12 Enabling Hybrid Cloud Management
With the introduction of Hybrid Cloud Management available with Enterprise Manager Cloud Control 12c Release 5 (12.1.0.5), Enterprise Manager Cloud Control now provides you with a single pane of glass for monitoring and managing both your on-premise and Oracle Cloud deployments, all from the same management console. By deploying Hybrid Cloud Agents onto the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts serving your Oracle Cloud services, you are able to manage Oracle Cloud targets just as you would any other.The communication between Management Agents and your on-premise Oracle Management Service instances is secure from external interference. In addition to a hardened architecture of its own, Enterprise Manager supports the use of additional external HTTP proxies that support tunneling, which you can configure for the gateway agents to connect to the Oracle Cloud.
This chapter consists of the following sections:
-
Configuring an Management Agent as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent
-
Configuring an External Proxy to Enable Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents to Communicate with Oracle Cloud
-
Patching Hybrid Cloud Agents and Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents
12.1 List of UnSupported Features
Table 12-1 lists the features that Hybrid Cloud Management does not currently support.
Table 12-1 Features Not Supported by Hybrid Cloud Management
| Targets | Features Not Supported |
|---|---|
|
WebLogic |
Cloning of on-premise domains to Oracle Cloud. |
|
Database |
Automatic Workload Repository Warehouse Collection from Oracle Cloud databases. SQL Performance Analyzer
Database Replay Disabled for database PaaS targets. Database Provisioning Except pluggable database (PDB) operations (create, plug, unplug, drop) on existing Oracle Cloud Container Database (CDB) instances. Change Management Data Synchronization. Database Cloning Between hosts on Oracle Cloud. Data Guard Management of standby databases on Oracle Cloud. |
|
Oracle Exadata Cloud |
|
|
Enterprise Manager |
|
12.2 Overview of Hybrid Cloud Management Terminology
The following terms are commonly used while discussing Hybrid Cloud Management:
-
Hybrid Cloud Agents: The Management Agents deployed on Oracle Cloud virtual hosts that enable Enterprise Manager Cloud Control (deployed in your private network) to monitor and manage Oracle Cloud targets.
-
Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents: The Management Agents (of version 12.1.0.5) that provide a communication channel between the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts and the OMS deployed in your private network (on-premise Cloud Control OMS).
-
Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy: The proxy process (deployed as part of every Hybrid Cloud Agent deployment) that enables the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent to communicate with the Hybrid Cloud Agent. The proxy process is always initiated by the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
12.3 Getting Started with Hybrid Cloud Management
To get started with the Hybrid Cloud Management functionality, you must:
-
Ensure that your on-premise Enterprise Manager Cloud Control OMS is of version 12.1.0.5, and that at least one 12.1.0.5 Management Agent exists in your enterprise.
If your on-premise Enterprise Manager Cloud Control OMS is of an earlier version, ensure that you upgrade the OMS to version 12.1.0.5. For information on how to do so, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Upgrade Guide.
To ensure that at least one 12.1.0.5 Management Agent exists in your enterprise, either deploy a new 12.1.0.5 Management Agent, or upgrade an existing Management Agent of an earlier version to version 12.1.0.5.
For information on how to deploy a new 12.1.0.5 Management Agent, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide. For information on how to upgrade an existing Management Agent of an earlier version to version 12.1.0.5, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Upgrade Guide.
-
Configure one or more version 12.1.0.5 Management Agents within your enterprise to act as Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents, which provide an SSH-based communication channel between the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts and the on-premise OMS.
To ensure high availability, Oracle recommends that you configure multiple 12.1.0.5 Management Agents to act as Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents. For more information, see Section 12.10.1.
-
Ensure that the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents and the on-premise OMS can communicate with the Oracle Cloud targets.
If the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents are unable to communicate with the Oracle Cloud targets directly, configure an external proxy for the communication. For information on how to do so, see Section 12.7.
To communicate with Oracle Cloud targets, the on-premise OMS uses the My Oracle Support (MOS) proxy. Ensure that the MOS proxy configured in your enterprise supports SSH tunneling, or configure a new MOS proxy that supports SSH tunneling.
-
Deploy Management Agents to the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts using the Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI. It is these Management Agents - called Hybrid Cloud Agents - that enable Enterprise Manager to manage the Oracle Cloud targets. As part of the Hybrid Cloud Agent deployment process, you will associate each with the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent that it will use for communication with the on-premise OMS.
12.4 Overview of Hybrid Cloud Architecture and Communication
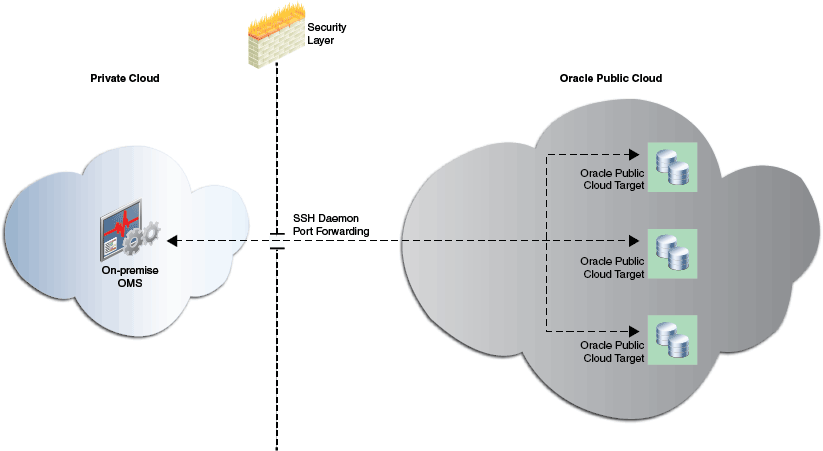
The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent starts a proxy process, the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy, on each of the Hybrid Cloud Agents that it is designated to communicate with. The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent then forwards communication received from the Hybrid Cloud Agent to the on-premise OMS managing the Oracle Cloud targets, and sends the responses back. The on-premise OMS is thus insulated from direct connections to Oracle Cloud.
