51 Securing Oracle Service Bus with Oracle Web Services Manager
Using Oracle Service Bus in conjunction with Oracle Web Services Manager provides scalable, standards-based, centrally managed approach to securing your SOA environment with WS-Security policies while leveraging your existing security providers.
Oracle Web Services Manager is a run-time framework for security policy creation, management, and governance. You create policies, attach them to services in Oracle Service Bus, and enforce those policies at various points in the messaging life cycle with Oracle Web Service Manager agents.
Note:
In future releases of Oracle Service Bus, Oracle Web Services Manager policies will replace and enhance the functionality of WLS 9.2 security policies. While this version of Oracle Service Bus continues to support WLS 9.2 policies, you should consider using Oracle Web Services Manager policies for new service creation to prepare for the eventual deprecation of WLS 9.2 policy support.This section includes the following topics:
-
Section 51.1, "About Oracle Web Services Manager Integration with Oracle Service Bus"
-
Section 51.2, "Setting Up and Using Oracle Web Services Manager with Oracle Service Bus"
-
Section 51.3, "Use Cases: Oracle Service Bus and WLS 9.2 Policies with Oracle Web Services Manager"
For more information about Oracle Web Services Manager, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.
51.1 About Oracle Web Services Manager Integration with Oracle Service Bus
Oracle Web Services Manager is a component of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, a run-time framework that provides centralized management and governance of Oracle SOA Suite environments and applications. You create and configure Oracle Web Services Manager policies in Oracle Enterprise Manager, and those policies are persisted in a policy store (a database is recommended). Oracle Web Services Manager lets you define policies against an LDAP directory and generate standard security tokens (such as SAML tokens) to propagate identities across multiple Web services used in a single transaction.
In Oracle Service Bus, when defining a business or proxy service that lets you attach security policies, you can attach available "OWSM" policies.
Because Oracle Web Services Manager is a run-time component, attaching policies to Oracle Service Bus services requires a connection to an Oracle Service Bus domain that has Oracle Web Services Manager enabled. For example, when creating and managing services that use Oracle Web Services Manager policies in Eclipse, your Oracle Service Bus configuration must be deployed on an Oracle Web Services Manager-enabled domain to attach the policies. With no run-time connection to Oracle Web Services Manager from the development environment, you can only view or remove policies previously attached to services.
Oracle Web Services Manager support in Oracle Service Bus is not available automatically. Enable Oracle Web Services Manager support in Oracle Service Bus by selecting the "Oracle Service Bus OWSM Extension" template when you create or extend an Oracle Service Bus domain. Once Oracle Web Services Manager support is enabled in an Oracle Service Bus domain, you cannot disable it. See Section 51.2.1, "Adding Oracle Web Services Manager and Oracle Enterprise Manager to an Oracle Service Bus Domain."
51.1.1 Security Providers
This section describes the security services that Oracle Service Bus and Oracle Web Services Manager use for authentication and authorization.
Oracle Web Service Manager uses Java Platform Security (JPS), so Oracle Service Bus uses JPS providers for Oracle Web Services Manager policies. Oracle Service Bus also uses Oracle Common Security Services (CSS) for other aspects of message security.
For more information about Oracle security services, see "About Oracle Platform Security Services" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Overview and "Introduction to Oracle Platform Security Services" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Application Security Guide.
The following points describe which security providers Oracle Service Bus and Oracle Web Services Manager use for different security areas.
51.1.1.1 JPS Providers
When using Oracle Web Services Manager policies:
-
Oracle Web Services Manager policies use SAML providers from JPS and not from Oracle WebLogic Server. For information on configuring SAML with Oracle Web Services Manager, see "Configuring SAML" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.
-
For authentication, Oracle Web Services Manager uses the JPS Login Module, which in turn calls authentication providers configured on Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
Oracle Web Services Manager and Oracle Service Bus support the Java Keystore (JKS) and the Farm Level Keystore (FKS) provided by Oracle Platform Security Services. For Oracle Web Services Manager policies, a best practice is to configure the keystore on JPS, with both the Oracle WebLogic Server and the JPS keystore referencing the same kind of keystore. For example, if you use a JKS file keystore, JPS and Oracle WebLogic Server should point to the same file. If you use an FKS keystore, JPS and Oracle WebLogic Server should point to the same FKS configuration. For more information, see Section 51.2.1, "Adding Oracle Web Services Manager and Oracle Enterprise Manager to an Oracle Service Bus Domain."
