2 Understanding Key Concepts
This chapter provides information about Oracle Fusion Middleware concepts that are related to administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
2.1 Understanding Key Oracle Fusion Middleware Concepts
Oracle Fusion Middleware provides two types of components:
-
A Java component, which is an Oracle Fusion Middleware component that is deployed as one or more Java EE applications and a set of resources. Java components are deployed to an Oracle WebLogic Server domain as part of a domain template. Examples of Java components are the Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle WebCenter Portal components.
-
A system component, which is a manageable process that is not deployed as a Java application. Instead, a system component is managed by Oracle Process Manager and Notification (OPMN).
A Java component and a system component are peers.
After you install and configure Oracle Fusion Middleware, your Oracle Fusion Middleware environment contains the following:
-
An Oracle WebLogic Server domain, which contains one Administration Server and one or more Managed Servers. The Administration Server contains Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control. The Managed Servers contain components, such as Oracle WebCenter Portal and Oracle SOA Suite as shown in Figure 1-1.
See Section 2.5 for information about Oracle WebLogic Server domains.
-
One or more Oracle instances, if your environment includes system components. See Section 2.6 for information about Oracle instances.
-
A database that is used as a metadata repository, if the components you installed require one. For example, Oracle SOA Suite requires a metadata repository. See Section 2.7 for information about metadata repositories.
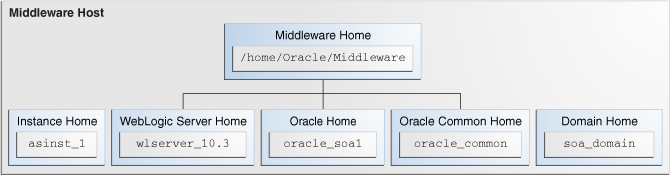
2.2 What Is a Middleware Home?
A Middleware home is a container for the Oracle WebLogic Server home, and, optionally, one Oracle Common home and one or more Oracle homes. A Middleware home can reside on a local file system or on a remote shared disk that is accessible through NFS.
A Middleware home can reside on a local file system or on a remote shared disk that is accessible through a network file system (NFS). The default Oracle Middleware home is /Oracle/Middleware on a UNIX operating system or \Oracle\Middleware on a Windows operating system. MW_HOME represents the location of a Middleware home in path names. The contents of an Oracle Middleware Home with a SOA installation are are shown in Figure 2-1.
See Section 2.3 for information about Oracle homes. See Section 2.4 for information about Oracle WebLogic Server homes.
2.3 What Is an Oracle Home and the Oracle Common Home?
An Oracle home contains installed files necessary to host a specific component or software suite. An Oracle home resides within the directory structure of the Middleware home. Each Oracle home can be associated with multiple Oracle instances or Oracle WebLogic Server domains. There can be multiple Oracle homes within each Middleware home.
The Oracle Common home contains the binary and library files required for Fusion Middleware Control and Java Required Files (JRF). There can be only one Oracle Common home within each Middleware home.
2.4 What Is a WebLogic Server Home?
A WebLogic Server home contains installed files necessary to host a WebLogic Server. The WebLogic Server home directory is a peer of Oracle home directories and resides within the directory structure of the Middleware home.
2.5 What Is a Domain Home?
The top-level directory of an Oracle WebLogic Server administration domain is referred to as the domain home. The directory structure of a domain is separate from the directory structure of the WebLogic Server home. A domain home can reside anywhere; it need not be within the Middleware home directory.
An Oracle WebLogic Server administration domain is a logically related group of Java components. A domain includes a special WebLogic Server instance called the Administration Server, which is the central point from which you configure and manage all resources in the domain. Usually, you configure a domain to include additional WebLogic Server instances called Managed Servers. You deploy Java components, such as Web applications, EJBs, and Web services, and other resources, to the Managed Servers and use the Administration Server for configuration and management purposes only.
A domain is a peer of an Oracle instance. Both contain specific configurations outside of their Oracle homes.
Figure 2-2 shows a SOA installation with an Oracle WebLogic Server domain containing an Administration Server and four managed servers.
Figure 2-2 Directory Structure after a WebLogic Domain is Created
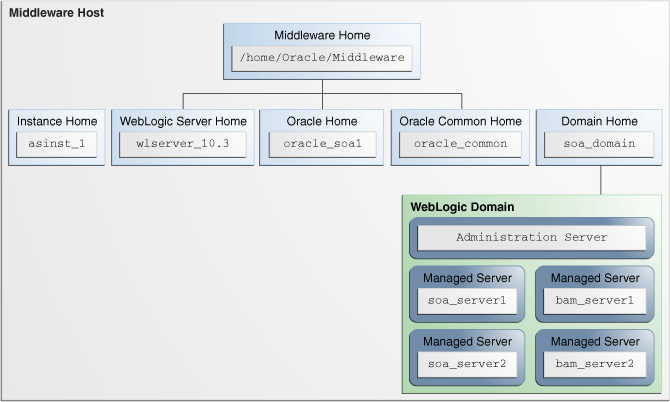
Description of "Figure 2-2 Directory Structure after a WebLogic Domain is Created"
See Also:
Oracle Fusion Middleware Understanding Domain Configuration for Oracle WebLogic Server for more information about domain configuration
The following topics describe entities in the domain:
2.5.1 What Is the Administration Server?
The Administration Server operates as the central control entity for the configuration of the entire domain. It maintains the domain's configuration documents and distributes changes in the configuration documents to Managed Servers. The Administration Server serves as a central location from which to manage and monitor all resources in a domain.