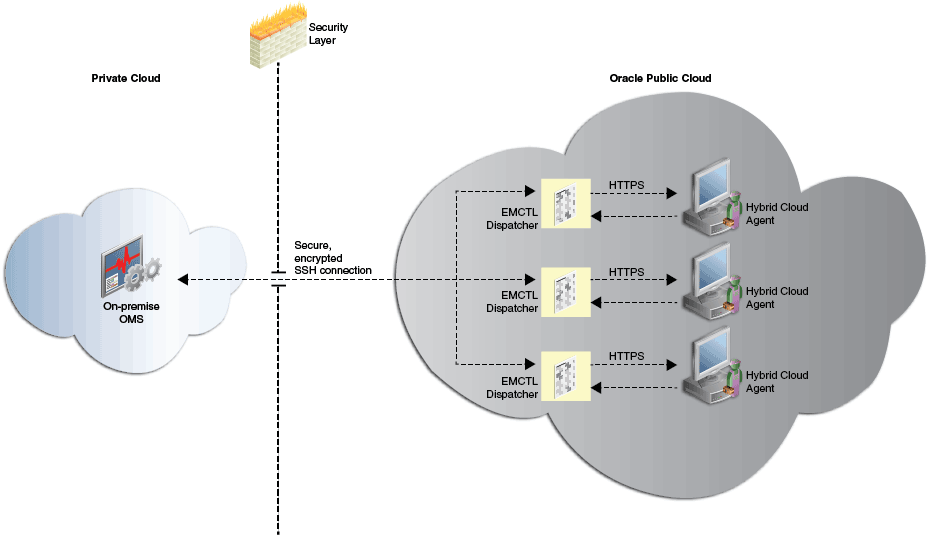
The on-premise OMS communicates with a Hybrid Cloud Agent over SSH, using an EMCTL dispatcher on the Oracle Cloud. The EMCTL dispatcher forwards communication from the on-premise OMS to the Hybrid Cloud Agent, and streams the responses from the Hybrid Cloud Agent back to the on-premise OMS.
Figure 12-1 depicts the communication from the on-premise OMS to the Hybrid Cloud Agents using the EMCTL dispatcher.
Figure 12-1 Communication from the On-Premise OMS to the Hybrid Cloud Agents Using the EMCTL Dispatcher
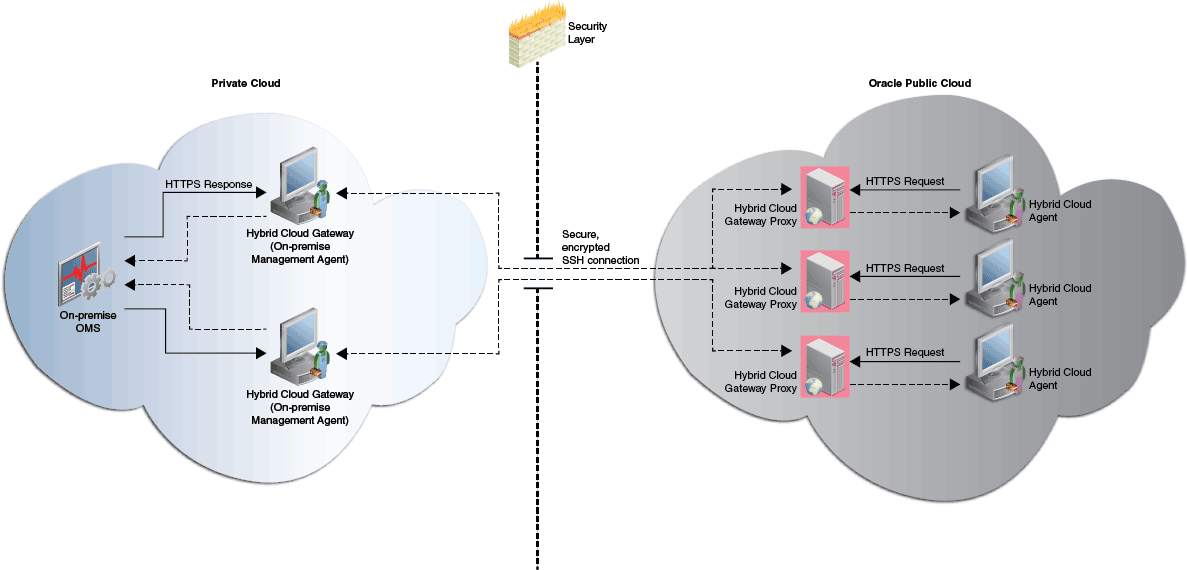
Hybrid Cloud Agents use the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy on the Oracle Cloud and the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents on the on-premise side to communicate with the on-premise OMS. The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy receives HTTPS requests from the Hybrid Cloud Agent and streams the requests to the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent over SSH. The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent forwards the requests to the on-premise OMS, and streams the responses it receives from the on-premise OMS back to the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy. The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy then sends the responses back to the Hybrid Cloud Agent.
Figure 12-2 depicts the communication from the Hybrid Cloud Agents to the on-premise OMS using Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxies.
Figure 12-2 Communication from the Hybrid Cloud Agents to the On-Premise OMS Using Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxies
Note:
The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent monitors the connection to the proxy to ensure that it is up and running. Therefore, when the Hybrid Cloud Agent Virtual Machine goes down for some reason, the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent automatically relaunches the proxy when the virtual machine is up again. The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent might take a few seconds to a few minutes to do this and the actual time taken varies depending on how long the virtual machine was down. You do not have to manually restart the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent for this purpose. However, if you still prefer to do so, follow these steps:-
Identify the name of the
oracle_hybridcloud_connectiontarget. The following command might list numerousoracle_hybridcloud_connectiontargets, so use a suitable filter tool, such as grep, to filter and identify the name of theoracle_hybridcloud_connectiontarget.emctl config agent listtargets -
Reload the dynamic properties of the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent:
emctl reload agent dynamicproperties <oracle_hybridcloud_connection_target_name>:oracle_hybridcloud_connection
The on-premise OMS communicates with the targets deployed in Oracle Cloud using SSH port forwarding (SSH tunneling). Figure 12-3 depicts this.
