| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS Adapter for TCP/IP HL7 User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS Adapter for TCP/IP HL7 User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
Oracle Java CAPS Adapter for TCP/IP HL7 User's Guide
Oracle Java CAPS Adapter for TCP/IP HL7 Overview
About Oracle Java CAPS Adapter for TCP/IP HL7
The TCP/IP HL7 Adapter Architecture
Oracle Java Composite Application Suite Functionality
Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow and Architecture
Outbound Standard Messaging Mode
Outbound Adapter Roles for Delayed ACK Scenarios
HL7 Sequence Numbering Protocol
Stopping the Collaboration with a Fatal Alert
Support for HL7 Version 2.5 SFT Segments
Schematron Support in the HL7 Adapter
Schematron Configuration in HL7 Adapter
Obtaining the Validator Object
Adding and Configuring a TCP/IP HL7 Adapter in a Connectivity Map
Adding a TCP/IP HL7 External Application to a Connectivity Map
To Add a TCP/IP HL7 External Application
Modifying the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter Properties in the Connectivity Map
Modifying Adapter Properties in the Connectivity Map
TCP/IP HL7 V2 Adapter Inbound Connectivity Map Properties
General Inbound Settings - TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings - Server Port Binding -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings - Client Connection Establishment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings - Inbound Connection Management -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Schedules - Listener Schedule -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Schedules - Service Schedule TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
HL7 Acknowledgment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
Lower Layer Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
Sequence Number Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
HL7 MSH Segment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
HL7 SFT Segment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
Communication Control -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
HL7 Recourse Action -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Inbound Adapter
TCP/IP HL7 V2 Adapter Outbound Connectivity Map Properties
General Outbound Settings -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
TCPIP Outbound Settings -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
TCPIP Outbound Settings - Client Connection Establishment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
TCPIP Outbound Settings - Server Port Binding -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
HL7 Acknowledgment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
Lower Layer Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
Sequence Number Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
HL7 MSH Segment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
HL7 SFT Segment -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
Communication Control -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
HL7 Recourse Action -- TCP/IP HL7 V2 Outbound Adapter
TCP/IP HL7 V3 Adapter Inbound Connectivity Map Properties
General Inbound Settings -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings - Server Port Binding -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings - Client Connection Establishment -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Settings - Inbound Connection Management -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Schedules - Listener Schedule -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
TCPIP Inbound Schedules - Service Schedule -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
HL7 Acknowledgment -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
Lower Layer Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
Sequence Number Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
HL7v3 Transmission Wrapper -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
Communication Control -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
HL7 Recourse Action -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
Schematron Validation -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Inbound Adapter
TCP/IP HL7 V3 Adapter Outbound Connectivity Map Properties
General Outbound Settings -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
TCPIP Outbound Settings -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
TCPIP Outbound Settings - Client Connection Establishment -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
TCPIP Outbound Settings - Server Port Binding -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
HL7 Acknowledgment -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
Lower Layer Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
Sequence Number Protocol -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
HL7v3 Transmission Wrapper -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
Communication Control -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
HL7 Recourse Action -- TCP/IP HL7 V3 Outbound Adapter
Configuring Oracle Java CAPS Adapter for TCP/IP HL7 Environment Properties
Configuring TCP/IP HL7 Adapter Environment Properties
To Configure the Environment Properties
TCP/IP HL7 Inbound Adapter Environment Properties
HL7 Inbound Adapter - TCPIP Inbound Settings
HL7 Inbound Adapter - MDB Pool Settings
HL7 Inbound Adapter - Sequence Number Protocol
