Chapter 5 Managing Servers and Server Groups
This chapter provides conceptual and procedural information about N1 System Manager server management and server group management.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Introduction to Server and Group Management
The N1 System Manager enables you to manage hundreds of heterogeneous servers by using one interface. The N1–ok shell provides a simple command set with which to identify and manage servers, as well as to provision or update operating systems and firmware and to redeploy manageable servers.
Use the discover command to initiate the management of manageable servers. See Chapter 4, Discovering Manageable Servers for details.
After successful completion of the Discovery job, a managed server is identified by its management name. Depending on how the managed server was discovered, its management name is initially set to the server's management IP address. You can rename discovered servers at any time.
For aggregate installation of firmware updates, you can create groups of discovered servers, or managed servers, according to make and model. Create functional groups for the aggregate installation of operating systems, or OS profiles, and OS updates. Managed nodes can belong to more than one server group, so you can create new server groups for aggregate maintenance tasks.
The sections in this chapter describe the prerequisites and instructions for performing server and server group maintenance tasks using the command line. You can also use the View Selector menu, the Actions menu, and server name links in the browser interface to perform the operations that are described in these sections.
For information about the management of diskless clients, see Managing Diskless Clients in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
Identifying Managed Servers and Server States
This section describes the information that the N1 System Manager reports for each managed server when you issue the show server command with the all keyword, or the show group command.
-
Name – The managed server or group name. The managed server name is initially set to the management IP address. For instructions on how to change the managed server name, see Modifying Managed Server and Group Information.
-
Hardware – Describes the type of managed server. See the Sun System Handbook documentation for your managed server.
-
Hardware Health – The status for attributes such as memory, processor information, and Network Interface Card (NIC) information.
-
OS Usage – If an OS profile is loaded, the OS name appears here.
-
OS Resource Health – If an OS profile is loaded, the OS state appears here if monitoring is enabled.
-
Jobs – If a job is in progress or has completed on the managed server, the job ID appears here.
Managed Server Power States
Server power is indicated by the following states:
-
On – The managed server is powered on and running.
-
Standby – The managed server is powered off but still responsive to commands, for example, start.
-
Unknown – The managed server is not returning any power status information.
-
Unreachable – The managed server cannot be contacted for power status information.
Hardware Health States
The hardware health of managed servers is indicated by the following states:
-
Good – The managed server hardware is working properly.
-
Unreachable – The managed server cannot be contacted for information about the status of hardware health. This state is most often caused by a network problem.
-
Warning Failure – A potential or impending fault condition has been detected on the managed server. Take action to prevent the problem from becoming more serious. See Monitoring Threshold Values for information about hardware sensor threshold values.
-
Critical Failure – A fault condition has occurred on the managed server. Corrective action is required.
-
Nonrecoverable Failure – The managed server has completely failed. Recovery is not possible.
-
Unknown – The managed server is not returning any hardware health status.
-
Offline – The server is not managed.
Supported Actions on Managed Servers
The following aggregate server actions are supported:
-
Starting, stopping, and resetting power.
-
Listing and refreshing server data.
-
Loading managed servers with OS profiles, updates, and firmware. See Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide.
-
Enabling and disabling managed server monitoring. See Chapter 6, Monitoring Servers and Server Groups.
-
Adding managed server to groups. SeeCreating and Maintaining Groups of Managed Servers.
-
Removing managed servers from the N1 System Manager.
Creating and Maintaining Groups of Managed Servers
This section describes the following tasks:
Creating Groups and Adding Managed Servers to Groups
After successful completion of the Discovery job, a managed server is identified by its management name. The managed server's management name is initially set to the server's management IP address. You can rename managed servers at any time.
For aggregate installation of firmware updates, you can create groups of managed servers, according to the make and model. Then, you can create functional groups for the aggregate installation of operating systems, or OS profiles, and OS updates. For details about provisioning operating systems, see Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide. Managed servers can belong to more than one group, so you can create new groups for aggregate maintenance tasks as needed.
To create groups, use the create group command. To add managed servers to a group, use the add group command with the server subcommand.
To create a group and add managed servers in a single operation, use the create group command and the server subcommand. This task can also be performed during the service processor discovery process. Add an option to the discover command to create a new group and add the servers to the new group. See To Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based Discovery Using the Command Line or To Discover Manageable Servers Using OS-Based Discovery Using the Command Line for instructions.