-
A JPS keystore serves as both a keystore and a truststore for Oracle Web Services Manager policies.
51.1.1.2 CSS Providers
Oracle Service Bus uses:
-
CSS providers to enforce WLS 9.2 policies
-
CSS providers to enforce transport security
-
Oracle WebLogic Server authorization providers for authorization policies
-
Custom Oracle WebLogic Server authentication providers and identity asserters for custom authentication policies
-
Oracle WebLogic Server credential providers and mappers
-
Oracle WebLogic Server keystore and truststore for WLS 9.2 policies
-
Authentication and identity assertion through Oracle Web Services Manager agents
51.2 Setting Up and Using Oracle Web Services Manager with Oracle Service Bus
This section includes the following topics:
51.2.1 Adding Oracle Web Services Manager and Oracle Enterprise Manager to an Oracle Service Bus Domain
To use Oracle Web Services Manager policies in Oracle Service Bus, you must create the proper database schemas for the Oracle Web Services Manager policy store, then extend an Oracle Service Bus domain to include Oracle Web Services Manager.
Note:
After you add Oracle Web Services Manager to an Oracle Service Bus domain, you cannot disable Oracle Web Services Manager in the domain.-
Use the Oracle Repository Creation Utility (RCU) to create the Oracle Web Services Manager database schemas in a supported database. Select the following schemas to create:
-
SOA and BPM Infrastructure
-
Metadata Services and AS Common Schemas are automatically selected when you select SOA Infrastructure
Make a note of the settings used to create the schemas, in particular the schema owner for Metadata Services.
For more information on running RCU, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide.
-
-
Extend your Oracle Service Bus domain with Oracle Web Services Manager and Oracle Enterprise Manager. Select the following domain templates when running the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard:
-
Oracle Service Bus OWSM Extension
-
Oracle WSM Policy Manager (automatically selected when you select the OWSM Extension)
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager (optional, needed for creating and managing Oracle Web Services Manager policies)
As part of the domain extension, the Oracle Configuration Wizard creates an OWSM MDS Schema in the JDBC configuration window. Select the schema and set the database information based on the RCU settings used to create the Oracle Web Services Manager schemas in the previous step, in particular the schema owner for Metadata Services (MDS).
For more information, see "Creating a Domain" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle SOA Suite.
-
-
As a best practice, configure the keystore on JPS, with both the Oracle WebLogic Server and the JPS keystore referencing the same kind of keystore. For example, if you use a JKS file keystore, JPS and Oracle WebLogic Server should point to the same file. If you use an FKS keystore, JPS and Oracle WebLogic Server should point to the same FKS configuration.
For information on creating the keystore, see "Setting up the Keystore for Message Protection" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.
After successful extension of the domain and creation of the keystore for Oracle Web Services Manager, you can create Oracle Web Services Manager policies using the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and attach policies to services in Oracle Service Bus. Oracle Web Services Manager automatically provides commonly used policies.
With the domain running, you can access Oracle Enterprise Manager with the following URL:
http://host:port/em
For more information on managing Oracle Web Services Manager policies, see "Managing Web Service Policies" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.
51.2.2 Attaching Oracle Web Services Manager Policies to Oracle Service Bus Services
This section provides guidelines for attaching Oracle Web Services Manager policies to Oracle Service Bus services.
After you extend your Oracle Service Bus domain to include Oracle Web Services Manager and create policies using Oracle Enterprise Manager, you can attach those policies to the following types of proxy and business services in Oracle Service Bus on the Policies page:
-
WSDL
-
Any SOAP
You can attach Oracle Web Services Manager policies only at the service level, and you cannot embed them in service WSDLs. For a given service, you must use either Oracle Web Services Manager policies or WLS 9.2 policies, but not both. You can, however, use one type of policy in a proxy service and another type in a corresponding business service.
In Eclipse, when adding Oracle Web Services Manager policies to services, you must be connected to a running domain that has Oracle Web Services Manager enabled. If you are not connected to a running server in the development environment, you can only view and remove previously added Oracle Web Services Manager policies, and Oracle Service Bus shows a warning that the Oracle Web Services Manager policies will be validated only on publish.
Note:
When working with multiple servers in Eclipse, Eclipse chooses the first valid Oracle Service Bus server in the list of servers for retrieval of Oracle Web Services Manager policies.Oracle Service Bus provides an "Add Compatible" feature on business service configurations that lets you replace WSDL embedded WS-Security policies not natively supported by Oracle Service Bus with compatible OWSM policies.