HL7 Inbound Adapter - Database Settings
TCP/IP HL7 Inbound Adapter Environment Properties
HL7 Outbound Adapter - TCPIP Outbound Settings
HL7 Outbound Adapter - Connection Pool Settings
HL7 Outbound Adapter - Sequence Number Protocol
Using the TCP/IP HL7 Predefined Templates
Prerequisites for the HL7 V3 Sample Projects
Creating a Copy of an HL7 Sample Project
Customizing Predefined Collaborations for HL7
Creating Copies of HL7 Collaborations
To Create Copies of HL7 Collaborations
Adding an HL7 Message Library to an Existing Collaboration
To Add HL7 Message Library to an Existing Collaboration
About TCP/IP HL7 V2 Collaborations
TCP/IP HL7 V2 Adapter Projects Overview
TCP/IP HL7 V2 Adapter Collaborations
Inbound HL7 V2 Collaboration Overview
Inbound HL7 V2 Collaboration - Part 1
Inbound HL7 V2 Collaboration - Part 2
Inbound HL7 V2 Collaboration - Part 3
Outbound HL7 V2 Collaboration Overview
Outbound HL7 V2 Collaboration - Part 1
Outbound HL7 V2 Collaboration - Part 2
Outbound HL7 V2 Collaboration - Part 3
HL7 V2 Outbound Test Collaboration
About TCP/IP HL7 V3 Collaborations
TCP/IP HL7 V3 Adapter Projects Overview
TCP/IP HL7 V3 Adapter Collaborations
Inbound HL7 V3 Immediate Collaboration Overview
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Immediate Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 1
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Immediate Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 2
Inbound HL7 V3 Deferred Collaboration Overview
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Deferred Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 1
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Deferred Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 2
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Deferred Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 3
MLLP V2 and the Sample Projects
Creating and Configuring the MLLP V2.0 Database
To Create and Connect to the Database
To Run the MLLP V2.0 Database Scripts
To Create the Connection Pool and JDBC Resource
Associating the MLLP Database With the Adapter
MLLP V2 Content Exchange Model
Standard Inbound HL7 V2 Collaboration Overview over MLLPV2
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 -- Part 1
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 -- Part 2
HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 -- Part 3
The following topics provide a brief overview of HL7 V3, and describe the HL7 V3 Collaborations and provide instructions on copying and customizing the Collaborations:
For more information about HL7 V3, refer to the HL7 V3 Guide.
HL7 V3, like V2.x, is a standard for exchanging messages among healthcare information systems. However, HL7 V3 is not compatible with V2. V3 defines a more fully-specified data model with less flexibility for customization. This presents a tighter standard that is easier to use, and provides a higher level of formal modeling, complexity, and internal consistency.
HL7 V3 is based on information models, which define the specifications of sets of data that are specific to one area of interest. There are different types of information models, including:
Reference Information Model (RIM) – Defines the information content for a domain.
Domain Information Model (D-MIM) – Defines a set of class clones, attributes, and relationships, and is a subset of the RIM. Domains include the following:
Domains under Administrative Management:
Accounting and Billing
Claims & Reimbursements
Patient Administration
Personnel Management
Scheduling
Domains under Health and Clinical Management:
Clinical Document Architecture
Medical Records
Public Health Reporting
Clinical Genomics
Specimen Domain
Regulated Studies
Refined Message Information Model (R-MIM) – Defines message-specific content, and is a subset of the D-MIM).
The V3 standard also includes interactions, such as Create Patient Billing Account.
There are three modes of Acknowledgement process in HL7 V3:
Immediate Mode
Deferred Mode
Queued Mode
Several HL7 V3 sample Projects are provided with the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter to illustrate different scenarios for connecting with external HL7 systems. You can download the sample Projects from the Downloads page of the Java CAPS Suite Installer.
While this section focuses on the standard inbound and outbound HL7 scenarios, you can choose from any of the following samples:
HL7 Adapter Inbound Collaboration Project for HL7V3 PRPA_IN403001UV01 Interaction over MLLPV2
HL7 Adapter Outbound Collaboration Project for HL7V3 PRPA_PRPA_IN403001UV01 Interaction over MLLPV2
HL7 Adapter Inbound Collaboration Project for HL7V3 PRPA_IN403001UV01 With Schematron Validation Enabled
HL7 Adapter Collaboration Project for HL7 V2 to V3 Conversion and ebXML Wrapper on HL7V3 Message
HL7 Adapter Inbound Collaboration Project That Invokes Sub Collaborations for HL7V3
This section describes two inbound Collaboration (jcdHL7V3Inbound and jcdHL7V3DefrdInbound) and an outbound Collaboration (jcdHL7v3Outbound), provided within the standard sample Projects for inbound and outbound HL7 V3 messaging. These Collaborations are designed to work as is for HL7 V3 compliant interfaces, and can be configured for your specific needs using the property configuration files. If an interface requires special functionality, the Collaboration's Java code is easily accessible for modification, much of which can be created graphically using the Collaboration Editor's Business Rules Designer.