For syntax and parameter details, type help create group or help add group at the N1–ok command line.
 To Create a Group of Managed Servers
To Create a Group of Managed Servers
This task shows you how to create groups of managed servers. Managed nodes can belong to more than one server group, so you can create new groups for aggregate maintenance tasks as needed.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the following command:
N1-ok> create group group
The new group is created. See create group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Example 5–1 Creating a Group and Adding Servers in a Single Operation
The following example shows how to create a group named dev and add managed servers named server1 and server2. Then, the show group command output provides the list of servers in the dev group.
N1-ok> create group dev server server1,server2 N1-ok> show group dev Name Hardware Power Health OS Usage server1 V20z On Good -- server2 V20z On Good RH30 |
 To Add a Managed Server to a Group
To Add a Managed Server to a Group
Note –
Managed Servers can belong to more than one group.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the following command:
N1-ok> add group group server server
The managed server is added to the group. See add group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Removing A Managed Server From A Group
To remove a managed server from a group, use the remove group command with the server subcommand. For syntax and parameter details, type help remove group at the N1–ok command line.
 To Remove a Managed Server From a Group
To Remove a Managed Server From a Group
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the following command:
N1-ok> remove group group server server
The server is removed from the group. See remove group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Replacing Managed Servers
This section describes how to replace a failed managed server in the N1 System Manager.
 To Replace a Server
To Replace a Server
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Command Line for details.
-
Type the following command:
N1-ok> stop server server force
The managed server is shut down and powered off. See stop server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
-
Disconnect the manageable server from the rack.
-
Remove the manageable server from the system.
N1-ok> delete server server
-
Connect the new manageable server.
Follow the instructions in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
-
Discover the replacement manageable server using your chosen method of discovery.
Follow the instructions in Chapter 4, Discovering Manageable Servers.
The replacement server is managed. See discover in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details. You can now set up monitoring. See Supporting OS Monitoring and Enabling and Disabling Monitoring for details.
Troubleshooting
The discover command credential attributes are used for security. SSH, IPMI, and Telnet require a username and a password. SNMP requires that you input a valid value for the read security community string. If credentials are not specified, the discovery process uses the default credentials that were defined during installation. For default credentials, see Setting Up Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Discovery might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the discover command fails with an error message indicating that there are invalid credentials or SSH key changed: Cannot connect to host and no true security breach has occurred, remove the known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the managed server. Then, retry the discover command. See To Update the ssh_known_hosts File in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
The problem of stale SSH entries on the management server can be avoided if, during the n1smconfig configuration process, you modify SSH policies by accepting changed or unknown host keys. Accepting changed or unknown host keys carries a security risk but avoids the problem of stale SSH entries on the management server. For more information, see To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Listing and Viewing Managed Servers and Groups
This section describes the following tasks:
Listing Managed Server and Groups
To list servers, use the View Selector menu. Alternatively, use the show server command with all subcommand to list all servers in the N1 System Manager.
 To List Managed Server and Groups
To List Managed Server and Groups
This procedure uses the N1 System Manager command line. You also can use the browser interface for this procedure, by choosing All Servers from the View Selector menu. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
See To Access the N1 System Manager Browser Interface for details.
-
Type the show server command with the all keyword to view all managed servers in the system.
N1-ok> show server all
A list of all managed servers in the system appears. See show server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Example 5–2 Filtering Managed Servers Based on IP Address
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on the server's management network IP address by using the show command:
N1-ok> show server ip 192.168.200.4 |
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on a range of management network IP addresses:
N1-ok> show server ip 192.168.200.4-192.168.200.60 |
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on subnet and mask length. In this case the subnet is 10.0.8 and the mask length is 24:
N1-ok> show server ip 10.0.8/24 |
Example 5–3 Filtering Managed Servers Based on Job Count
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on job count. In this case the job count is 0:
N1-ok> show server jobcount 0 |
Example 5–4 Filtering Managed Servers Based on Model
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on the server model. In this case the server model is Sun Fire v240 machines:
N1-ok> show server model SF-V240 |
Example 5–5 Filtering Managed Servers Based on Name
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on the managed server's name. In this case the name is server3:
N1-ok> show server name server3 |
Example 5–6 FilteringManaged Servers Based on Running OS
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on the OS that is running on the server. In this case an implicit, case-sensitive wildcard is used for SUSE Linux:
N1-ok> show server runningos SLES |
Example 5–7 Filtering Managed Servers Based on OS Health
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on the health of the OS that is running on the server. In this case, all managed servers that have OS health monitored are listed:
N1-ok> show server oshealth monitored |
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on the health of the OS that is running on the managed server. In this case, all servers that do not have OS health monitored are listed:
N1-ok> show server oshealth unmonitored |
The following example shows how to filter a list of managed servers in the system based on the health of the OS that is running on the managed server. In this case, all servers that are sending no OS health information because the OS monitoring feature has not been added, are listed:
N1-ok> show server oshealth uninitialized |
For information on adding the OS monitoring feature, see Supporting OS Monitoring.