12.5 Prerequisites for Configuring a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent
Before configuring a 12.1.0.5 Management Agent to act as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, meet the following prerequisites:
-
Ensure that the CPU, RAM, and hard disk space requirements are met.
The CPU, RAM, and hard disk space requirements for a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent are described in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.
Note that the hardware requirements for Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents and regular Management Agents are the same.
-
(Recommendation) Even though you can designate any 12.1.0.5 Management Agent as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, as a best practice, Oracle recommends that you choose a Management Agent that is monitoring only a few targets. This ensures that the performance of the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent is not affected.
Also, Oracle recommends that you do not designate the central agent as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. In an enterprise with a large number of targets, the designated central agent may compete with the OMS for resources.
-
Meet the prerequisites required for deploying Management Agents, as described in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.
-
Deploy the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent on any operating system, but make sure you deploy the Hybrid Cloud Agent only on an Oracle Linux x86-64 operating system.
12.6 Configuring an Management Agent as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent
To configure an existing version 12.1.0.5 Management Agent as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, follow these steps:
-
As SYSMAN user, log in to EM CLI. You can log in from the default EM CLI installation that is available in the OMS home, or from the EM CLI installation that is set up on any other host.
$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli login -username=sysman
EM CLI is set up by default on the on-premise OMS host (the EM CLI install location is the OMS home). Hence, if you choose to run EM CLI from the on-premise OMS host, no additional steps are required. This is the recommended option.
For example, if you are logging in from the EM CLI installation that is available in the OMS home, then run the following command:
/u01/app/oracle/Middleware/oms/bin/emcli login -username=sysmanIf you choose to run EM CLI from a custom location on a host that is not running the on-premise OMS, you must first set up EM CLI on the required host. For information on how to do so, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface Guide.
-
Designate the selected Management Agent to act as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway. To do so, run the following EM CLI verb from the OMS home or from any other host where EM CLI is set up.
$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli register_hybridgateway_agent -hybridgateway_agent_list="<list_of_hybrid_cloud_gateway_agents>"
For example, if you want to run it from the OMS home, then run the following command:
/u01/app/oracle/Middleware/oms/bin/emcli register_hybridgateway_agent -hybridgateway_agent_list="abc.example.com:3873 def.example.com:3873"Note that for
-hybridgateway_agent_list,you can specify more than one Management Agent (host name and port combination). Ensure that you specify the fully qualified name for the Management Agents, and separate the Management Agent names using a space. -
Verify that the Management Agent has been configured as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. You can do this only while installing the Hybrid Cloud Agent as described in Section 12.9.1.
While instal the Hybrid Cloud Agent, on the Installation Details page, in the Optional Details section, when you select Configure Hybrid Cloud Agent and click the search icon (the magnifying glass icon) to select a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, ideally you should see the Hybrid Cloud Gateway that you configured by converting the on-premise Management Agent.
12.7 Configuring an External Proxy to Enable Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents to Communicate with Oracle Cloud
For security reasons, you can choose to configure external proxies between the Hybrid Cloud Agents and the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents. However, only proxies that support tunneling (for example, SOCK4, SOCK5, HTTP) are supported.
To configure an external proxy between a Hybrid Cloud Agent and a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, follow these steps:
-
Set up a proxy server. HTTP, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5 proxy servers are supported. Ensure that the proxy server supports tunneling.
-
From the Setup menu, select Manage Cloud Control, then select Agents.
-
Search for and click the name of the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent for which you want to configure an external proxy.
-
From the Agent menu, select Properties.
-
For Show, select Basic Properties. For externalProxyPort, specify the communication port that must be used to connect to Oracle Cloud.
Click Apply.
-
For Show, select Advanced Properties. Expand the Runtime Settings section. For externalProxyHost, specify the host name of the proxy. For externalProxyType, select whether the proxy uses HTTP, SOCKS4, or SOCKS5 for communication.
If the proxy server that you set up requires user name and password authentication, specify values for externalProxyUsername and externalProxyPassword.
-
Click Apply.
-
Verify that the external proxy is able to handle the authentication as expected using the SSH tunnel. To do so, run the following command:
ssh -l <user> -o "ProxyCommand /usr/bin/nc -X connect -x <proxy host>:<proxy port> %h %p" <host> <command>
12.8 Prerequisites for Installing Hybrid Cloud Agents
Before deploying Hybrid Cloud Agents, meet the following prerequisites:
-
Ensure that the CPU, RAM, and hard disk space requirements are met.
The CPU, RAM, and hard disk space requirements for a Hybrid Cloud Agent are described in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.
-
Ensure that you configure at least one version 12.1.0.5 Management Agent to act as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. A Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent provides a communication channel between the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts and the on-premise OMS.
For information on how to configure a version 12.1.0.5 Management Agent to act as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, see Section 12.6.
-
Ensure that port 22 is open on the destination Oracle Cloud virtual host (the virtual host on which you want to install a Hybrid Cloud Agent), and the SSH Daemon process must be running on it. To verify whether the SSH Daemon process is running on the destination virtual host, run the following command from the virtual host:
ps –ef | grep sshd
-
Ensure that port 1748, or at least one port in the range 1830 - 1848 is free on every destination Oracle Cloud virtual host.
By default, Cloud Control uses port 1748 as the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy port. If port 1748 is not free, the application uses a free port in the range 1830 - 1848.
-
Ensure that you have set up at least one named credential that uses SSH public key authentication.
Note the following:
-
Only named credentials that use SSH public key authentication are supported for Hybrid Cloud Agent deployment. Named credentials that use only a user name and a password are not supported.
-
Deploying Hybrid Cloud Agents using a locked user account (a user account for which
no direct loginis set) and a privilege delegation provider is not supported. -
SSH keys with a passphrase are not supported.