When attaching policies in the development environment, keep in mind that services in the development environment can be out of sync with services in the Oracle Service Bus Administration Console, so take care when updating services from Eclipse to the Console.
If you copy a service to create a same type of service (for example, copy a business service to create a new business service), be sure to review your Oracle Web Services Manager policies in the new service and make any necessary adjustments.
51.2.2.1 Policy Overrides
After adding Oracle Web Services Manager policies to a service, you can provide policy overrides on the Security page.
For the policies used, the user interface displays the override keys (properties) and their default values. The key names come from the policy binding. If allowed, a text box appears next to a key's default value where you can provide an override value.
Oracle Service Bus does not provide well-known keys for override, such as sign key alias or CSF key, which points to user credentials in a CSF store. (Oracle Service Bus provides user credentials in the service account.)
Override keys you provide are passed to the Oracle Web Service Manager agent during invocation.
51.2.3 Configuring SAML
See Chapter 54, "Using SAML with Oracle Service Bus." For information on configuring SAML with Oracle Web Services Manager, see "Configuring SAML" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services.
51.2.4 Advertising WSDLs to Support WS Standards
When WSDLs contain embedded Oracle Web Service Manager policies, you can advertise the policies to be compatible with the following policy standards, supported by Oracle Service Bus and Oracle SOA Suite:
-
WS-Policy 1.2 (default) and 1.5
-
WS-Security Policy 1.1 (default), 1.2, and 1.3
Using special query parameters in URLs to access WSDLs embedded with Oracle Web Services Manager policies, Oracle Service Bus generates WSDLs that comply with the required standards. For more information on accessing WSDLs with a URL, see "Viewing Resources in a Web Browser" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Service Bus.
Note:
This feature is not available in the Oracle Service Bus "Export WSDL" or "Generate WSDL" functionality.The special query parameters are &wsp (WS-Policy) and &wssp (WS-Security Policy), and you can use them in conjunction with the WSDL, PROXY, and BIZ URL patterns for retrieving WSDLs. For example:
-
http://localhost:7001/proxy/myProxy?WSDL&wsp=1.5&wssp=1.2
Returns the WSDL for myProxy, a WSDL-based proxy service, so that the Oracle Web Services Manager policy reference conforms to WS-Policy 1.5 and WS-Security Policy 1.2.
Note:
In the previous URL, /proxy/myProxy is the endpoint URI for the proxy service. -
http://localhost:7001/sbresource?PROXY/myProject/myProxy&wsp=1.5&wssp=1.2
Returns the WSDL for myProxy, a WSDL-based proxy service, so that the Oracle Web Services Manager policy reference conforms to WS-Policy 1.5 and WS-Security Policy 1.2.
-
http://localhost:7001/sbresource?BIZ/myProject/myBiz&wsp=1.5&wssp=1.3
Returns the WSDL for myBiz, a WSDL-based business service, so that the Oracle Web Services Manager policy reference conforms to WS-Policy 1.5 and WS-Security Policy 1.3.
-
http://localhost:7001/sbresource?WSDL/proxy/myProxy
Returns the WSDL for myProxy, a WSDL-based proxy service, so that the Oracle Web Services Manager policy reference conforms to WS-Policy 1.2 and WS-Security Policy 1.1. Because no query parameters are used, Oracle Service Bus uses the defaults.
-
http://localhost:7001/proxy/myProxy?WSDL&wssp=1.3
Because WS-Security Policy 1.3 is compatible only with WS-Policy 1.5, this returns the WSDL for myProxy so that the Oracle Web Services Manager policy reference conforms to WS-Security Policy 1.3 and WS-Policy 1.5.
-
Invalid Values/Combinations
WS-Security Policy 1.2 and 1.3 are compatible only with WS-Policy 1.5. For invalid value examples, see Table 51-1.
Tip:
In a Web browser, try different query parameter versions see how the returned WSDL changes.For a quick reference of query parameter combinations, see the following section, Section 51.2.4.1, "WSDL Query Parameter Reference for WS Policies."
51.2.4.1 WSDL Query Parameter Reference for WS Policies
This section provides a quick reference showing valid and invalid combinations of the &wsp and &wssp query parameters described in the previous section, Section 51.2.4, "Advertising WSDLs to Support WS Standards."
The examples use ?WSDL to retrieve the WSDL. You can also use the ?PROXY and ?BIZ methods of WSDL retrieval, as described in "Viewing Resources in a Web Browser" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Service Bus.