Example 5–8 Listing Groups
N1-ok> show group all |
A list of all groups in the system appears. See show group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
 To View Failed Managed Servers
To View Failed Managed Servers
This procedure describes how to view failed managed servers using the N1 System Manager command line. You can also use the browser interface by choosing Servers By Health from the View Selector menu. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the show server command with the hardwarehealth keyword and the fault state that you want to view.
N1-ok> show server hardwarehealth nonrecoverable
N1-ok> show server hardwarehealth warning
N1-ok> show server hardwarehealth critical
N1-ok> show server hardwarehealth unreachable
N1-ok> show server hardwarehealth unknown
See Hardware Health States for a description of fault states.
Example 5–9 Viewing Failed Critical Servers
The following example shows how to view Managed Servers that have a health status of critical.
N1-ok> show server hardwarehealth critical Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 10.0.0.26 V20z Failed Critical On Solaris Unknown |
See Also
For descriptions of the failure levels of managed servers, see Hardware Health States. For descriptions of monitoring thresholds, see Monitoring Threshold Values.
Viewing Managed Server Details and Group Members
To view detailed server information and group members, use the show server command or show group commands. For syntax and parameter details, type help show server or help show group at the N1–ok command line. Information about managed servers is also provided on the Server Details page in the browser interface.
 To View Managed Server Details and Server Group Members
To View Managed Server Details and Server Group Members
This procedure describes how to view managed server details and server group members by using the command line. You can also use the browser interface by choosing All Servers from the View Selector menu. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the show server command with the server's name.
N1-ok> show server server
Detailed server information appears. See show server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Example 5–10 Viewing Server Group Members
The following example shows how to view the list of managed servers in a server group named devgroup, by using the show server command.
N1-ok> show group devgroup |
The list of servers in the group appears. See show group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Modifying Managed Server and Group Information
This section describes the following tasks:
Use the set server command with the name subcommand. For syntax and parameter details, type help set server or help set group at the N1–ok command line.
Renaming a Managed Server or a Group
Managed servers are identified by the management IP address that is specified during discovery. This name is also referred to as the management name. You might want to rename a server with the DNS host name or track the host name by adding it to the server notes.
Managed server and group names must be unique and may include numbers, letters, and some special symbols. The following special symbols are prohibited: comma, asterisk, single quote, double quote, parenthesis, question mark, equal sign, and newline.
 To Rename a Managed Server or a Group
To Rename a Managed Server or a Group
This procedure describes how to rename a managed server or a group by using the command line. You also can use the browser interface for this procedure, by choosing All Servers from the View Selector menu. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the set server command to change the name of the managed server.
N1-ok> set server server name=newname
Server names must be unique and may include letters A through Z, digits 0 through 9, hyphens, and underscores.
See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Example 5–11 Renaming a Group
The following example shows how to change a server group name by using the set group command.
N1-ok> set group devgroup name=labgroup |
The group name is changed from devgroup to labgroup. See set group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Adding a Server Note
Consider saving the following types of data as a server note:
-
Physical location such as rack, slot, building, and geographic region
-
DNS host name
-
Provisioning parameters and the network configuration information that is set for the OS profile installation
-
Internal asset tracking identifiers
To add server notes, use the set server command with the note subcommand. For syntax and parameter details, type help set server at the N1–ok command line or refer to set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual.
 To Add a Server Note
To Add a Server Note
This procedure describes how to add a server note by using the command line. You also can use the browser interface for this procedure, by choosing All Servers from the View Selector menu. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the set server command to show any existing notes for the managed server.
N1-ok> show server
The output shows any existing notes.
-
Use the set server command with the note keyword to add a note for the managed server.