The Collaborations contain a number of Message Libraries that extend functionality for HL7 V3 message handling, logging, error messaging, journaling, and sequence numbering. These include both HL7 Message Libraries for the V3 domains, and the Resource Adapter that communicates to the external system and offers services to the application server. The Collaborations control messaging protocol and all business logic.
There are four inbound Collaborations in the prjHL7V3Inbound Project:
Inbound HL7 V3 Immediate Collaboration
Inbound HL7 V3 Deferred Collaboration
Inbound HL7 V3 Queue Manager
Inbound HL7 V3 Message Publisher
The Inbound HL7 V3 Collaboration, jcdHL7V3Inbound, contains Message Libraries for the HL7 V3 Resource Adapter, JMS Data, JMS Journal, and JMS Error, as well as the HL7 V3 Patient Administration Domain Interaction Event (PRPA_IN403001UV01) and the corresponding HL7 V3 Acknowledgements (MCCI_IN000004UV01). The Collaboration works with its own internal code and the properties configuration files.
Note - Immediate mode contains only one type of Acknowledgement Message Library, MCCI_IN000004UV01.
The following topics describe the business logic defined in the jcdHL7V3Inbound Collaboration:
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Immediate Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 1
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Immediate Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 2
An HL7 V3 message triggers an inbound Collaboration received from an external system or an outbound HL7 V3 client. The Collaboration calls the HL7 V3 user Collaboration rule by executing receive().
The receive method is the entry point to the HL7 V3 User Collaboration, with the following signature:
public void receive(com.stc.connector.appconn.tcpip.hl7.HL7ServerApplication input, com.stc.connectors.jms.JMS otdJMS_DATA, xsd.hl7v3.PRPA_IN403001UV01.PRPA_IN403001UV01_ otd_PRPA_IN403001UV01_1 xsd.hl7v3.MCCI_IN000004UV01.MCCI_IN000004UV01_ otd_MCCI_IN000004UV01 otdHL7_ACK_1,com.stc.connectors.jms.JMS otdJMS_JOURNAL, com.stc.connectors.jms.JMS otdJMS_ERROR) throws Throwable.
Note - The above text has been wrapped to fit the page.
Figure 15 Immediate Mode of ACK Process — Part 1
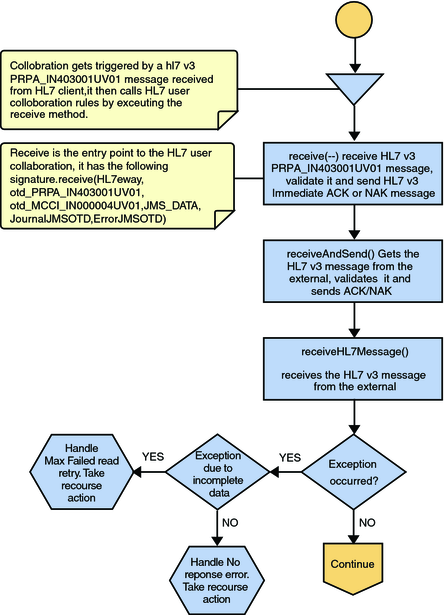
Once the message is received, the Collaboration determines whether the message needs to be validated. The HL7 V3 message is then validated, making sure that the message structure is correct. Various fields in the Transmission Wrapper of the message are also validated, such as Version Code, Processing Code, Processing Mode Code, and Interaction ID. If these fields do not match the configuration, a NAK is returned.
The Collaboration receives the HL7 V3 message from the external using receiveHL7Message(). If an exception occurs due to incomplete data, and the adapter fails to read the data within the configured number of retries, the associated recourse action is taken. If the exception is due to no response, the associated recourse action is taken.