As shown in Table 51-1, when one or more parameters is omitted, Oracle Service Bus provides the valid default. For the invalid value exceptions, WS-Security Policy 1.2 and 1.3 are compatible with only WS-Policy 1.5, and vice versa.
Table 51-1 Valid and Invalid Combinations of the &wsp and &wssp Query Parameters
| Query Parameter Combinations | WS-Policy Version | WS-Security Policy Version |
|---|---|---|
|
...?WSDL |
1.2 |
1.1 |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.2 |
1.2 |
1.1 |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.5 |
1.5 |
1.3 |
|
...?WSDL&wssp=1.1 |
1.2 |
1.1 |
|
...?WSDL&wssp=1.2 |
1.5 |
1.2 |
|
...?WSDL&wssp=1.3 |
1.5 |
1.3 |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.2&wssp=1.1 |
1.2 |
1.1 |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.5&wssp=1.2 |
1.5 |
1.2 |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.5&wssp=1.3 |
1.5 |
1.3 |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.2&wssp=1.2 |
Invalid value exception |
Invalid value exception |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.2&wssp=1.3 |
Invalid value exception |
Invalid value exception |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.5&wssp=1.1 |
Invalid value exception |
Invalid value exception |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=3.0&wssp=1.2 |
Invalid value exception |
Invalid value exception |
|
...?WSDL&wsp=1.2&wssp=2.0 |
Invalid value exception |
Invalid value exception |
51.2.5 Deployment Considerations
When you export Oracle Service Bus configurations that contain services with Oracle Web Services Manager policy references, the references are maintained. You must ensure that the referenced policies also exist in the target environment. If the target environment is the IDE, warnings are displayed saying that policies will be validated on publish.
51.2.6 Auditing
To audit policy events in Oracle Enterprise Manager, you must set up an audit data repository and set up event collection. For more information, see the following topics in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services:
-
"Viewing Audit Reports" – Pre-defined audit reports for Oracle Web Services Manager in Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher include statistics for Oracle Service Bus.
You can audit the following policy-level events:
-
Policy creation, deletion, or modification
-
Assertion template creation, deletion, or modification
51.2.7 Monitoring Statistics
For this release, Oracle Enterprise Manager policy monitoring statistics and usage/impact analysis for Oracle Service Bus are not available. Therefore, you are not able to see the impact of policy modifications on the services those policies are attached to. However, Oracle Service Bus collects WS-Security error statistics for Oracle Web Services Manager policy enforcement errors as it does for WLS 9.2 policies, and those statistics are available in the Oracle Service Bus service monitoring dashboard.
51.2.8 Supported Assertions and Seed Policies
This section lists the Oracle Web Services Manger assertions and seed policies that Oracle Service Bus supports. User-defined assertions are also supported.
The assertion or policy "enabled/disabled" option in the user interface does not determine whether or not an assertion or policy is supported in Oracle Service Bus.
Note:
In the development environment, if you use unsupported seed policies:-
An effective WSDL generated in the development environment will skip unsupported policies.
-
Validation is performed on service publish.
51.2.8.1 Unsupported Assertions
Following is a list of unsupported Oracle Web Services Manager assertions. Any assertions not listed are supported, including user-defined assertions.
-
binding-permission-authorization
-
http-security
-
OptimizedMimeSerialization (MTOM)
-
RMAssertion (Reliable Messaging)
-
sca-component-authorization
-
sca-component-permission-authorization
-
UsingAddressing
-
wss-saml-token-bearer-over-ssl (Authentication)
51.2.8.2 Supported Seed Policies
Following is a list of supported Oracle Web Services Manager seed policies. User-defined policies are also supported.
Table 51-2 Supported OWSM Seed Policies
51.3 Use Cases: Oracle Service Bus and WLS 9.2 Policies with Oracle Web Services Manager
This section provides use cases that highlight the interaction between Oracle Service Bus services using WLS 9.2 policies and Oracle Web Services Manager features in providing security throughout the service pipeline.
When using Oracle Web Services Manager with WLS 9.2 policies in Oracle Service Bus services, no configuration is required, and you do not have to extend an Oracle Service Bus domain with Oracle Web Services Manager. You implement Oracle Web Services Manager features at the desired client and service locations, and the interaction and enforcement occurs automatically.
