Usage Policies
The administrator of a cluster can define high-level usage policies that are customized according to whatever is appropriate for the site. Four usage policies are available:
-
Urgency. Using this policy, each job's priority is based on an urgency value. The urgency value is derived from the job's resource requirements, the job's deadline specification, and how long the job waits before it is run.
-
Functional. Using this policy, an administrator can provide special treatment because of a user's or a job's affiliation with a certain user group, project, and so forth.
-
Share-based. Under this policy, the level of service depends on an assigned share entitlement, the corresponding shares of other users and user groups, the past usage of resources by all users, and the current presence of users within the system.
-
Override. This policy requires manual intervention by the cluster administrator, who modifies the automated policy implementation.
Policy management automatically controls the use of shared resources in the cluster to best achieve the goals of the administration. High-priority jobs are dispatched preferentially. Such jobs receive higher CPU entitlements if the jobs compete for resources with other jobs. The grid engine software monitors the progress of all jobs and adjusts their relative priorities correspondingly and with respect to the goals defined in the policies.
Using Tickets to Administer Policies
The functional, share-based, and override policies are defined through a grid engine system concept that is called tickets. You might compare tickets to shares of a public company's stock. The more stock shares that you own, the more important you are to the company. If shareholder A owns twice as many shares as shareholder B, A also has twice the votes of B. Therefore shareholder A is twice as important to the company. Similarly, the more tickets that a job has, the more important the job is. If job A has twice the tickets of job B, job A is entitled to twice the resource usage of job B.
Jobs can retrieve tickets from the functional, share-based, and override policies. The total number of tickets, as well as the number retrieved from each ticket policy, often changes over time.
The administrator controls the number of tickets that are allocated to each ticket policy in total. Just as ticket allocation does for jobs, this allocation determines the relative importance of the ticket policies among each other. Through the ticket pool that is assigned to particular ticket policies, the administration can run a grid engine system in different ways. For example, the system can run in a share-based mode only. Or the system can run in a combination of modes, for example, 90% share-based and 10% functional.
Using the Urgency Policy to Assign Job Priority
The urgency policy can be used in combination with two other job priority specifications:
-
The number of tickets assigned by the functional, share-based, and override policies
A job can be assigned an urgency value, which is derived from three sources:
-
The job's resource requirements
-
The length of time a job must wait before the job runs
-
The time at which a job must finish running, that is, the job's deadline
The administrator can separately weight the importance of each of these sources in order to arrive at a job's overall urgency value. For more information, see Chapter 5, Managing Policies and the Scheduler, in Sun N1 Grid Engine 6.1 Administration Guide.
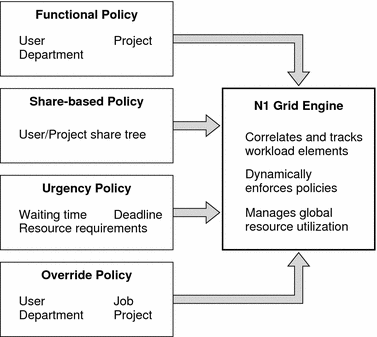
Figure 1–2 shows the correlation among policies.
Figure 1–2 Correlation Among Policies in a Grid Engine System
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
