. No installation or initialization of the WAR file is done during the first stage. The WAR file is further deployed with the supported application server to configure DSCC.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
