| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
System Administration Guide: IP Services Oracle Solaris 11 Express 11/10 |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
System Administration Guide: IP Services Oracle Solaris 11 Express 11/10 |
1. Planning an IPv4 Addressing Scheme (Tasks)
2. Planning an IPv6 Addressing Scheme (Overview)
Address Autoconfiguration and Neighbor Discovery
Improved Support for IP Header Options
Application Support for IPv6 Addressing
IPv6 Requests for Comments and Internet Drafts
Transitional Global Unicast Addresses
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol Overview
IPv6 Address Autoconfiguration
Stateless Autoconfiguration Overview
3. Planning an IPv6 Network (Tasks)
4. Configuring TCP/IP Network Services and IPv4 Addressing (Tasks)
5. Enabling IPv6 on a Network (Tasks)
6. Administering a TCP/IP Network (Tasks)
8. Troubleshooting Network Problems (Tasks)
9. TCP/IP and IPv4 in Depth (Reference)
12. Planning for DHCP Service (Tasks)
13. Configuring the DHCP Service (Tasks)
14. Administering DHCP (Tasks)
15. Configuring and Administering the DHCP Client
16. Troubleshooting DHCP (Reference)
17. DHCP Commands and Files (Reference)
18. IP Security Architecture (Overview)
20. IP Security Architecture (Reference)
21. Internet Key Exchange (Overview)
23. Internet Key Exchange (Reference)
24. IP Filter in Oracle Solaris (Overview)
Part IV Networking Performance
26. Integrated Load Balancer Overview
27. Configuration of Integrated Load Balancer Tasks
28. Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (Overview)
29. VRRP Configuration (Tasks)
30. Implementing Congestion Control
Part V IP Quality of Service (IPQoS)
31. Introducing IPQoS (Overview)
32. Planning for an IPQoS-Enabled Network (Tasks)
33. Creating the IPQoS Configuration File (Tasks)
34. Starting and Maintaining IPQoS (Tasks)
35. Using Flow Accounting and Statistics Gathering (Tasks)
This section introduces terms that are fundamental to the IPv6 network topology. The following figure shows the basic parts of an IPv6 network.
Figure 2-1 Basic Components of an IPv6 Network
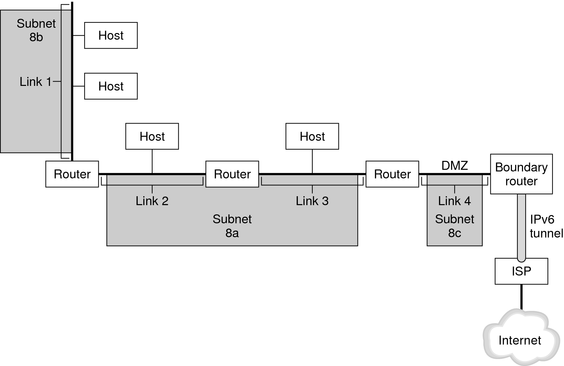
The figure depicts an IPv6 network and its connection to an ISP. The internal network consists of Links 1, 2, 3, and 4. Each link is populated by hosts and terminated by a router. Link 4, which is the network's DMZ, is terminated on one end by the boundary router. The boundary router runs an IPv6 tunnel to an ISP, which provides Internet connectivity for the network. Links 2 and 3 are administered as Subnet 8a. Subnet 8b consists only of systems on Link 1. Subnet 8c is contiguous with the DMZ on Link 4.
As illustrated in Figure 2-1, an IPv6 network has essentially the same components as an IPv4 network. However, IPv6 terminology differs slightly from IPv4 terminology. Here is a list of familiar terms for network components as they are used in an IPv6 context.
Any system with an IPv6 address and interface that is configured for IPv6 support. This generic term applies to both hosts and routers.
A node that forwards IPv6 packets. At least one of the router's interfaces must be configured for IPv6 support. An IPv6 router can also advertise the registered IPv6 site prefix for the enterprise over the internal network.
A node with an IPv6 address. An IPv6 host can have more than one interface that is configured for IPv6 support. As in IPv4, IPv6 hosts do not forward packets.
A single, contiguous network medium that is bounded on either end by a router.
An IPv6 node that is on the same link as the local node.
The administrative segment of an IPv6 network. Components of an IPv6 subnet can directly correspond to all nodes on a link, as in IPv4. Nodes on a link can be administered in separate subnets, if required. Additionally, IPv6 does support multilink subnets, where nodes on more than one link can be components of a single subnet. Links 2 and 3 in Figure 2-1 are components of multilink Subnet 8a.
A tunnel that provides a virtual point-to-point path between an IPv6 node and another IPv6 node endpoint. IPv6 supports manually configurable tunnels and automatic 6to4 tunnels.
The router at the edge of a network that provides one end of the IPv6 tunnel to an endpoint outside the local network. This router must have at least one IPv6 interface to the internal network. For the external network, the router can have an IPv6 interface or an IPv4 interface.