To set up a named credential that uses SSH public key authentication, you must first ensure that you have a set of SSH keys. If you already have a set of SSH keys, follow Step 2: Uploading SSH Keys to Enterprise Manager. If you do not have a set of SSH keys, follow Step 1: Generating SSH Keys, then follow Step 2: Uploading SSH Keys to Enterprise Manager.
Step 1: Generating SSH Keys
-
Log in to the Oracle Cloud virtual host as the desired user.
-
Run the following command:
cd $HOME/.ssh
-
Run the following command:
ssh-keygen -N "" -b 2048 -t rsa -f id_rsa -C "<my_comment>"
Here,
<my_comment>represents a comment or phrase that you can use to identify the SSH keys.Two files,
id_rsaandid_rsa.pubwill be created in the.sshdirectory. -
Append the content of
id_rsa.pubto the end of theauthorized_keysfile. Run the following command to do so:cat id_rsa.pub >> authorized_keys
Step 2: Uploading SSH Keys to Enterprise Manager
-
From the Setup menu, select Security, then select Named Credentials. Click Create. For Credential Name, specify the name of the credential, for Credential Type, select SSH Key Credentials, and for Scope, select Global.
-
Upload the private SSH key created in Step 1. In the Credential Properties section, specify the location of the private SSH key as a value for the Upload Private Key field. Click Save.
-
Upload the public SSH key created in Step 1. In the Credential Properties section, specify the location of the public SSH key as a value for the Upload Public Key field. Click Save.
-
-
Ensure that the Hybrid Cloud Agent install user has the root privileges to run the
root.shscript. If the Hybrid Cloud Agent install user does not have the root privileges, ensure that you run theroot.shscript manually on all the destination virtual hosts, after the deployment operation. -
Meet the prerequisites required for deploying on-premise Management Agents, as described in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.
-
Ensure that the Hybrid Cloud Agent is deployed only on an Oracle Linux x86-64 operating system. The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent is supported on all operating systems, but the Hybrid Cloud Agent is supported only on Oracle Linux x86-64 operating system.
-
If you want to install a Hybrid Cloud Agent on a virtual host, then instead of installing it on the local file system of the virtual host, create a mount using an external storage device and install the Hybrid Cloud Agent on it. Otherwise, you will lose all the data that is stored in the boot volume every time you stop, start, or restart the virtual host.
12.9 Installing a Hybrid Cloud Agent
This section describes the following methods to install a Hybrid Cloud Agent:
Note:
Since a Hybrid Cloud Agent connects to the on-premise OMS via an SSH bridge, manual deployment is not supported for Hybrid Cloud Agents. You can only deploy Hybrid Cloud Agents using the Add Host Targets Wizard, or EM CLI.You can deploy a Hybrid Cloud Agent only on an Oracle Linux x86-64 operating system. The Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent is supported on all operating systems, but the Hybrid Cloud Agent is supported only on Oracle Linux x86-64 operating system.
12.9.1 Installing a Hybrid Cloud Agent Using the Add Host Targets Wizard
Follow these steps to install a Hybrid Cloud Agent using the Add Host Targets Wizard:
-
In Cloud Control, from the Setup menu, select Add Target, then click Add Targets Manually. On the Add Targets Manually page, select Add Host Targets, then click Add Host.
-
On the Host and Platform page, do the following:
-
Accept the default name assigned for this session or enter a unique name of your choice. The custom name you enter can be any intuitive name, and need not necessarily be in the same format as the default name. For example,
add_host_hybrid_cloud_operation_1 -
Click Add to enter the IP address and select the platform of the Oracle Cloud virtual host on which you want to install the Hybrid Cloud Agent. The IP address for the virtual host running each of your Oracle Cloud services would have been provided to you by Oracle.
Note:
-
Hybrid Cloud Agent deployment is supported for the Linux x86-64 platform only.
-
You must enter only one IP address per row. Entering multiple addresses separated by a comma is not supported.
Alternatively, you can click Load from File to add the IP addresses that are stored in a file.
Specify the platform as Linux x86-64 for all the virtual hosts. To do so, you can specify the platform as Linux x86-64 for the first virtual host, then from the Platform list, you can select Same for All Hosts.
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
On the Installation Details page, do the following:
-
In the Deployment Type section, select Fresh Agent Install.
-
From the table, select the first row that indicates the virtual hosts grouped by their common platform name.
-
In the Installation Details section, provide the installation details common to the virtual hosts selected in Step 3 (b). For Installation Base Directory, enter the absolute path to the base directory on the Oracle Cloud virtual host where you want the software binaries, security files, and inventory files of the Hybrid Cloud Agent to be copied.
For example,
/u01/app/Oracle/.If the path you enter does not exist, the application creates a directory at the specified path, and copies the Hybrid Cloud Agent software binaries, security files, and inventory files there.
-
For Instance Directory, accept the default instance directory location or enter the absolute path to a directory of your choice where all Hybrid Cloud Agent-related configuration files can be stored.
For example,
/u01/app/Oracle/agent_inst.If you are entering a custom location, then ensure that the directory has write permissions. Oracle recommends that you maintain the instance directory inside the installation base directory.
If the path you enter does not exist, the application creates a directory at the specified path, and stores all the Hybrid Cloud Agent-related configuration files there.
-
For Named Credential, select the named credential that you want to use to set up SSH connectivity between the on-premise OMS and the destination Oracle Cloud virtual hosts, and to install a Hybrid Cloud Agent on each of the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts.
Ensure that you only specify a named credential that uses SSH public key authentication. Password based authentication is not supported. Also, note that deploying Hybrid Cloud Agents using a locked user account (by switching to the locked user account using a privilege delegation provider) is not supported.
For information on how to create a named credential that uses SSH public key authentication, see Section 12.8.
-
For Privileged Delegation Setting, use the default value. Privilege delegation providers and locked accounts are not supported for Hybrid Cloud Agent deployment.