N1-ok> set server server note="your note"
The note is added to the server information. See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Starting, Stopping, and Resetting Managed Servers and Groups
This section describes the following activities:
Starting Managed Servers and Groups
Use the start server or start group commands to power on a server or a server group. If boot PROMS are configured, the servers boot. You can also use the Actions menu on the Servers By Group page in the browser interface to initiate the start operation. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
For syntax and parameter details, type help start server or help start group at the N1–ok command line.
 To Power On and Boot a Managed Server or a Group
To Power On and Boot a Managed Server or a Group
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the start server or start group commands.
N1-ok> start server server
The server is powered on and, if boot PROMs are configured, the server boots. See start server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for syntax details.
N1-ok> start group group
The group is powered on and, if boot PROMs are configured, the manageable servers in the group boot. Job completion takes longer for large groups. See start group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for syntax details.
Note –RSC servers can take several minutes to start. The job status for the RSC server can indicate that the server has already started or rebooted before the startup or reboot process has actually completed with the server's OS running. Any subsequent jobs started on the RSC server before the startup or reboot process has completed and before the server's OS is running will fail.
For details about setting up RSC servers, see Preparing RSC-based Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide. See also Discovery of RSC Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide.
Example 5–12 Starting a Managed Server From the Network
The following example shows how to boot a managed server from the network.
N1-ok> start server 10.5.7.2 netboot=true |
Example 5–13 Starting a Group From the Network
The following example shows how to boot a group of managed servers from the network.
N1-ok> start group dev netboot=true |
Stopping Managed Servers and Groups
To shut down and power off a managed server or a group, use the stop server or stop group commands. Stopping a server or server group initiates graceful shutdown of the operating systems and subsequent power off the managed servers. If managed servers do not have an OS installed or do not shutdown, you can use the force subcommand to power off the server group.
For syntax and parameter details, type help stop server or help stop group at the N1–ok command line.
 To Shut Down and Power Off a Managed Server or
a Group
To Shut Down and Power Off a Managed Server or
a Group
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Type one of the following commands:
N1-ok> stop server server
The managed server is stopped. See stop server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for syntax details.
N1-ok> stop group group
The group is stopped. See stop group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for syntax details.
Example 5–14 Forcing a Managed Server to Power Off
The following example shows how to force the shutdown of the OS.
N1-ok> stop server 10.0.7.2 This operation is not supported. Please use the force option. N1-ok> stop server 10.0.7.2 force=true Server 10.0.7.2 powered off. |
Example 5–15 Forcing a Group of Servers to Power Off
The following example shows how to force shutdown of the OS for a server group.
N1-ok> stop group dev This operation is not supported. Please use the force option. N1-ok> stop group dev force=true Group dev powered off. |
Troubleshooting
If you use the force option, run one of the following file system check commands on the client via the console that you access from the service processor, when the server reboots.
-
For the Solaris OS, run fsck
-
For Linux, run reiserfsck or e2fsck
To find out how to run the fsck command on a managed servers, see Issuing Remote Commands on Servers and Server Groups.
Resetting Managed Servers and Groups
To initiate graceful shutdown of the operating system followed by power off for managed server or group, use the reset server or reset group commands. The managed servers are powered on and, if boot PROMs are configured, the servers reboot. If servers do not have an OS installed or do not shutdown, you can use the force subcommand to reboot the server or group.
For syntax and parameter details, type help reset server or help reset group at the N1–ok command line.
 To Reboot a Managed Server or a Group
To Reboot a Managed Server or a Group
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use one of the following commands:
N1-ok> reset server server [force=true]
The managed server is rebooted. See reset server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
N1-ok> reset group group [force=true]
The servers in the group reboot. See reset group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Example 5–16 Forcing Reset of a Managed Server
The following example shows how to force reset of the OS.
N1-ok> reset server 10.5.7.2 force=true |
Example 5–17 Forcing Reset of a Group
If the OS does not gracefully shut down, the following example shows the forced reset of the operating systems for servers in the group.
N1-ok> reset group dev force=true |
Example 5–18 Rebooting a Managed Server From the Network
The following example shows how to reboot a managed server from the network.
N1-ok> reset server 10.5.7.2 netboot=true |
Example 5–19 Rebooting a Group from the Network
The following example shows how to reboot a server group from the network.
N1-ok> reset group dev netboot=true |
Troubleshooting
If you use one of the above force commands, run one of the following file system check commands on the service processor when the server reboots.