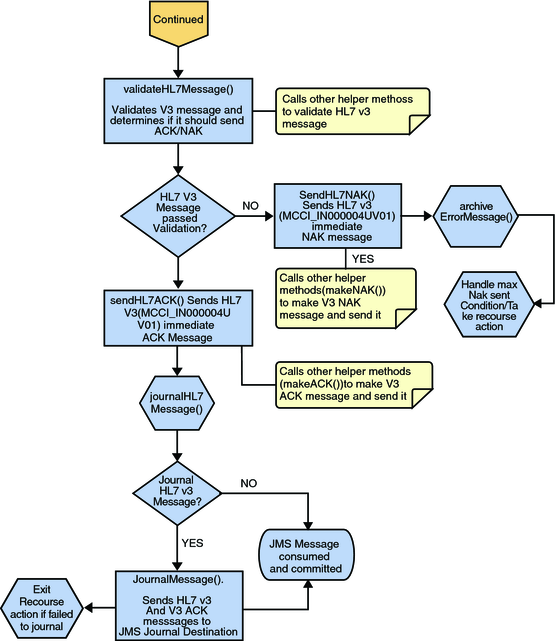
If no exception occurs, validateHL7Message() is called, which validates the message to determine whether to ACK or NAK the message. Other helper methods are also called to validate the HL7 V3 message.
If the HL7 V3 message does not pass validation, the Collaboration calls makeNak() and sendHL7Nak() to create and send the NAK to the external. The HL7 V3 message, with the NAK, is archived to the error queue. If the number of consecutive NAKs sent surpasses the maximum number of retries, the associated recourse action is taken.
If the HL7 V3 message passes validation, the Collaboration calls makeAck() and sendHL7Ack() to create and send the ACK to the external.
After the ACK is sent, the HL7 V3 message and the ACK are journaled to the JMS queue journal destination. If the message fails to journal the associated recourse action is taken.
Figure 16 Immediate Mode of ACK Process — Part 2
The Inbound HL7 V3 Collaboration, jcdHL7V3DeferredInbound, contains Message Libraries for the HL7 V3 Resource Adapter, JMS Data, JMS Journal, JMS Error, and JMS APP ACK as well as the HL7 V3 Patient Administration Domain Interaction Event (PRPA_IN403001UV01) and the corresponding HL7 V3 Commit Acknowledgement (MCCI_IN000006UV01) and Application Acknowledgement (MCCI_IN000007UV01). The Collaboration works with its own internal code and the Properties Configuration files.
Note - Deferred mode contains the following two types of Acknowledgement Message Libraries:
Commit Acknowledgement (MCCI_IN000006UV01)
Application Acknowledgement (MCCI_IN000007UV01)
The above JCD (jcdHL7V3DeferredInbound) will also work for both immediate mode and deferred mode.
The following topics describe the business logic defined in the jcdHL7V3DeferredInbound Collaboration:
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Deferred Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 1
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Deferred Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 2
HL7 V3 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow (For Deferred Mode of ACK Process) -- Part 3
A HL7 V3 message triggers an inbound Collaboration received from an external system or an outbound HL7 V3 Client. The Collaboration calls the HL7 V3 user Collaboration rule by executing receive().
The receive method is the entry point to the HL7 V3 User Collaboration, with the following signature:
public void receive(com.stc.connector.appconn.tcpip.hl7.HL7ServerApplication input, com.stc.connectors.jms.JMS otdJMS_DATA, xsd.hl7v3.PRPA_IN403001UV01.PRPA_IN403001UV01_ otd_PRPA_IN403001UV01_1 xsd.hl7v3.MCCI_IN000004UV01.MCCI_IN000004UV01_ otd_MCCI_IN000004UV01 xsd.hl7v3.MCCI_IN000006UV01.MCCI_IN000006UV01_ otd_MCCI_IN000006UV01 xsd.hl7v3.MCCI_IN000007UV01.MCCI_IN000007UV01_ otd_MCCI_IN000007UV01 com.stc.connectors.jms.JMS otdJMS_APPACK otdHL7_ACK_1,com.stc.connectors.jms.JMS otdJMS_JOURNAL, com.stc.connectors.jms.JMS otdJMS_ERROR) throws Throwable.
Note - The above text is wrapped to fit the page.