If the Hybrid Cloud Agent install user has root privileges, then
root.shis run automatically on the destination virtual hosts post deployment. Else, you must manually runroot.shon every destination virtual host post deployment. -
For Port, accept the default port (3872) that is assigned for the Hybrid Cloud Agent to communicate, or enter a port of your choice.
The custom port you enter must not be busy. If you are not sure, you can leave this field blank. Cloud Control automatically assigns the first available free port within the range of 1830 - 1849.
-
If you want to run certain scripts before or after deploying the Hybrid Cloud Agents, in the Optional Details section, enter the absolute path to the locations where the scripts that you want to run are available. Note that only shell scripts are supported, and only one preinstallation or one postinstallation script can be specified.
If you want to run the script as root, then select Run as Root. If the script is on the host where the on-premise OMS is running and is not on the virtual host where you want to install the Hybrid Cloud Agent, then select Script on OMS. In this case, the script will be copied from the on-premise OMS host to the destination virtual hosts, and then run on the destination virtual hosts.
-
If you want to specify certain additional parameters for the deployment, in the Optional Details section, for Additional Parameters, enter a white space-separated list of the additional parameters.
For example, if you want to provide the inventory pointer location file, then enter
-invPtrLocfollowed by the absolute path to the file location. However, note that this parameter is supported only on UNIX platforms, and not on Microsoft Windows platforms. -
In the Optional Details section, select Configure Hybrid Cloud Agent to specify the details for the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent that the Hybrid Cloud Agent must communicate with.
For Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, specify the Management Agent within your enterprise that you want to use as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent for the Hybrid Cloud Agent to communicate with. Click the magnifying glass icon, and select a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent from the displayed list (only those Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents that are up and running are displayed).
Note that for this field, you can only select a Management Agent that has already been designated as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway. For information on how to designate a particular Management Agent as a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, see Section 12.6.
For Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy Port, specify the port for communication between the Hybrid Cloud Agent and the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy. If you do not specify a value, port 1748 is used, and if port 1748 is not free, then a free port between 1830 and 1848 is used.
-
Repeat Step 3 (b) to Step 3 (j) for every other row you have in the table.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On the Review page, review the details you have provided for the installation and if you are satisfied with the details, then click Deploy Agent to install the Hybrid Cloud Agent.
If you want to modify the details, then click Back repeatedly to reach the page where you want to make the changes.
When you click Deploy Agent and submit the deployment session, you are automatically taken to the Agent Deployment Details page that enables you to monitor the progress of the deployment session. To understand the tasks you can perform on this page, click Help.
-
To verify that the Hybrid Cloud Agent was deployed on Oracle Cloud, from the Setup menu, select Manage Cloud Control, then select Agents. Search for, then click the name of the Hybrid Cloud Agent to access its home page. Beside the Hybrid Cloud Agent target name, 'Running in Oracle Cloud', and a cloud icon must be displayed. This is depicted in Figure 12-4.
Note:
The following features are not supported, or are partially supported for Hybrid Cloud Agents:-
Buddy Agent
-
Management Agent to Management Agent communication
-
Distributed Software Library
-
Target Relocation
-
Support for third party Management Agent certificates
-
Support Workbench
12.9.2 Installing a Hybrid Cloud Agent Using EM CLI
Follow these steps to install a Hybrid Cloud Agent using EM CLI:
-
Log in to EM CLI from the
/bindirectory present within the EM CLI install location:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli login -username=<user_name>
Once you run this command, EM CLI will prompt you for a password. Enter the password for the user name you specified.
EM CLI is set up by default on the on-premise OMS host (the EM CLI install location is the OMS home). Hence, if you choose to run EM CLI from the on-premise OMS host, no additional steps are required. This is the recommended option.
If you choose to run EM CLI from a custom location on a host that is not running the on-premise OMS, you must first set up EM CLI on the required host. For information on how to do so, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface Guide.
-
Run the
list_add_host_platformsverb to obtain a list of the platforms for which the Hybrid Cloud Agent software is available in Software Library:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli list_add_host_platforms [-all] [-noheader] [-script | -format]Note that the parameters mentioned in
[ ]are optional.For example,
$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli list_add_host_platforms -allIf the Management Agent software for a particular platform is not available, download and apply it using Self Update. For information on how to download and apply the Management Agent software for a platform, see Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Basic Installation Guide.