-
For the Solaris OS, run fsck
-
For Linux, run reiserfsck or e2fsck
To find out how to run the fsck command on managed servers, see Issuing Remote Commands on Servers and Server Groups for instructions.
Issuing Remote Commands on Servers and Server Groups
This section describes how to issue remote commands on managed server and groups.
To issue a remote command on a managed server or group, use the start server or start group command with the command subcommand. For syntax and parameter details, type help start server or help start group at the N1–ok command line.
 To Issue Remote Commands on a Managed Server or
a Group
To Issue Remote Commands on a Managed Server or
a Group
This procedure describes how to issue a remote command. A remote command is a UNIX command that is sent to a managed server to be run on that managed server.
Before You Begin
You must add the base management feature before you can issue remote commands on servers or server groups. See Adding and Upgrading Base Management and OS Monitoring Features for details.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use one of the following commands:
N1-ok> start server server command "command"
The remote command is issued on the managed server. See start server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
N1-ok> start group group command "command"
The remote command is issued on the group. See start group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
-
View the Remote Command job.
N1-ok> show job job
The Remote Command output appears in the Results section.
Example 5–20 Issuing a Remote Command on a Managed Server
The following example shows how to issue a remote command on a server by using the start command.
N1-ok> start server hdco25 command "/bin/ls -l /" Job "23" started. |
The following example shows how to view the results of the remote command by using the show command.
N1-ok> show job 23 Job ID: 23 Date: 2005-02-15T08:31:20-0700 Type: Remote Command Status: Completed Command: start server hdco25 command "/bin/ls -l /" Owner: root Errors: 0 Warnings: 0 Step 1: Type: 103 Description: native procedure /bin/sh /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/remotecmd.sh :[RCMD_KEY] Start: 2005-02-15T08:31:22-0700 Completion: 2005-02-15T08:31:26-0700 Result: Complete Exception: No Data Available . . . Result : Server: hdco25 Status: 0 Message: Command executed successfully. Command: /bin/ls -l / Standard Output: total 321 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Feb 11 13:21 bin -> ./usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 4 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:25 boot drwxr-xr-x 3 root sys 512 Feb 11 14:27 cr drwxr-xr-x 15 root sys 4096 Feb 11 14:09 dev drwxr-xr-x 5 root sys 512 Feb 11 14:06 devices drwxr-xr-x 58 root root 4096 Feb 14 12:36 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:46 export dr-xr-xr-x 1 root root 1 Feb 11 14:11 home drwxr-xr-x 12 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:25 kernel lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Feb 11 13:21 lib -> ./usr/lib |
Example 5–21 Issuing a Remote Command With a Timeout
Timeouts are measured in seconds. The default timeout is two hours. If you want to turn the timeout off, use a value of zero seconds. The following example shows how to issue a remote command with a timeout that is set to 20 seconds.
N1-ok> start server hdco25 command "/root/sleep.sh 60" timeout 20 Job "10" started. |
The following example shows how to view the results of the remote command by using the show command.
N1-ok> show job 10 Job ID: 10 Date: 2005-02-15T16:46:45-0700 Type: Remote Command Status: Completed Command: start server hdco25 command "/root/sleep.sh 60" timeout 20 Owner: root Errors: 0 Warnings: 0 Step 1: Type: 103 Description: native procedure /bin/sh /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/remotecmd.sh :[RCMD_KEY] Start: 2005-02-15T16:46:48-0700 Completion: 2005-02-15T16:47:10-0700 Result: Complete Exception: No Data Available . . . Result: Server: hdco25 Status: -2 Message: Command running on hdco25 did not finish within the specified time limit of 20 seconds. Command: /root/sleep.sh 60 Standard Output: Sleeping for 60 seconds... |
Example 5–22 Issuing a Remote Command on a Group
The following example shows how to issue a remote command on a server group by using the start group command.
N1-ok> start group g1 command "/bin/ls -l /" Job "24" started. |
The following example shows how view the results of the remote command by using the show job command.
