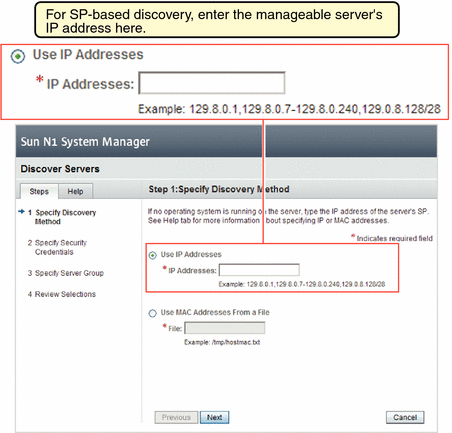
How to Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based Discovery
The To Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based Discovery Using the Command Line procedure shows how to use the command line to execute this task. You can also use the browser interface to execute this task. Use the discover button in the Servers table to call the Discover Servers wizard. See the Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Online Help for details.
As shown by Table 2–6, you cannot execute the discover command without having the JobRead privilege.
 To Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based
Discovery Using the Command Line
To Discover Manageable Servers Using SP-Based
Discovery Using the Command Line
Note –
Servers discovered through their SP are automatically monitored for hardware health.
Before You Begin
Before you discover a new hardware component, read Chapter 2, Sun N1 System Manager System and Network Preparation, in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide for details on setting up a server for discovery.
Do not use the N1 System Manager to discover servers that have system management software installed on them such as Sun Management Center, Sun Control Station, or any other system management applications including the N1 System Manager.
Step
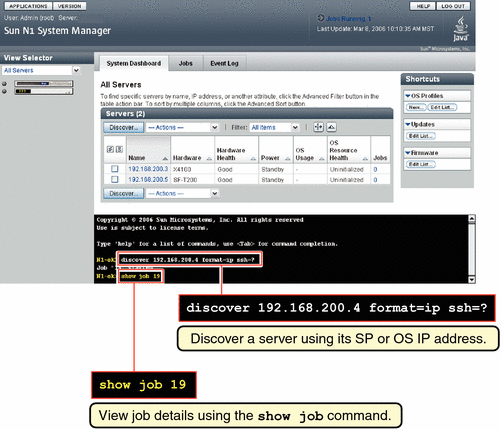
Use the discover command to discover a server through its SP.
N1-ok> discover IP,IP-IP,subnet/mask format ip [group group] [ipmi username/password] [snmp credential/credential] [ssh username/password] [telnet username/password] |
IP addresses, IP address ranges, and IP subnets can be input as a comma-separated list. Overlapping IP address ranges are allowed.
Note –
When you specify the range of IP addresses for discovery, ensure that the IP address range does not include the IP addresses of the N1 System Manager management server.
Security credentials for IPMI, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), SSH and Telnet are optional. If credentials are not specified, the manufacturer defaults are used. See Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide for information about the default accounts.
See discover in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Command Line Reference Manual for more details about the syntax used in the discover command.
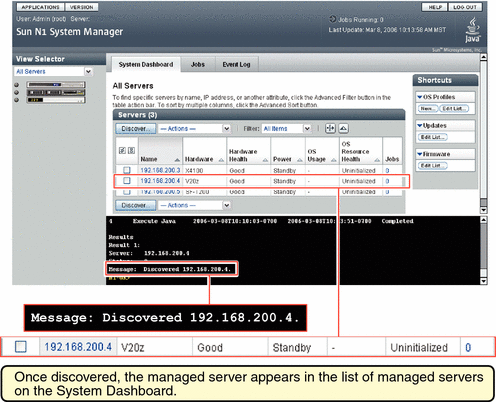
After successful completion of the Discovery job, a managed server is identified by its management name. If the server was discovered using SP-based discovery, its management name is initially set to the server's management IP address. You can rename discovered servers at any time.
Example 4–1 Using SP-based Discovery With Management Network IP Addresses
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover servers through their service processor. The servers have the following management network IP addresses: 192.168.1.1–192.168.1.3, 192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95, and 192.168.1.107.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.1-192.168.1.3,192.168.1.5-192.168.1.95,192.168.1.107 format ip group dev ssh root/admin Job 3 started. |
The group subcommand adds the successfully discovered servers into a server group called dev. The ssh option specifies the user name and password configured for access on the management port. In this example, the SSH user name root and password admin are used to authenticate the hardware discovery.
The following example command shows how to view the Discovery job and the job status.
N1-ok> show job all Job ID Date Type Status Owner 3 2005-06-28T06:53:53-0700 Discovery Completed root 2 2005-06-28T06:01:20-0700 Create OS Distribution Completed root 1 2005-06-28T05:57:14-0700 Create OS Distribution Completed root |
The following example command shows how to verify that the discovered servers were added to the server group.
N1-ok> show group all Name us Jobs Servers Spare dev 7 |
The following example command shows how to view the list of managed servers in the group and the power and hardware health status.
N1-ok> show group dev Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
Example 4–2 Using SP-Based Discovery With Netmask
The following example of the discover command shows how to discover any servers through their SP, using the netmask. The servers have management network IP addresses assigned in the 192.168.1.0/8 netmask.
N1-ok> discover 192.168.1.0/8 ssh root/admin Job 18 started. |
The following example shows how to view the discovered servers.
N1-ok> show server all Name Hardware Hardware Health Power OS Usage OS Resource Health 192.168.1.1 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.2 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.5 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.15 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.25 X4100 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.95 X4200 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.107 SF-V240 Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.200 V20z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.245 V40z Good On -- Uninitialized 192.168.1.255 NETRA-240 Good On -- Uninitialized |
Troubleshooting
The discover command credential attributes are used for security. If used, SSH, IPMI, and Telnet require a username and a password. SNMP requires that you input a valid value for the read security community string. If credentials are not specified, the discovery process uses the default credentials that were defined during installation.
Sun Fire X4000 series servers only initialize custom accounts once. For Sun Fire X4000 series servers discovered using a username and password combination:
-
If user is root and the password supplied is not the default, and the SP root password is the default: the SP root password is changed by the N1 System Manager to the password.
-
If user is not root and if user does not exist, and the SP root password is the default: the N1 System Manager creates the new user with a password of password. The N1 System Manager also changes the root password to the password.
For information about default credentials, see Setting Up Manageable Servers in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide.
Discovery might fail due to stale SSH entries on the management server. If the discover command fails with an error message indicating that there are invalid credentials or SSH key changed: Cannot connect to host and no true security breach has occurred, remove the known_hosts file or the specific entry in the file that corresponds to the managed server. Then, retry the discover command. See To Update the ssh_known_hosts File in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
The problem of stale SSH entries on the management server can be avoided if, during the n1smconfig configuration process, you modify SSH policies by accepting changed or unknown host keys. Accepting changed or unknown host keys carries a security risk but avoids the problem of stale SSH entries on the management server. For more information, see To Configure the N1 System Manager in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Discovery might fail due to a firmware version problem with drivers. See Cannot Discover a Manageable Server in Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Troubleshooting Guide for details.
The OS does not belong to the server in question if the add command fails with the following error:
Internal error: No mac address match found
Discovery can fail with the following error message:
Check the Standard Output field for possible reasons for this failure
To see the Standard Output field, check the job details in the browser interface or by using the show job command with the job number of the discovery job that failed.
See Also
Sun N1 System Manager 1.3 Site Preparation Guide and Troubleshooting Discovery.
Next Steps
Open the server's serial console. To view information about accessing a server's serial console, in the Sun N1 System Manager online help, find the topic `To Open the Serial Console for a Server'.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