To view more information on the syntax and the usage of the
list_add_host_platformsverb, run the following command:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli help list_add_host_platforms
-
If you want to deploy Hybrid Cloud Agents on the selected Oracle Public Cloud virtual hosts in a rolling manner, such that the deployment proceeds continuously from one deployment phase to another, ignoring the failed hosts in each deployment phase, specify the following in the
$OMS_HOME/sysman/prov/agentpush/agentpush.propertiesfile:oracle.sysman.prov.agentpush.continueIgnoringFailedHost=true -
Run the
submit_add_hostverb, specifying the-configure_hybrid_cloud_agent, -hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent,and-hybrid_cloud_gateway_proxy_portoptions to submit the Add Host session and install the Hybrid Cloud Agents:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli submit_add_host -host_names=<list_of_hosts> -platform=<platform_ID> -installation_base_directory=<install_directory_of_agent> -credential_name=<named_credential_for_agent_install> -configure_hybrid_cloud_agent -hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent=<hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent_name> [-hybrid_cloud_gateway_proxy_port=<hybrid_cloud_gateway_proxy_port>] [-credential_owner=<named_credential_owner>] [-instance_directory=<agent_instance_directory>] [-port=<agent_port>] [-session_name=<add_host_session_name>] [-deployment_type=<type_of_agent_deployment>] [-privilege_delegation_setting=<privilege_delegation>] [-additional_parameters=<additional_params_for_install>] [-source_agent=<source_agent_for_cloned_agent_install>] [-master_agent=<master_agent_for_shared_agent_install>] [-properties_file=<properties_file_having_inputs>] [-preinstallation_script=<pre_install_script>] [-preinstallation_script_on_oms] [-preinstallation_script_run_as_root] [-postinstallation_script=<post_install_script>] [-postinstallation_script_on_oms] [-postinstallation_script_run_as_root] [-wait_for_completion]Note that the parameters mentioned in
[ ]are optional.For example,
$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli submit_add_host -host_names=opc1.example.com -platform=226 -installation_base_directory=/opt/agent -credential_name=oracle -configure_hybrid_cloud_agent -hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent=abc.example.com -hybrid_cloud_gateway_proxy_port=1748This example installs a Hybrid Cloud Agent on the Oracle Public Cloud virtual host
opc1.example.comhaving the platform ID226,in the directory/opt/agent,using the named credentialoracle.The deployed Hybrid Cloud Agent will useabc.example.comas the Hybrid Cloud Gateway, and use port1748to communicate with the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Proxy.To view more information on the syntax and the usage of the
submit_add_hostverb, run the following command:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli help submit_add_host
12.10 Performing Additional Hybrid Cloud Management Tasks
This section describes the additional Hybrid Cloud Management tasks that you can perform. It consists of the following:
-
Configuring Hybrid Cloud Agents for High Availability (Recommended)
-
Disassociating a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent from a Set of Hybrid Cloud Agents
12.10.1 Configuring Hybrid Cloud Agents for High Availability (Recommended)
When you deploy a Hybrid Cloud Agent, you associate it with a single Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent by default. Throughout the lifecycle of the Hybrid Cloud Agent, the Hybrid Cloud Agent is dependent on the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent to forward the collected monitoring data to the on-premise Cloud Control OMS. Hence, if the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent is down or is not reachable, the Hybrid Cloud Agent monitoring data will not reach the on-premise OMS. Thus, Oracle recommends that you enable every Hybrid Cloud Agent to use multiple Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents, to decrease the probability of a loss in monitoring data.
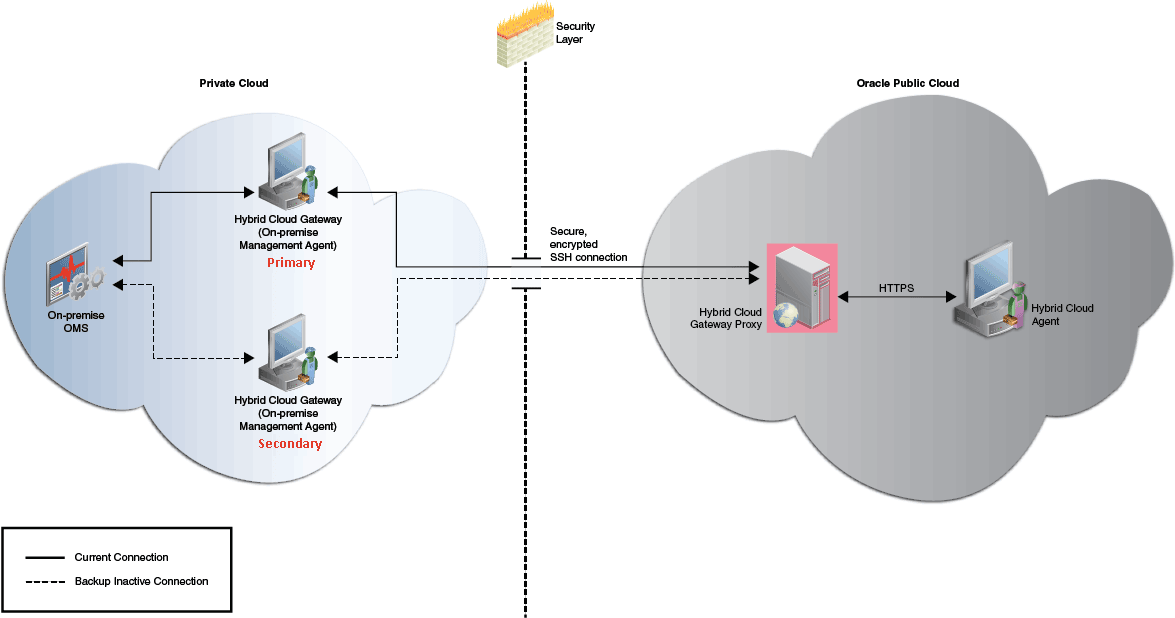
While deploying a Hybrid Cloud Agent, the first Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent that you select is designated as the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. If you enable the deployed Hybrid Cloud Agent to use additional Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents, then the additional Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents are designated as secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents. This way, if the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent for a Hybrid Cloud Agent is down or is unreachable, then one of the secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents takes over. If the secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent that took over also goes down or becomes unreachable at some point of time, then the next available secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent takes over.
Figure 12-5 depicts the communication from the Hybrid Cloud Agents to the on-premise OMS through multiple Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents.
Figure 12-5 Communication from the Hybrid Cloud Agents to the On-Premise OMS Using Multiple Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents for High Availability
To configure a Hybrid Cloud Agent for high availability, you must associate one or more secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents with the Hybrid Cloud Agents. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Log in to EM CLI from the
/bindirectory present within the EM CLI install location:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli login -username=<user_name>
Once you run this command, EM CLI will prompt you for a password. Enter the password for the user name you specified.
EM CLI is set up by default on the on-premise OMS host (the EM CLI install location is the OMS home). Hence, if you choose to run EM CLI from the on-premise OMS host, no additional steps are required. This is the recommended option.
If you choose to run EM CLI from a custom location on a host that is not running the on-premise OMS, you must first set up EM CLI on the required host. For information on how to do so, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface Guide.
-
Associate a secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent with one or more Hybrid Cloud Agents.