N1-ok> show job 24 Job ID: 24 Date: 2005-02-15T08:31:20-0700 Type: Remote Command Status: Completed Command: start group g1 command "/bin/ls -l /" Owner: root Errors: 0 Warnings: 0 Step 1: Type: 103 Description: native procedure /bin/sh /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/remotecmd.sh :[RCMD_KEY] Start: 2005-02-15T08:31:22-0700 Completion: 2005-02-15T08:31:26-0700 Result: Complete Exception: No Data Available . . . Result : Server: server1 Status: 0 Message: Command executed successfully. Command: /bin/ls -l / Standard Output: total 321 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Feb 11 13:21 bin -> ./usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 4 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:25 boot drwxr-xr-x 3 root sys 512 Feb 11 14:27 cr drwxr-xr-x 15 root sys 4096 Feb 11 14:09 dev drwxr-xr-x 5 root sys 512 Feb 11 14:06 devices drwxr-xr-x 58 root root 4096 Feb 14 12:36 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:46 export dr-xr-xr-x 1 root root 1 Feb 11 14:11 home drwxr-xr-x 12 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:25 kernel lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Feb 11 13:21 lib -> ./usr/lib Server: server2 Status: 0 Message: Command executed successfully. Command: /bin/ls -l / Standard Output: total 321 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Feb 11 13:21 bin -> ./usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 4 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:25 boot drwxr-xr-x 3 root sys 512 Feb 11 14:27 cr drwxr-xr-x 15 root sys 4096 Feb 11 14:09 dev drwxr-xr-x 5 root sys 512 Feb 11 14:06 devices drwxr-xr-x 58 root root 4096 Feb 14 12:36 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:46 export dr-xr-xr-x 1 root root 1 Feb 11 14:11 home drwxr-xr-x 12 root sys 512 Feb 11 13:25 kernel lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Feb 11 13:21 lib -> ./usr/lib |
Connecting to the Serial Console for a Managed Server
To remotely access the serial console for a managed server, use the connect server command.
Note –
The command line pane in the browser interface does not support this operation. You must use the n1sh shell to access the connect command.
This feature is particularly useful for performing diagnosis before and during the OS deployment and during the server power cycle. For example, the best way to monitor an OS provisioning job is to use the serial console of the system being deployed, as this displays the console output of an OS deployment.
You can perform this operation from the browser interface's Server Details page, as shown in the illustration. To view information about using the browser interface to access the serial console for a server, in the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help, find the topic 'To Open the Serial Console for a Server.'
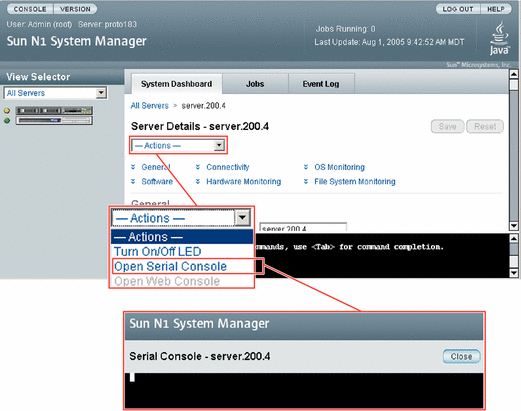
The management server redirects output of the managed server's serial console to the terminal emulator applet that is running in the browser interface.
The terminal emulator applet that is used by the browser interface for the serial console feature does not provide a certificate-based authentication of the applet. The applet also requires that you enable SSHv1 for the management server. For certificate-based authentication or to avoid enabling SSHv1, use the serial console feature by running the connect command from the n1sh shell.
The serial emulator appears and takes you either to the root prompt or a read-only prompt.
Note –
If a managed server is powered off, the console still connects, but no output appears until the managed server is powered on.
To use the Serial Console feature from the Server Details page in the browser interface, the Sun Java Plugin 1.4.2 or later must be installed on the system where you are running the browser. Not all of the supported browsers for the N1 System Manager have the Sun Java Plugin 1.4.2 installed, so you might have to install the plugin.
Note –
Use of the serial console is not supported for Sun Fire X2100 servers.
This procedure describes how to remotely access the serial console of managed servers.
Example 5–23 Connecting to the Serial Console
When in serial console mode, the n1sh shell sends all user input to the remote serial console. The N1 System Manager neither blocks nor supplements the platform-specific exit-control sequence. Note that the connect command is not implemented in the browser interface's Command Line pane. The connect command may only be run from the n1sh shell.
This example shows how to connect to the serial console as a root user. However, any user role with the ServerConsole privilege may issue the connect command.
% ssh -l root server1.central:6789 password: Copyright (c) 2005 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved Use is subject to license terms. N1-ok> connect server server1 |
After you have opened the serial console, you can view the detailed output during an OS deployment or a power cycle. For instructions, see Deploying OS Profiles in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide and To Reboot a Managed Server or a Group.