Note:
In future releases of Oracle Service Bus, Oracle Web Services Manager policies will replace and enhance the functionality of WLS 9.2 security policies. While this version of Oracle Service Bus continues to support WLS 9.2 policies, you should consider using Oracle Web Services Manager policies for new service creation to prepare for the eventual deprecation of WLS 9.2 policy support.For more information about Oracle Web Services Manager, see:
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Security and Administrator's Guide for Web Services
Oracle Web Services Manager 10.1.3 documentation at
http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E10291_01/index.htm -
"Overview of Interoperability with Oracle Service Bus 10g Security Environments" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Interoperability Guide for Oracle Web Services Manager
This document describes the following security use cases with Oracle Web Services Manager:
Note:
There is no equivalent of Gateway in Oracle Web Services Manager 11.1.1.51.3.1 Message Protection
This section describes the following use cases:
51.3.1.1 Message Protection with Client Agent
You can implement this use case with the following versions of Oracle Web Services Manager:
-
11.1.1.x
-
10.1.3.x
Figure 51-1 illustrates using the Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent for message protection.
Figure 51-1 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent
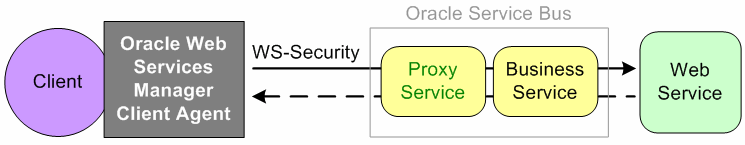
Description of "Figure 51-1 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent"
The proxy service has an inbound message protection policy. The Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent sends a signed and encrypted request to the proxy service. The proxy service receives the secured request and, acting as an active intermediary, decrypts and verifies signature and routes the request to the business service. The business service invokes the Web service, gets the response back, and sends it to the proxy service. The proxy service signs and encrypts the response and sends it to the Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent. The Client Agent receives the secure response, decrypts and verifies the signature, and passes the response to the client.
51.3.1.2 Message Protection with Server Agent
You can implement this use case with the following versions of Oracle Web Services Manager:
-
11.1.1.x
-
10.1.3.x
Figure 51-2 illustrates using the Oracle Web Services Manager Server Agent for message protection.
Figure 51-2 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Server Agent
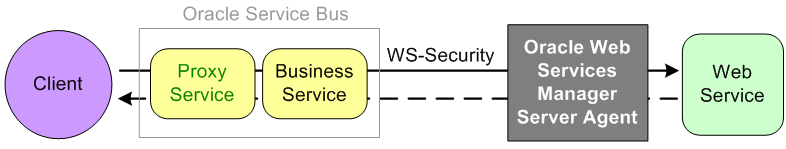
Description of "Figure 51-2 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Server Agent"
The client sends a plain request through the proxy and business services in Oracle Service Bus. The business service signs and encrypt the request and sends the message to the Oracle Web Services Manager Server Agent. The Server Agent decrypts and verifies the request. The plain message response is passed back to the client.
51.3.1.3 Message Protection with Client and Server Agents
You can implement this use case with the following versions of Oracle Web Services Manager:
-
11.1.1.x
-
10.1.3.x
Figure 51-3 illustrates using the Oracle Web Services Manager Client and Server Agents for message protection.
Figure 51-3 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Client and Server Agents
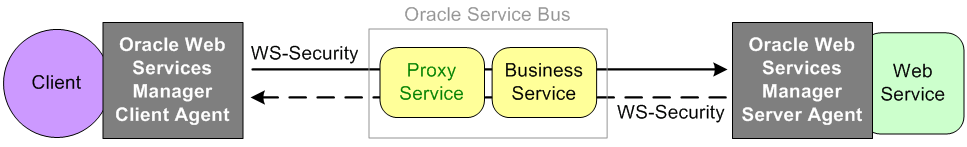
Description of "Figure 51-3 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Client and Server Agents"
The Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent signs and encrypts a client request and sends the request through to the proxy service. The proxy service decrypts and verifies the signature and passes the request to the business service, which signs and encrypts the request. The Web service has a Server Agent injected in it. The Server Agent has an inbound message protection policy that decrypts and verifies the signature, then signs and encrypts the response. The response is sent back to the business service, which verifies the message and passes the response to the proxy service. The proxy service generates a signed and encrypted response and sends it to the Client Agent. The Client Agent decrypts and verifies the response, then returns the plain response to the client.
51.3.1.4 Message Protection with Gateway
You can implement this use case with the following versions of Oracle Web Services Manager:
-
10.1.3.x
Figure 51-4 illustrates using the Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway for message protection.
