7 Installing Monitors
This chapter describes how to install Business Transaction Management monitors. Instructions are provided for installing both singleton monitors and monitor groups.
A singleton monitor is a single instance of a monitor that receives observations directly from an observer. A monitor group is a group of replicated monitor instances situated behind a load balancer. In the case of a monitor group, the observer sends observations to the load balancer, which then distributes the observations to the monitors in the group.
A monitor can receive observations from an unlimited number of observers. Theoretically, you could deploy a single monitor to process observations from all the observers in your system. However, if the rate and/or size of observations produced by your system is large, a single monitor might be overwhelmed. Such a situation could result in reduced performance of your monitoring system and possible loss of monitoring data.
You can eliminate such a potential bottleneck by deploying multiple monitors. You can deploy as many monitors as required for your monitoring needs. You can deploy the monitors as singleton monitors, as monitor groups, or as a mix of the two. You could, for example, deploy a dedicated monitor for each observer. Note that an observer can send observations to only one singleton monitor or one monitor group. If you have an observer that produces observations faster than a singleton monitor can process them, you will need to deploy a monitor group for that observer.
Using monitor groups not only gives you the ability to scale your monitoring system, but makes it more fault tolerant. Monitor groups require a third-party load balancer that supports TCP for routing messages from your observers to your monitors. Monitor groups also require access to an Oracle 10g or 11g database, which is used to share data between the replicated instances of the monitor. This database can be the same database used by other Business Transaction Management components. Although the replicated instances of any one monitor group can be widely dispersed across your network, they must all have access to this same database (for more information about the monitor group database, see Setting up a Monitor Group Database.). A generalized deployment of a monitor group is shown below.
Figure 7-1 Generalized deployment of a monitor group
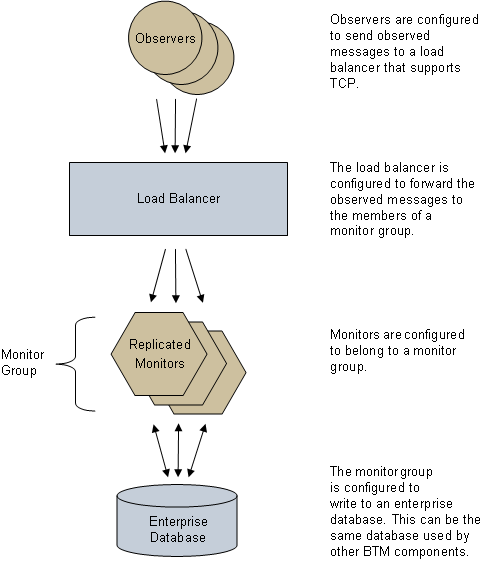
Description of "Figure 7-1 Generalized deployment of a monitor group"
Overview of Installing Monitors
This section provides an overview of the tasks you must perform to install monitors. Subsequent sections provide details on how to perform these tasks. To ensure a properly configured system, you must perform the steps in the order shown.
-
Configure security if needed (see Chapter 4, "Configuring Security").
Note:
If you configured the assertion secret and encryption key on your central servers, then you must also configure your monitors to use the same assertion secret and encryption key. If, on the other hand, you are using the default security configuration on your central servers, then you must use the default security configuration on your monitors (see Configuring the Assertion Secret and Encryption Key). -
Ensure that all prerequisite requirements and setup described in Chapter 5 are satisfied, including:
-
Optional – Configure the persistent storage directories for the monitors. Use the same procedure as described for the central servers in Configuring Persistent Storage Directories.
-
Deploy and register the monitors (see Deploying and Registering Monitors).
-
Ensure that the central servers are installed and running.
-
Deploy monitors to the target application servers using your application server's deployment tools.
-
Register your monitors using the registerMonitor CLI command.
-
-
For replicated monitors only – Set up a monitor group (see Setting Up a Monitor Group).
-
Create a monitor group.
-
Assign monitors to the monitor group.
-
-
For replicated monitors only – Configure your load balancer (see Configuring Your Load Balancer).
-
Apply an Observer Communication Policy (see Applying an Observer Communication Policy).