If the Open Serial Console menu item does not appear, SSHv1 is not enabled. To enable SSHv1, use the n1smconfig utility. See To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Connecting to the Sun ILOM Web GUI for a Managed Server
To remotely access the Sun ILOM Web GUI for a Sun Fire X4000 Series server, use the connect server command.
Note –
The command line pane in the browser interface does not support this operation. You must use the n1sh shell to access the connect command.
This feature is supported only for Sun Fire X4000 Series servers. Use the n1smconfig script to enable auto-log to the ILOM Web GUI. For further information on enabling auto-log to the ILOM Web GUI, and on subsequently disabling it, see Configuring the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
This feature is particularly useful for ILOM managed servers, for performing diagnosis before and during the OS installation and during the server power cycle.
You can perform this operation from the browser interface. To view information about using the browser interface to access the Sun ILOM Web GUI for a server, in the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help, find the topic 'To Open the Sun ILOM Web GUI for a Sun Fire X4000 Series Server.'
The management server redirects output of the managed server's console to the terminal emulator applet that is running in the browser interface.
The terminal emulator applet that is used by the browser interface for the ILOM Web GUI feature does not provide a certificate-based authentication of the applet. The applet also requires that you enable SSHv1 for the management server.
The emulator appears and takes you either to the root prompt or a read-only prompt.
Note –
If a server is powered off, the console still connects, but no output appears until the server is powered on.
To use the Sun ILOM Web GUI feature from the Server Details page in the browser interface, the Sun Java Plugin 1.4.2 or later must be installed on the managed server where you are running the browser. Not all of the supported browsers for the N1 System Manager have the Sun Java Plugin 1.4.2 installed, so you might have to install the plugin.
This procedure describes how to remotely access the Sun ILOM Web GUI for managed servers of the Sun Fire X4000 series.
Note –
Use of the Sun ILOM Web GUI is only supported for Sun Fire X4000 series servers.
Example 5–24 Connecting to the Sun ILOM Web GUI
The only way to connect to the Sun ILOM Web GUI is through the simple option in the browser interface. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
If the Open ILOM Web GUI menu item does not appear, SSHv1 is not enabled. To enable SSHv1, use the n1smconfig utility. See To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
The Sun ILOM Web GUI autlogin feature for Sun Fire X4100 and Sun Fire X4200 servers exposes the server's service processor credentials. See Security Considerations in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide for details.
After you have opened the Sun ILOM Web GUI, you can view the detailed output during an OS deployment or a power cycle. For instructions, see Deploying OS Profiles in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Operating System Provisioning Guide and To Reboot a Managed Server or a Group.
Refreshing and Finding Managed Servers and Groups
This section describes the following tasks:
Refreshing Managed Server and Group Data
To update managed server and group data, use the set server command with the refresh subcommand. This command updates the following data:
-
Hardware health information including power status, memory, processor information and NIC information
-
Firmware information
-
OS resource usage, such as CPU and filesystem usage, if an OS is loaded and if OS monitoring is supported and enabled
-
OS update information if an OS update is loaded and if OS monitoring is supported and enabled
 To Refresh Data for a Managed Server or a Group
To Refresh Data for a Managed Server or a Group
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use one of the following commands:
N1-ok> set server server refresh
The managed server data is updated. See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
N1-ok> set group group refresh
The group data is updated. See set group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Note –Refresh job completion will be longer for server groups.
Finding a Managed Server in a Rack
To illuminate the server's LED locator light, use the set server command with the locator subcommand. For syntax and parameter details, type help set server at the N1–ok command line.
 To Find a Managed Server in a Rack
To Find a Managed Server in a Rack
This procedure describes how to illuminate the LED locator light on a managed server.
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use the following command:
N1-ok> set server server locator=true
The LED locator light on the managed server illuminates. See set server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
Deleting Managed Servers and Groups
To remove a server or group from the N1 System Manager, use the delete server or delete group command.
For syntax and parameter details, type help delete server or help delete group at the N1–ok command line.
 To Delete a Managed Server or a Group
To Delete a Managed Server or a Group
Steps
-
Log in to the N1 System Manager.
-
Use one of the following commands:
N1-ok> delete server server
The managed server is deleted from the N1 System Manager. See delete server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
N1-ok> delete group group
The group is deleted from the N1 System Manager. This command will not remove managed servers from the N1 System Manager. See delete group in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for details.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