$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli add_hybridgateway_for_hybrid_agent -hybrid_agent_name="<hybrid_cloud_agent1>:<port> <hybrid_cloud_agent2>:<port> <hybrid_cloud_agentN>:<port>" -hybridgateway_agent_list="<secondary_hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent>:<port>"
For example,
emcli add_hybridgateway_for_hybrid_agent -hybrid_agent_name="abc.example.com:1831 def.example.com:3872" -hybridgateway_agent_list="secondary1.example.com:1831"
12.10.2 Disabling Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents
To disable the gateway functionality of a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, that is, to ensure that a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent functions like a regular Management Agent again and does not forward communication from the Hybrid Cloud Agents to the on-premise OMS, follow these steps:
-
Log in to EM CLI from the
/bindirectory present within the EM CLI install location:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli login -username=<user_name>
Once you run this command, EM CLI will prompt you for a password. Enter the password for the user name you specified.
EM CLI is set up by default on the on-premise OMS host (the EM CLI install location is the OMS home). Hence, if you choose to run EM CLI from the on-premise OMS host, no additional steps are required. This is the recommended option.
If you choose to run EM CLI from a custom location on a host that is not running the on-premise OMS, you must first set up EM CLI on the required host. For information on how to do so, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface Guide.
-
Disable the gateway functionality of a set of Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents.
$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli deregister_hybridgateway_agent -hybridgateway_agent_list="<hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent1>:<port> <hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent2>:<port> <hybrid_cloud_gateway_agentN>:<port>"
For example,
emcli deregister_hybridgateway_agent -hybridgateway_agent_list="abc.example.com:3873 def.example.com:3873"Note that for
-hybridgateway_agent_list,you can specify more than one Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. Ensure that you specify the fully qualified name for each Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, and separate the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent names using a space.
12.10.3 Disassociating a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent from a Set of Hybrid Cloud Agents
To disassociate a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent from a set of Hybrid Cloud Agents, such that the specified set of Hybrid Cloud Agents do not communicate with the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents and the on-premise OMS anymore, follow these steps:
-
Log in to EM CLI from the
/bindirectory present within the EM CLI install location:$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli login -username=<user_name>
Once you run this command, EM CLI will prompt you for a password. Enter the password for the user name you specified.
EM CLI is set up by default on the on-premise OMS host (the EM CLI install location is the OMS home). Hence, if you choose to run EM CLI from the on-premise OMS host, no additional steps are required. This is the recommended option.
If you choose to run EM CLI from a custom location on a host that is not running the on-premise OMS, you must first set up EM CLI on the required host. For information on how to do so, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface Guide.
-
Disassociate a set of Hybrid Cloud Agents from a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
$<emcli_install_location>/bin/emcli delete_hybridgateway_for_hybrid_agent -hybrid_agent_name="<hybrid_cloud_agent1>:<port> <hybrid_cloud_agent2>:<port> <hybrid_cloud_agentN>:<port>" -hybridgateway_agent_list="<hybrid_cloud_gateway_agent_to_disassociate>:<port>"
For example,
emcli delete_hybridgateway_for_hybrid_agent -hybrid_agent_name="abc.example.com:1831 def.example.com:3872" -hybridgateway_agent_list="gateway1.example.com"
12.10.4 Decommissioning Hybrid Cloud Agents
To decommission a Hybrid Cloud Agent, follow these steps:
-
Stop the Hybrid Cloud Agent.
-
On the Agent Home page of the Hybrid Cloud Agent, from the Agent menu, select Target Setup, then select Agent Decommission.
12.11 Patching Hybrid Cloud Agents and Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents
You can patch Hybrid Cloud Agents and Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents using patch plans. Patch plans are consolidated plans that include one or more patches to be rolled out as a group. The patching procedure remains the same for normal Management Agents, Hybrid Cloud Agents, and Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents.
Caution:
The database instance created on Oracle Cloud before the first week of June 2015 is typically based on the database patchset update released in January 2015 (Jan DB PSU). If you want to patch such a database instance with the database patchset update released in April 2015 (Apr DB PSU), then as a prerequisite, before you apply the patchset update, create the following file and add the absolute path to the directory where the Hybrid Cloud Agent is available./var/opt/oracle/patch/files_to_save.ora
If you do not follow the aforementioned instruction, you will notice that the Hybrid Cloud Agent in /u01/app/oracle is automatically moved to /u01/app.ORG/oracle as part of the database patching process. You will then have to manually copy the directory back to its original location. To circumvent this issue and avoid any manual effort from your end, Oracle recommends that you follow the aforementioned instruction to create a file as described and add the Hybrid Cloud Agent location to it.
To patch Hybrid Cloud Agents on the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts, follow these steps:
-
If the patch you are applying accesses the
sbindirectory of the agent home, then first follow the instructions outlined in the ReadMe file of the patch. -
Patch the Hybrid Cloud Agents by following the instructions outlined in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Lifecycle Management Guide. The patching procedure remains the same for normal Management Agents and Hybrid Cloud Agents.
To patch Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents, follow the instructions outlined in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Lifecycle Management Guide.
12.12 Discovering and Monitoring Oracle Cloud Targets
Once the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent is deployed in the on-premise environment and the Hybrid Cloud Agent is deployed in the Oracle Cloud environment, the Oracle Cloud virtual hosts become manageable targets in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. To discover and monitor the targets running on these manageable virtual hosts, you should follow the instructions outlined in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Administrator's Guide. The procedure to discover and promote the targets running on an Oracle Cloud virtual host is the same as the procedure to discover and promote targets running on any normal host in the on-premise environment.
However, for discovering FMW domains running on Oracle Cloud virtual hosts, such as WebLogic JCS domains, you should use the public IP address and port 9001 (representing the custom t3 channel that is configured by default on these Admin Servers).
12.13 Frequently Asked Questions About Hybrid Cloud Management
This section provides answers to the following frequently asked questions about Hybrid Cloud Management.
-
How Do I Relocate the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent to Another Host without Deinstalling Anything Else?
-
If I Change My SSH Keys on Oracle Cloud, What Should I Do in Enterprise Manager?
-
What Are the User Restrictions on Hybrid Cloud Agents and the Targets on Oracle Cloud?
-
On What Operating System Can I Deploy a Hybrid Cloud Agent and a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent?