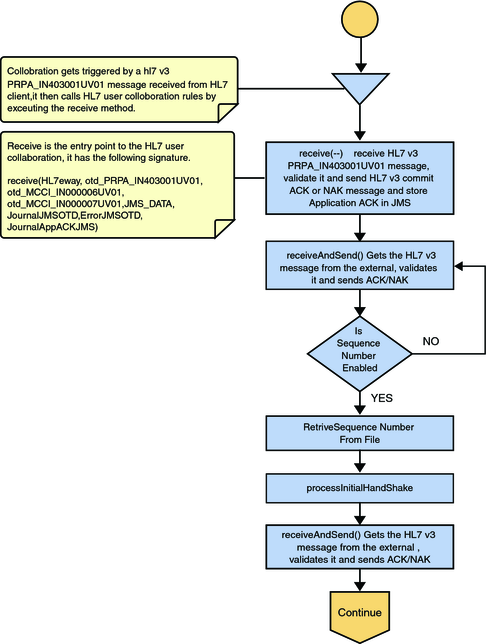
Once the message is received, the Collaboration determines whether the message needs to be validated. The HL7 V3 message is then validated, making sure that the message structure is correct. Various fields in the Transmission Wrapper of the message are also validated, such as Version Code, Processing Code, Processing Mode Code, and Interaction ID. If these fields do not match the configuration, a NAK is returned.
If sequence numbering is enabled the Collaboration checks to see if the messages sequence number is valid. If the sequence number is not valid, the adapter sends a NAK. The validated HL7 V3 message moves on to processInitialHandshake().
Figure 17 Deferred Mode of ACK Process — Part 1
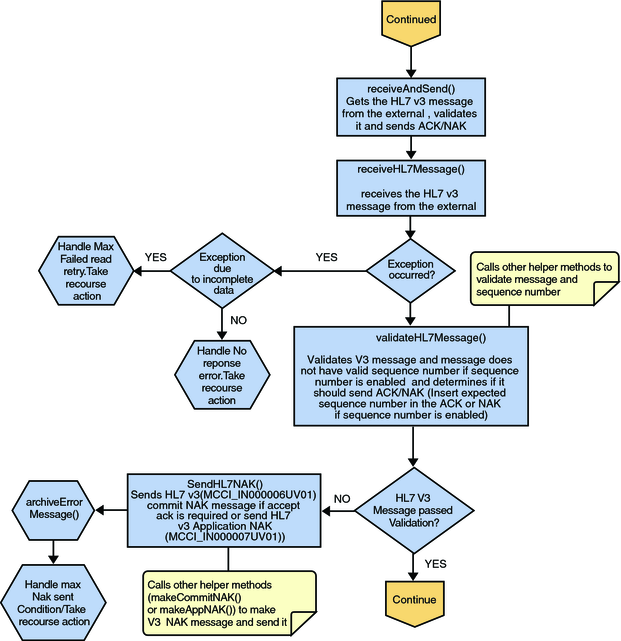
The Collaboration receives the HL7 V3 message from the external using receiveHL7message(). If an exception occurs due to incomplete data, and the adapter fails to read the data within the configured number of retries, the associated recourse action is taken. If the exception is due to no response, the associated recourse action is taken.
If no exception occurs, validateHL7Message() is called, which validates the message to determine whether to ACK or NAK the message. Other helper methods are also called to validate the HL7 V3 message.
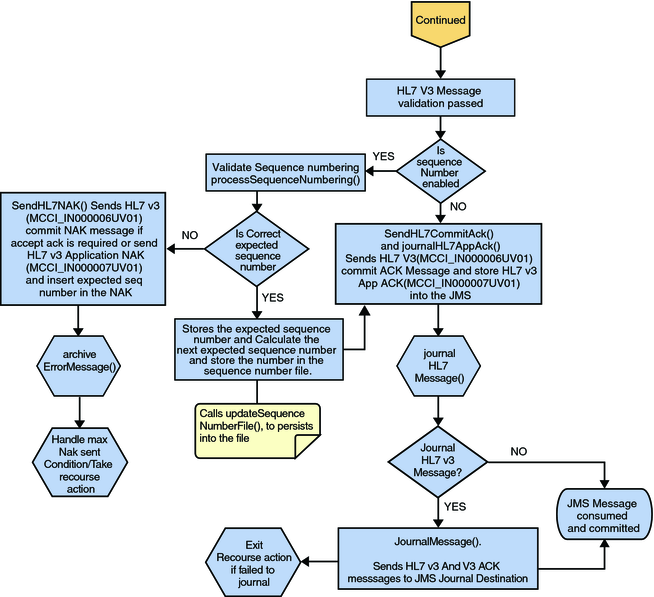
If the HL7 V3 message passes validation, the Collaboration calls makeCommitAck() and sendHL7CommitAck() to create and send the Commit ACK (MCCI_IN000006UV01) to the external. It then calls journalHL7AppAck() to create Application ACK (MCCI_IN000007UV01) and store it into the JMS.