Deploying and Registering Monitors
This section pertains to both singleton and replicated monitors. You must perform this task for all installation scenarios.
-
Ensure that the Business Transaction Management central services are installed and running.
-
Using your application server's deployment tools, install the btmMonitor.ear deployment package on each application server that will host a monitor.
Notes:
Do not deploy more than one monitor per application server. Also, do not deploy the monitor into an application server that is hosting any of the Business Transaction Management central services.(An application server is sometimes referred to as a container in the Business Transaction Management Console and elsewhere in the documentation.)
-
Start the monitor deployments.
-
Use the registerMonitor CLI command to register each of the monitors that you deployed, for example:
btmcli registerMonitor -e http://my_monitor_host:8080/btmmonitor/agent/agent -fn My_BTM_Monitor -s http://localhost:8080/btmcentral/sphere -l my_admin_username:my_admin_passwordTable 7-1 Flags for the registerMonitor CLI command
Flag Description -e | -endpointUrl
Required.
Specify the URL of the monitor to register, for example:
http://my_monitor_host:8080/btmmonitor/agent/agent
Replace the host name and port number with appropriate values. This URL always ends with btmmonitor/agent/agent.
-fn | -friendlyName
Optional.
Specify a friendly name for the endpoint of the monitor.
-s | -sphereUrl
Required unless the AP_SPHERE_URL environment variable is set.
Specify the URL of the sphere, for example:
http://mySphereHost:8080/btmcentral/sphere/
Replace the host name and port number with appropriate values. This URL always ends with btmcentral/sphere/.
-l | -userLogin
Required unless the AP_USER_LOGIN environment variable is set.
Specify the credentials of a user belonging to the btmadmin role in the format: username:password.
You can encrypt passwords using the encryptPassword CLI command, for example:
btmcli encryptPassword -password "myPassword"
See Chapter 15, "Invoking the CLI" for information about how to invoke a CLI command. Refer to the Business Transaction Management online help for other information about the CLI.
-
Verify that all monitors and system services are running properly.
Setting Up a Monitor Group
This section pertains to replicated monitors, only. You must perform this task if you plan to use replicated monitors.
-
Create a monitor group:
-
In the Business Transaction Management Console, choose Admin > Create System Policy > Monitor Agent Group.
-
Enter a name for your monitor group (you can optionally provide descriptive information in the Version and Notes fields).
-
Specify the connection string for your database.
If you use the default string, replace the text within the curly braces (and the curly braces themselves) with values appropriate for your database. Each member of the monitor group must have access to this database. For more information about the monitor group database, see Setting up a Monitor Group Database.
-
Specify a user name and password for accessing your database.
-
Click Apply.
-
-
Assign monitors to the monitor group you just created:
Note:
If your monitor will not be using the default Observer Communication policy, you must complete Applying an Observer Communication Policy before continuing with this section. One scenario in which this would be necessary is if multiple monitors are running on the same machine, in which case they would have to listen on different socket ports and would therefore require separate Observer Communication policies.-
In the Business Transaction Management Console's Navigator, choose Administration > Monitors.
-
In the main area, select the monitor that you want to assign to a group.
-
Choose Modify > Edit Profile for Monitor Agent.
-
Type the name of the monitor group in the Monitor Group field.
This name must match the value of the Name field in the monitor group policy you used to register the monitor group.
-
Click Apply.
-
Configuring Your Load Balancer
This section pertains to replicated monitors, only. You must perform this task if you plan to use replicated monitors.
-
Configure your load balancer to communicate with the observers by defining both an HTTP virtual server and a socket virtual server.
Your load balancer requires two observer communication channels—one referred to as the HTTP virtual server, and the other referred to as the socket virtual server:
-
The HTTP virtual server is used for administrative purposes. For example, observers retrieve their configurations from any one of the replicated monitors by way of the HTTP virtual server.
-
The observers transmit observational data to the socket virtual server, and the load balancer distributes this data across the replicated monitors. We refer to the messages containing such data as observation messages.
Note:
The replicated monitors communicate with the Business Transaction Management central servers and database directly—not by way of the load balancer.
-
-
Take note of the IP address and port of your socket virtual server.
You will need this information when you configure the Observer Communication policy (see Applying an Observer Communication Policy).