12.13.1 If I have deployed a Hybrid Cloud Agent on the Oracle Cloud virtual host. Can I deployed another Hybrid Cloud Agent on the same virtual host?
Yes, you can. However, make sure you first decommission the Hybrid Cloud Agent that is already present on the Oracle Cloud virtual host, and then deploy another one.
To decommission the Hybrid Cloud Agent that is already present on the Oracle Cloud virtual host, follow these steps:
-
On the Agent Home page of the Hybrid Cloud Agent, from the Agent menu, select Target Setup, then select Agent Decommission.
-
Deploy a new Hybrid Cloud Agent as described in Section 12.9.
12.13.2 Can I deinstall and deconfigure a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent without deinstalling a Hybrid Cloud Agent with Which It Is Associated?
No, you can't. You must first decommission the Hybrid Cloud Agent that is present on the Oracle Cloud virtual host. When you decommission the Hybrid Cloud Agent, the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent with which it is associated is automatically removed.
If you have a single Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, and if you want to deinstall it, then follow these steps:
-
Stop the Hybrid Cloud Agent.
-
On the Agent Home page of the Hybrid Cloud Agent, from the Agent menu, select Target Setup, then select Agent Decommission.
If you have multiple Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents, and if you want to deinstall the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, then follow these steps:
-
Shut down the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. This will automatically redirect the communication from the Hybrid Cloud Agent to the secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
-
Deinstall the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
Note:
No need to decommission the Hybrid Cloud Agent that is associated with the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. You only have to shut down the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent as described in Step (1).After Step (2), the secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent will act as the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
When you bring back the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent that you deinstalled in Step (2), it will come back only as a secondary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
12.13.3 How Do I Relocate the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent to Another Host without Deinstalling Anything Else?
You can't relocate the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent from one host to another host because the relocate logic is only for targets monitored by the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent and not for the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
12.13.4 How Can I Redistribute My Connections Once I Have Added the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents? Does It Need Reconfiguration?
Yes, you can redistribute the connections once you have added additional Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents. However, there is not automated way to do this. You must manually redistribute the connections.
For example, if you have one Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent and multiple Hybrid Cloud Agents associated with it, and if you now deploy another Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, then you can redistribute the connections between the two gateways.
To do so, follow these steps:
-
Remove the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent from serving the Hybrid Cloud Agent. To do so, run the following command. This command causes the OMS to switch the primary gateway to the secondary gateway.
emcli delete_hybridgateway_for_hybrid_agent -hybrid_agent_name="<hybrid_agent_name>:<port>" -hybridgateway_agent_list="<primary_gateway_agent>:<port>" -
Add back the old primary gateway to the Hybrid Cloud Agent. To do so, run the following command. This command restores the old primary gateway as a secondary gateway to the Hybrid Cloud Agent.
emcli add_hybridgateway_for_hybrid_agent -hybrid_agent_name="<hybrid_agent_name>:<port>" -hybridgateway_agent_list="<old_primary_gateway_agent>:<port>"
12.13.5 After an Oracle PaaS Instance Is Decommissioned from the Oracle Cloud Portal, What Should I Do with the Hybrid Cloud Agent and the Related Targets in the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console?
After an Oracle PaaS instance is decommissioned from Oracle Cloud, the Hybrid Cloud Agent will be in a unreachable state. To clean up the Hybrid Cloud Agent from the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console, follow these steps:
-
In the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console, from the Setup menu, select Manage Cloud Control, then select Agents.
-
Click the name of the Hybrid Cloud Agent you want to clean up from the console.
-
On the Agent Home page, from the Agent menu, select Target Setup, then click Agent Decommission.
-
Select the targets you want to remove, and click Submit.
12.13.6 If I Change My SSH Keys on Oracle Cloud, What Should I Do in Enterprise Manager?
Update the monitoring credentials with the new SSH keys so that all Hybrid Cloud Agents can automatically honor them for new deployments. Once the new keys are saved, the SSH tunnelling uses the new keys to communicate with the Hybrid Cloud Agents.
To update the monitoring credentials, follow these steps:
-
In the Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Console, from the Setup menu, select Security, then select Monitoring Credentials.
-
On the Monitoring Credentials page, in the table click Hybrid Cloud Connection.
-
On the Hybrid Cloud Connection Monitoring Credentials page, select the target name where you want to update the new SSH keys, and click Set Credentials.
-
In the Enter monitoring credentials dialog, enter the new SSH private key and the SSH public key, and click Save.
12.13.7 What Are the Guidelines for Sizing the Number of Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents? What Is the Indication That My Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent is Overloaded?
Currently, there are no statistics available. You can continue to use utilities such as EM Diag Kit to assess the load on the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent.
12.13.8 In a High-Availability Configuration with Multiple Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents, When I Patch One Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent, the Monitoring Switches to the Other Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent. Once the First Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent Is Up After Being Patched, Will It Monitor the Hybrid Cloud Agents?
No. The only time there is a switch of a primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent is when the primary Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent goes down.
To list the Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agents for a given Hybrid Cloud Agent, run the following query:
SELECT emd_url FROM MGMT_TARGETS
WHERE target_name LIKE '%PAAS_AGENT_NAME%' AND
target_type='oracle_hybridcloud_connection'
12.13.9 What Are the User Restrictions on Hybrid Cloud Agents and the Targets on Oracle Cloud?
No restrictions as such for users. The Hybrid Cloud Agent install user can be different from the Oracle Cloud target install user, but both users must belong to the same primary operating system group. Otherwise, the discovery might fail.
For example, the Hybrid Cloud Agent install user can be opc, and the Oracle Cloud target install user can be oracle.However, both these users must belong to the oinstall operating system group.
In addition, the user must have sudo access. Otherwise, the root.sh script will have to be run as a manual step during agent deployment.
12.13.10 On What Operating System Can I Deploy a Hybrid Cloud Agent and a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent?
You can deploy a Hybrid Cloud Gateway Agent on any operating system, but you must deploy a Hybrid Cloud Agent only on an Oracle Linux x86-64 operating system.