Figure 51-4 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway
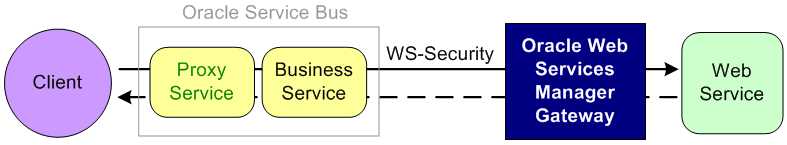
Description of "Figure 51-4 Message Protection With an Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway"
The client sends a plain request through the proxy and business services in Oracle Service Bus. The business service signs and encrypts the request and sends the message to the Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway. The Gateway decrypts and verifies the request. The plain message response is passed back to the client.
51.3.2 Authentication
You can implement this use case with the following versions of Oracle Web Services Manager:
-
11.1.1.x
-
10.1.3.x
Figure 51-5 illustrates using the Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent for authentication.
Figure 51-5 Authentication with an Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent
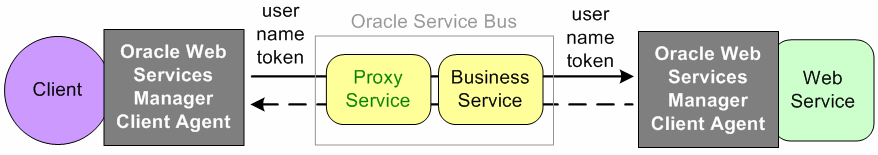
Description of "Figure 51-5 Authentication with an Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent"
The proxy service has a user name token policy. The client, through Oracle Web Services Manager Client Agent, sends a request to the proxy service with user credentials at the message level in a user name token. The proxy service maps the user credential from the user name token using credential mapping and sends it through the business service to the Web service for authentication. The Web service is protected using an Oracle Web Services Manager service agent with an inbound user name token policy. The Oracle Web Services Manager Service Client Agent extracts and authenticates the user credentials. The response is then sent back through the business service and the proxy service to the client.
51.3.3 Perimeter Security
You can implement this use case with the following versions of Oracle Web Services Manager:
-
10.1.3.x
Figure 51-6 illustrates using Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway for enforcing perimeter security.
Figure 51-6 Perimeter Security with Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway
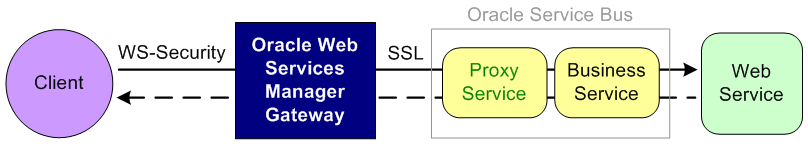
Description of "Figure 51-6 Perimeter Security with Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway"
Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway virtualizes the service exposed by the Oracle Service Bus proxy service. The inbound request to the Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway has a message protection policy. The client sends a secure request to the Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway virtualized service, which is signed and encrypted.
The Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway acts as a security enforcement point and decrypts and verifies the signature. Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway then routes the plain request to the proxy service over SSL. The proxy service forwards the request to the business service, which invokes the Web service and gets the plain response back. The response moves back through the proxy service and Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway to the client.
51.3.4 Identity Propagation
You can implement this use case with the following versions of Oracle Web Services Manager:
-
10.1.3.x
Figure 51-7 illustrates using the Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway for identity propagation using SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) token version 1.1.
Figure 51-7 Identity Propagation with Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway
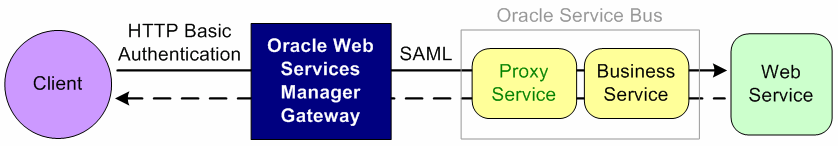
Description of "Figure 51-7 Identity Propagation with Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway"
The client sends a basic HTTP authentication request to the Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway. Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway authenticates the user using the user name and password from the HTTP header. Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway generates a SAML sender voucher assertion with the authenticated user identity (token mediation), inserts the SAML token, and sends the assertion to the proxy service. The proxy service receives the SAML assertion with the user identity and, acting as an active intermediary, verifies the user identity. The proxy service then passes the request to the business service. The response travels back through the business service, proxy service, and Oracle Web Services Manager Gateway to the client.