Figure 18 Deferred Mode of ACK Process — Part 2
After the Commit ACK is sent and the Application ACK is stored in JMS, the HL7 V3 message and the ACKs are journaled to the JMS queue journal destination. If the message fails to journal the associated recourse action is taken.
Figure 19 Deferred Mode of ACK Process — Part 3
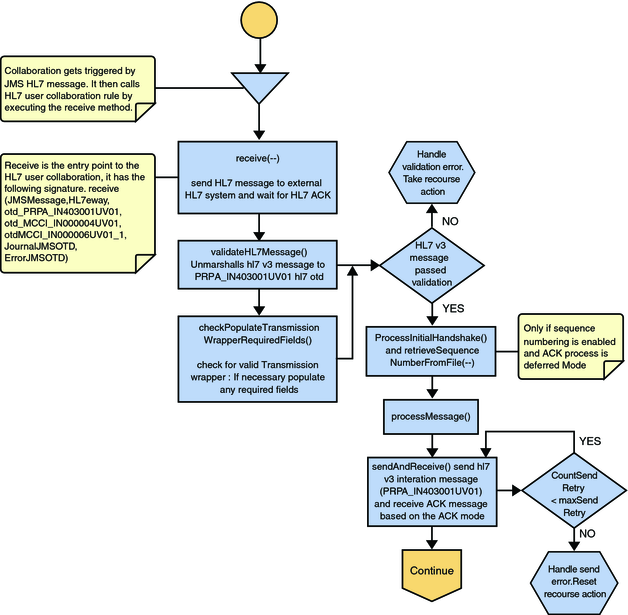
The Outbound HL7 V3 Collaboration, jcdHL7V3Outbound, contains Message Libraries for the HL7 V3 Resource Adapter, JMS Data, JMS Journal, and JMS Error, as well as the HL7 V3 Patient Administration Domain Interaction Event (PRPA_IN403001UV01) and the corresponding HL7 V3 Acknowledgements. MCCI_IN000004UV01 for Immediate Mode and MCCI_IN000006UV01 for Deferred Mode. The Collaboration works with its own internal code and the Properties Configuration files. The outbound Collaboration assumes that it is reading valid HL7 V3 messages, so the data flow that feeds this Collaboration must ensure this.
The Outbound Collaboration is for both immediate and deferred mode.
The following topics describe the processing logic defined in the jcdHL7V3Outbound Collaboration:
The Collaboration is triggered by a JMS HL7 V3 message. The Collaboration then calls the HL7 V3 User Collaboration Rule by executing the receive method. Receive is the entry point to the HL7 V3 User Collaboration, with the following signature:
receive (input, otdHL7eWay_1, otdJMS_JOURNAL, otdJMS_ERROR, otd_MCCI_IN000004UV01_1, otd_MCCI_IN000006UV01_1, otd_PRPA_IN403001UV01_1)
The incoming HL7 V3 message is then validated, making sure that the message structure is correct. Various fields in the Transmission Wrapper of the message are also validated, such as Version Code, Processing Code, Processing Mode Code, and Interaction ID.
If the message does not pass validation, an error occurs and the associated recourse action is applied. If the HL7 V3 message passes validation, the message moves on to processInitialHandshake() to receive a sequence number (if sequences numbering is enabled only for Deferred Mode). The Collaboration takes the sequence number from the sequencing numbering file and determines the next number to use. This number is then inserted into the HL7 V3 message.