Each domain must have one server instance that acts as the Administration Server.
To interact with the Administration Server, you can use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST), or create your own Java Management Extentions (JMX) client. In addition, you can use Fusion Middleware Control for some tasks.
Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control run in the Administration Server. Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console is the Web-based administration console used to manage the resources in an Oracle WebLogic Server domain, including the Administration Server and Managed Servers. Fusion Middleware Control is a Web-based administration console used to manage Oracle Fusion Middleware, including components such as Oracle HTTP Server, Oracle SOA Suite, Oracle WebCenter, and Oracle Identity Management.
See Also:
-
"Getting Started Using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for more information about Fusion Middleware Control
-
"Getting Started Using Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide, as well as the Oracle Fusion Middleware Introduction to Oracle WebLogic Server and the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online help, for more information about Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console
2.5.2 What are Managed Servers and Managed Server Clusters?
Managed Servers host business applications, application components, Web services, and their associated resources. To optimize performance, Managed Servers maintain a read-only copy of the domain's configuration document. When a Managed Server starts, it connects to the domain's Administration Server to synchronize its configuration document with the document that the Administration Server maintains.
When you create a domain, you create it using a particular domain template. That template supports a particular component or group of components, such as the Oracle SOA Suite. The Managed Servers in the domain are created specifically to host those particular Oracle Fusion Middleware components.
Oracle Fusion Middleware Java components (such as Oracle SOA Suite, Oracle WebCenter Portal, and some Identity Management components), as well as customer-developed applications, are deployed to Managed Servers in the domain.
If you want to add other components, such as Oracle WebCenter Portal, to a domain that was created using a template that supports another component, you can extend the domain using the domain extension template for the component you want to add, this will create the additional Managed Servers for that component in the domain. See "Extending a Domain to Support Additional Components" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for more information.
For production environments that require increased application performance, throughput, or high availability, you can configure two or more Managed Servers to operate as a cluster. A cluster is a collection of multiple WebLogic Server instances running simultaneously and working together to provide increased scalability and reliability. In a cluster, most resources and services are deployed identically to each Managed Server (as opposed to a single Managed Server), enabling failover and load balancing. A single domain can contain multiple Oracle WebLogic Server clusters, as well as multiple Managed Servers that are not configured as clusters. The key difference between clustered and nonclustered Managed Servers is support for failover and load balancing. These features are available only in a cluster of Managed Servers.
See Also:
"Understanding WebLogic Server Clustering" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server
2.5.3 What Is Node Manager?
Node Manager is a Java utility that runs as a separate process from Oracle WebLogic Server and allows you to perform common operations for a Managed Server, regardless of its location with respect to its Administration Server. While use of Node Manager is optional, it provides valuable benefits if your Oracle WebLogic Server environment hosts applications with high-availability requirements.
If you run Node Manager on a computer that hosts Managed Servers, you can start and stop the Managed Servers remotely using the Administration Console or the command line. Node Manager can also automatically restart a Managed Server after an unexpected failure.
2.6 What Is an Oracle Instance?
An Oracle instance contains one or more system components, such as Oracle Web Cache, Oracle HTTP Server, or Oracle Internet Directory as shown in Figure 2-3. The system components in an Oracle instance must reside on the same computer. An Oracle instance directory contains updatable files, such as configuration files, log files, and temporary files.
An Oracle instance is a peer of an Oracle WebLogic Server domain. Both contain specific configurations outside of their Oracle homes.
The directory structure of an Oracle instance is separate from the directory structure of the Oracle home. It can reside anywhere; it need not be within the Middleware home directory.
Figure 2-3 Directory Structure of the Instance Home with an Oracle HTTP Server
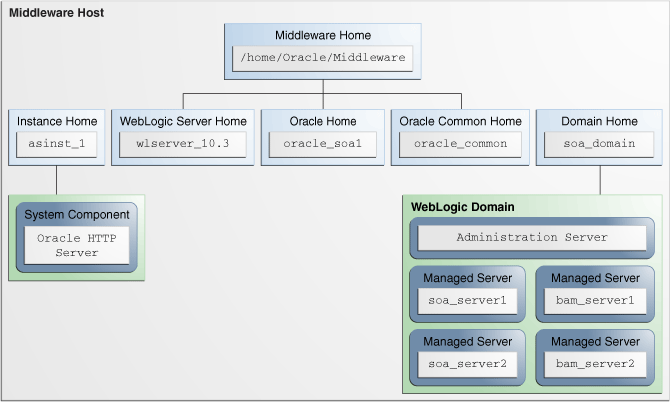
Description of "Figure 2-3 Directory Structure of the Instance Home with an Oracle HTTP Server "
2.7 What is the Oracle Metadata Repository?
The metadata repository contains metadata for Oracle Fusion Middleware system components, such as Oracle BPEL Process Manager, Oracle B2B, and Oracle WebCenter Portal. It can also contain metadata about the configuration of Oracle Fusion Middleware and metadata for enterprise applications.
A metadata repository can be database-based or file-based. If it is database-based, Oracle Metadata Repository can be installed into an existing database using the Repository Creation Utility (RCU).
Oracle Fusion Middleware supports multiple repository types. A repository type represents a specific schema or a set of schemas that belongs to a specific Oracle Fusion Middleware component (for example, Oracle SOA Suite or Oracle Internet Directory.)
For more information, see "Managing the Oracle Metadata Repository" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
A particular type of repository, the MDS Repository, contains metadata for most Oracle Fusion Middleware components, such as Oracle B2B, and for certain types of applications. For more information about the MDS Repository see "Managing the MDS Repository" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.