-
Configure your load balancer to distribute observation messages across the replicated monitors as follows:
-
Create a pool for the socket virtual server.
-
Assign each monitor to the pool by assigning the port on which the monitor will receive observations.
-
-
Take note of the monitor port number(s) that you assign to the socket virtual server's pool.
You will need this information when you configure the Observer Communication policy (see Applying an Observer Communication Policy).
Note:
Configuring the Observer Communication policy will be easier if all the monitors listen on the same port number. -
Configure your load balancer to distribute administrative messages across the replicated monitors as follows:
-
Create a pool for the HTTP virtual server.
-
Assign each monitor to the pool by assigning the port on which the monitor's application server listens.
-
-
Ensure that the application servers that host the observers have their AP_NANO_CONFIG_URL Java system property or AmberPoint:NanoConfigUrl Windows key (depending on the platform) set to the URL of the monitor by way of the load balancer's HTTP virtual server.
For example, if the HTTP virtual server's IP address is 10.147.46.152, and its port number is 5072, then the URL of the monitor by way of the HTTP virtual server would be:
http://10.147.46.152:5072/btmmonitor/agent/agent/
For more information on this topic, see Chapter 8, "Installing Observers Overview".
Applying an Observer Communication Policy
This section pertains to both singleton and replicated monitors. You must perform this task for all installation scenarios. However, the way in which you complete this task depends on whether you are using singleton or replicated monitors, and whether your monitors all listen on the same port.
The Observer Communication policy sets up communication between observers and a monitor or monitor group. By default, an Observer Communication policy is applied to all monitors in the Business Transaction Management sphere. Depending on the monitor deployment scenario you employ, you might be able to simply edit the default policy, or you might have to apply additional policies.
The following scenarios require only a single Observer Communication policy. In these scenarios, you can simply edit the default policy:
-
All of your monitors are singleton, you want to configure them all to receive observations on the same port number, and (if they will receive observations over SSL) they all use the same private key/certificate and the security stores are in the same relative locations for all monitors and associated observers.
-
All of your monitors are replicated behind a single load balancer, you want to configure them all to receive observations on the same port number, and (if they will receive observations over SSL) they all use the same private key/certificate and the security stores are in the same relative locations for all monitors and associated observers.
The following scenarios require you to apply additional Observer Communication policies:
-
You want to configure your monitors to receive observations on different port numbers. In this case, you must apply a separate policy for each port number.
-
Your monitors are replicated behind multiple load balancers. In this case, you must apply a separate policy for each load balancer. In addition, if you want to configure the individual monitors to receive observations (from the load balancer) on different port numbers, you must apply a separate policy for each port number, per load balancer.
-
You have a mix of singleton and replicated monitors. In this case, you must apply one policy per port number for the singleton monitors and one policy per port number per load balancer for the replicated monitors.
-
Monitors will receive observations over SSL but not all monitors will use the same private key/certificate pairs. In this case, you must apply a different policy for each private key/certificate pair.
-
Monitors will receive observations over SSL but the location of the key store is different for different monitors, or the location of the trust store is different for different observers. In this case, you must apply a different policy for each location.
The following procedure describes how to apply the Observer Communication policy:
-
Open the Observer Communication policy you will use for configuring your observer and its associated monitor. Depending on your monitor deployment scenario, either edit the default policy instance or create a new policy instance.
-
To edit the default Observer Communication policy instance: Select Administration > System Policies in the Navigator, select the Default Observer Communication Policy in the main area, and then choose Modify > Edit Definition for Default Observer Communication Policy.
-
To create a new instance of an Observer Communication policy: Choose Admin > Create System Policy > Observer Communication.
-
-
In the Active Probes section, choose the types of business components that you want to discover and monitor.
This section lets you activate and deactivate probes.
Note:
A probe is the component within an observer that is responsible for discovering and monitoring a particular type of business component. Most types of observers have multiple probes. For more information about probes, see Architecture.In most cases, you can accept the default settings for this section. By default all probes, except JAVA, JDBC, and RMI are activated.
