6 Govern the Asset Lifecycle
The sixth step in getting started with Governance is to govern the lifecycle of your assets.
This chapter contains the following sections:
6.1 Overview
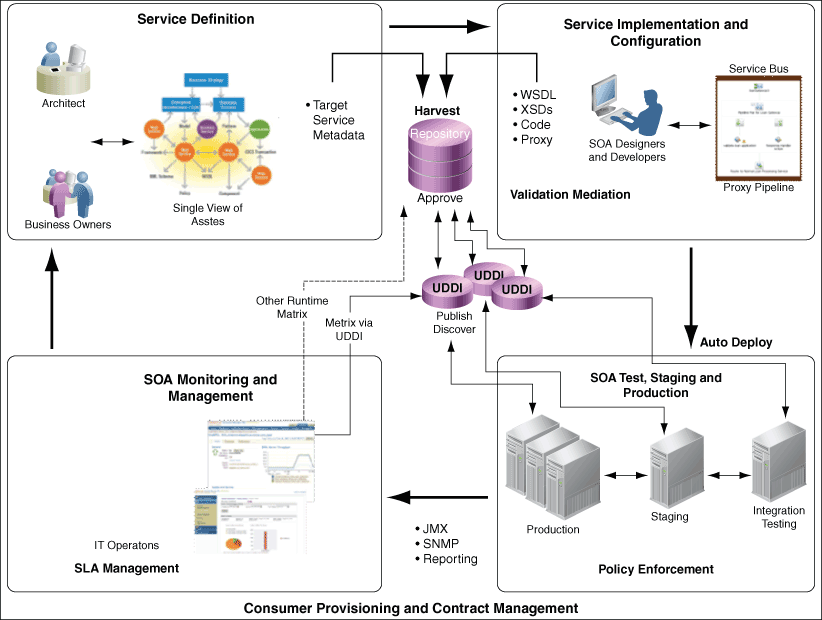
Once an organization has visibility into existing assets that they want to govern, the organization then should focus on inserting governance into the asset lifecycle process. Figure 6-1 illustrates the asset lifecycle process.
The process starts with the definition of a common capability that is needed by multiple groups across the enterprise. Once the capability is funded, a project is initiated to implement and/or configure the capability. After a capability is developed, it gets promoted from development to pre-production environments, which might include staging and testing. Finally, the capability is promoted to the production environment, where its performance can be monitored and measured, and its behavior can be enforced. This process is facilitated by Oracle Enterprise Repository's automated workflows.
6.2 Asset Lifecycle
This section describes the role of Governance in each of the asset lifecycle phases. This section contains the following topics:
6.2.1 Definition
When the organization recognizes that a capability is required, it should be made visible through the Enterprise Repository. These capabilities may come from architects who are working on the target architecture, or from business analysts who identify common requirements for their lines of business. Once in the enterprise repository, they can be evaluated and prioritized according to a common business or ROI model. Once evaluated and prioritized, these capabilities can be categorized into stages, such as proposed (meaning the capability has been identified and vetted), funded (there is an active project in the process of delivering the capability), and complete (the capability has been fully implemented).
There are several ways to make a capability visible through the Enterprise Repository:
-
Quick Submission
-
Advanced Submission
There is also information and a workbook available that will help you place a value on your capabilities. This can be used to help you justify and prioritize your asset investments:
-
Whitepaper: Determining the ROI of SOA through Reuse
-
Workbook: Determining the ROI of SOA through Reuse
For more information about how to determine the ROI of SOA through Reuse, see http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/repository/overview/index.html.
6.2.2 Implementation and Configuration
As capabilities are funded, projects are established to implement the capability. SOA Suite developers working in JDeveloper can see and reuse services from the enterprise repository to complete their projects. Service Bus developers working in Eclipse can see and reuse services from the enterprise repository to complete their projects. Developers can also submit their completed implementations directly to the Enterprise Repository. The Enterprise repository also supports VS .Net development.
-
For information about reusing assets through JDeveloper, Eclipse, and VS .Net, see "Configuring Your IDE to Support Integration with Oracle Enterprise Repository" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
For information about harvesting assets from JDeveloper, Eclipse, and VS .Net, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
6.2.3 Testing, Staging, and Production
Once an implementation has been harvested to Oracle Enterprise Repository, the repository's workflows process the implementation according to the governance rules and practices established by the organization. Oracle Enterprise Repository comes with several pre-configured workflows that can be customized to support the Governance practices of your organization.
For more information about Oracle Enterprise Repository's workflows, as well as the procedures for customizing the workflows, see "Configuring Oracle Enterprise Repository Workflow" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
As the implementation moves throughout the lifecycle, from testing, through staging, and into production, the endpoints for each environment are harvested into Oracle Enterprise Repository. This is accomplished by incorporating the Harvester into the Ant or WLST deployment script. After harvesting, Oracle Enterprise Repository provides visibility into a service with multiple endpoints, one for each environment.
For information about harvesting endpoints from the runtime environment using deployment scripts, see "Configuring and Using Automated Harvesting in Design-time and Runtime Environments" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
Oracle Enterprise Repository promotes the services and harvested endpoints to a Service Registry in each lifecycle environment. Oracle Enterprise Repository uses a tool called the Exchange Utility to perform the promotion. Once services are in the service registry, runtime tooling, such as OSB and SOA Suite, can dynamically discover changes in the runtime environment. OSB subscribes to the Service Registry's publish/subscribe API, such that OSB is automatically notified when a change occurs. Alternately, SOA Suite caches the WSDL and endpoint locations, as well as the UDDI service key, at design-time. If the WSDL or endpoints become invalid at any point in the lifecycle, SOA Suite will use the service key to dynamically discover and update the WSDL location and endpoint information.
-
For more information about configuring the Exchange Utility to promote assets from Oracle Enterprise Repository to Oracle Service Registry, see "Configuring Oracle Registry Repository Exchange Utility" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
For more information about Oracle Service Bus's dynamic Discovery capabilities, see the "UDDI" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Service Bus.
-
For more information about the dynamic discovery capabilities of Oracle SOA Suite, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite at http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E15523_01/integration.1111/e10224.pdf.
6.2.4 Consumer Provisioning and Contract Management
Some organizations may not want to automatically expose their production service endpoints to all consumers. Consumers may first be required to negotiate a service level agreement with the service provider. Oracle Enterprise Repository can facilitate this negotiation process.
For more information about the contract negotiation process, see http://download.oracle.com/otndocs/tech/soa/uddi/OracleSOAGovBootcampConsumerMgtLab.zip.
6.2.5 Monitoring and Management
It is important to both service providers and service consumers to understand how a service is performing in the runtime environment. In Oracle Enterprise Repository 11g, a summary of runtime service performance metrics can be brought into Oracle Enterprise Repository from Enterprise Manager SOA Management Pack Plus.
For information on configuring interoperability between Oracle Enterprise Repository and Enterprise Manager Management Pack Plus for SOA, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
Runtime metrics can also be brought into Oracle Enterprise Repository from Amberpoint, and similar tools, which publish service metrics to Oracle Service Registry. Bidirectional synchronization between Oracle Enterprise Repository and Oracle Service Registry is used to promote the runtime metrics from the registry to the repository.
Note that Oracle's Enterprise Manager Management Pack Plus for SOA provides runtime metrics directly to the Enterprise Repository.
For additional information about promoting metrics from Oracle Service Registry to Oracle Enterprise Repository, see "Metric Publishing" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.