Next, the message moves on to processMessage(), which calls the helper method, sendAndReceive(). The sendAndReceive method sends the HL7 V3 message, waits for an HL7 V3 ACK message, and processes the ACK or NAK. The validation also checks the message structure to see if the message is unmarshaled. If a valid ACK is not received, it continues to send the HL7 V3 message up to the configured number of retries, at which time an error occurs and the associated recourse action is taken.
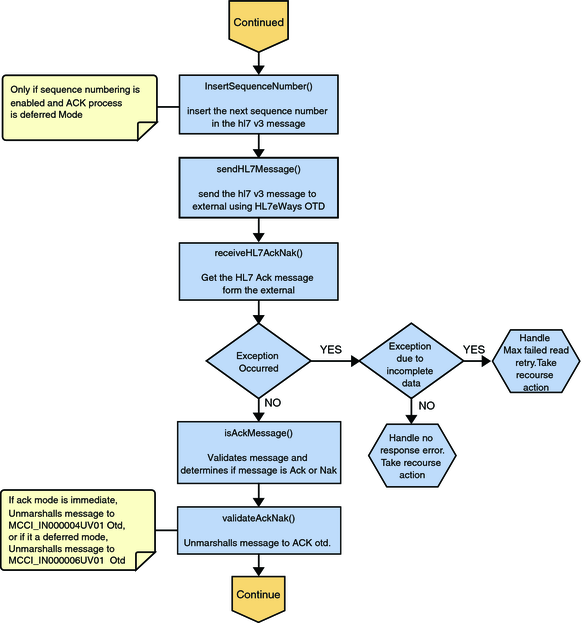
Figure 20 Immediate and Deferred Mode of ACK Process — Part 1
In processMessage(), the message moves on to insertSequenceNumber(). If sequence numbering is enabled and is in Deferred Mode, the insertSequenceNumber method inserts the sequence number and call sendHL7Message(). The sendHL7Message method sends the HL7 V3 message to the external using the HL7 V3 adapter Message Library
The Collaboration receives the HL7 V3 ACK or NAK from the external using receiveHL7AckNak(). If an exception occurs due to incomplete data, and the adapter fails to read the data within the configured number of retries, the associated recourse action is taken. If the exception is due to no response, the associated recourse action is taken. If no exception occurs, the ACK or NAK message moves on to isAckMessage(), which validates the message to determine whether the message is an ACK or a NAK.
Next, the validateAckNak method unmarshals the message to the ACK Message Library in MCCI_IN000004UV01 Message Library for Immediate Mode and MCCI_IN000006UV01 Message Library for Deferred Mode.
Figure 21 Immediate and Deferred Mode of ACK Process — Part 2
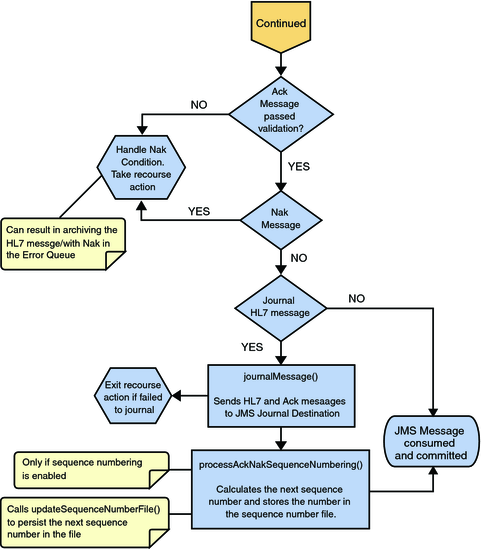
If the message does not pass validation it is handled as a NAK, the associated recourse action is taken, and the message is archived in the error queue.
If the message is a NAK, the associated recourse action is taken, and the message is archived in the error queue, along with the NAK message, as a JMS property
If the message is an ACK and passes validation, the message is sent on to the journalMessage method.
If the ACK message validates, the HL7 V3 message and ACK message are sent to the JMS journal Destination. If the message fails to journal, the associated recourse action is taken.
If sequencing numbering is enabled for Deferred Mode, the processAckNakSequenceNumbering method calculates the next sequence number and stores the number in the sequence number file, calling updateSequenceNumberFile to persist the next sequence number.
Figure 22 Immediate and Deferred Mode of ACK Process — Part 3
For information, see HL7 V2 Outbound Test Collaboration.