Notes:
The JAVA probe monitors local Java calls, which in most cases is not needed and can be distracting because of the typically large number of local Java calls that occur. In order to use the JAVA probe, you must first deploy and configure it. For information about deploying and configuring the JAVA probe, enter a service request at My Oracle Support (support.oracle.com).In most situations, you should leave the RMI probe deactivated. Most applications utilize RMI by way of higher level APIs, such as JAX-RPC, JAX-WS, EJB, and JMS. In such cases, it is better to activate only the probes for these higher-level components. However, if your application makes RMI calls directly you might want to activate the RMI probe.
There is no need to explicitly deactivate probes that are not installed—neither for the sake of performance nor for any other reason (uninstalled probes are inherently not activated). The only reason to deactivate a probe is if: (1) the probe is installed, AND (2) you do not want to monitor the type of business component the probe monitors. Furthermore, if you do deactivate (or activate) probes, you must do so in groups for some types of probes. These are the two groups of probes that you must deactivate/activate as a group: JavaEE probes (EJB, JAXRPC, JAXWS, and JMS) and the SOA Suite probes (SOA_BIZRULE, SOA_BPEL, SOA_BPMN, SOA_EDN, SOA_MEDIATOR, SOA_SPRING, SOA_WS, SOA_WSA).
Enable/disable the Enable Discovery checkbox to activate/deactivate the discovery mechanism for the associated component type. Components of that type are then discovered and displayed in the Management Console the next time they receive a message or call.
Enable the Monitor Upon Discovery checkbox for a component type if you want to immediately begin monitoring components of that type as they are discovered. Disable it if you don't want to monitor components of that type.
Note:
If you enable discovery but not monitoring and then later edit the policy and enable monitoring, the system will not begin monitoring previously discovered components. The system will begin monitoring only the components discovered after you enable monitoring. For information on enabling monitoring for previously discovered components, see the topic “Start and Stop Monitoring of Endpoints” in the online help. -
The way you perform the next steps depends on whether your monitors are singleton or replicated.
For singleton monitors:
-
Set the Communication path field to: Direct to monitor (this is the default setting).
-
Specify the port number on which your monitors listen in the Monitor port number field.
This is the port to which the observers send observations and at which the monitors receive observations. This setting configures both the monitors and observers.
Note:
You do not have to specify the host name for the monitor. The host name is obtained from the AP_NANO_CONFIG_URL Java system property or AmberPoint:NanoConfigUrl Windows key. You will set this system property/key on the application servers on which you install observers (see General Steps for Installing Observers). -
In the Criteria section, ensure that the policy is applied to the correct monitors.
Note:
You can apply only one Observer Communication policy to any one monitor. If you are applying an additional policy, you must ensure that the Criteria section of any other Observer Communication policies either do not include, or explicitly exclude the monitors to which you are applying this policy.
For replicated monitors:
-
Set the Communication path field to: Through router to monitor group
-
Specify the IP address and port number of your load balancer's socket virtual server in the Router IP address and Router port number fields.
These settings configure your observers to send their observations to your load balancer's incoming address (that is, to the load balancer's socket virtual server that you configured in Configuring Your Load Balancer).
-
Specify the port number on which your monitors will receive observations in the Monitor port number field.
This setting configures the monitors to listen on the specified port. This port number should coincide with the monitor port number that you assigned in the pool of your load balancer's socket virtual server in Configuring Your Load Balancer.
-
In the Criteria section, ensure that the policy is applied to the appropriate monitors.
You can apply the policy to all monitors in a particular monitor group by adding a Monitor Group clause, for example:
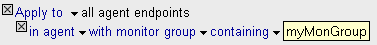
Note:
If you later add or delete a monitor to or from a monitor group, you must reconfigure your load balancer accordingly. -
-
If you want to use a secure connection for transporting observation messages from observers to monitors, leave the Enable SSL checkbox enabled and continue to the next step (SSL is enabled by default).
If, on the other hand, you prefer to use a nonsecured connection, disable the checkbox and click the Apply button. The policy editor then closes and you are finished with this procedure.
Additional fields are displayed when the Enable SSL checkbox is enabled.
-
If SSL is enabled, specify the protocol for the connection in the Protocol field.
Choose TLSv1 to use TLS 1.0.
Choose SSLv3 to use SSL 3.0 (SSLv3 is not supported by the .NET-based observers.).
Choose Any to let the components decide on the best protocol at runtime. This is the default setting.
-
By default, built-in, preconfigured security stores are used when SSL is enabled. If you want to use these built-in security stores, proceed to substep d.
If you want to use your own security stores, disable the Use Default Stores checkbox (in which case, additional fields are displayed) and complete all of the following substeps:
-
Specify the information for the Monitor's key store as follows:
Key Store Location – The location of the key store. You can specify this location as either an absolute path, if the key store file is local to your monitor, or as an HTTP(S) URL, if the file is accessible by HTTP GET.
Key Store Password – The password for accessing the key store.
Key Store Type – The type of the key store, for example, JKS, JCEKS, or PKCS12.
Key Name – The certificate and private key. You can specify a key alias or a certificate attribute of the form CN=value, UID=value, etc.
Key Password – The password for accessing the certificate and private key. If unspecified, the password for the key store is used.
-
If you want the monitor to automatically dispatch the trust store to your Java-based observers, enable the Auto Dispatch Trust Store to Java Observers checkbox.
-
Specify the information for the trust store as follows:
Trust Store Location – The location of the trust store. You can specify this location as either an absolute path, if the key store file is local to your observer (or local to your monitor, if you are using auto dispatch), or as an HTTP(S) URL, if the file is accessible by HTTP GET.
Trust Store Password – The password for accessing the trust store.
Trust Store Type – The type of the trust store, for example, JKS, JCEKS, or PKCS12.
-
If you are using .NET-based observers, ensure that you have deployed the appropriate certificate to the machines hosting those observers as described in Setting up a Secure Socket (SSL) for Observation Messages.
-
-
Enabling SSL requires the monitor to authenticate itself to the observer. Whether the observer authenticates itself to the monitor, however, depends on the setting of the Observer Authentication field. Adjust the setting of this field to one of the following values:
Use Connection Authentication – This is the default value and requires the observer to authenticate itself to the monitor each time it establishes a connection.
None – This value turns observer authentication off.
Use Message Authentication – This value requires the observer to authenticate itself each time it sends a message to the monitor. Note that the use of message authentication can significantly degrade performance. You should use this setting only when necessary. If your observer sends its messages to a monitor group whose load balancer is configured for per-message balancing (rather than per-connection), then you cannot use connection authentication. In this case, you must set this field to either None or Use Message Authentication.
-
Click Apply.
For more information about advanced settings, refer to the Business Transaction Management online help.
Adding and Removing Monitor Group Members
Replicated monitors in a monitor group are known as members. After setting up a monitor group, you might find that you need to add or remove members. You are free to do this, but you must perform the steps of the procedure as described in this section.
Adding Members to a Monitor Group
-
Deploy, and then register the monitor you want to add as described in Deploying and Registering Monitors.
-
Assign the monitor to membership in the monitor group as described in Setting Up a Monitor Group.
-
Assign the monitor to your load balancer's socket virtual server pool as described in Configuring Your Load Balancer.
Removing Members from a Monitor Group
-
Remove the member from your load balancer's socket virtual server pool.
-
Remove the member from the monitor group as follows:
-
In the Business Transaction Management Console's Navigator, choose Administration > Monitors.
-
In the main area, select the member that you want to remove from the monitor group.
-
Choose Modify > Edit Profile for Your_Monitor, where Your_Monitor is the name of your member you want to remove.
The Edit Profile tool opens.
-
Delete the name of the monitor group from the Monitor Group field.
-
Click Apply.
-
If you want to remove the monitor from membership in the monitor group but leave it as part of your Business Transaction Management system, stop now. If you want to remove the monitor completely from your system, perform the remaining steps.
-
-
Use your application server's management tools to undeploy the monitor.
-
Unregister the monitor as follows:
-
In the Business Transaction Management Console's Navigator, choose Administration > Monitors.
-
In the main area, select the monitor.
-
Choose Modify > Delete Your_Monitor Registration, where Your_Monitor is the name of your monitor.
The Delete Monitor Registration tool opens.
-
Click Delete.
-