11g Release 1 (11.1.2)
Part Number E16689-02
Contents
Previous
Next
|
Oracle® Fusion
Applications Security Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.2) Part Number E16689-02 |
Contents |
Previous |
Next |
This chapter contains the following:
Scope of the Security Reference Implementation: Explained
Role Types in the Security Reference Implementation: Explained
Function Security in the Security Reference Implementation: Explained
Data Security in the Security Reference Implementation: Explained
Segregation of Duties in the Security Reference Implementation: Explained
Extending the Security Reference Implementation: Critical Choices
FAQs for Security Reference Implementation
The Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation consists of predefined business processes, roles, role memberships, entitlement, and policies.
The security reference implementation includes the following.
A business process model (BPM)
Predefined data
Security policies
Security rules
Security implementation life cycle
The security reference implementation in Fusion Applications provides a predefined security implementation that is applicable to the needs of midsized (generally between 250 and 10,000 employees), horizontal enterprises and can be changed or scaled to accommodate expansion into vertical industries such as health care, insurance, automobiles, or food manufacturing.
The security reference implementation associates a full range of predefined roles with the business process model (BPM) levels. When assigned to users, the enterprise roles guide and control access to the task flows of the BPM and associated data. At the task level, task flows define the business actions that fulfill the intent of the BPM.
A security reference manual (SRM) for each offering presents all predefined roles, role hierarchies, business objects the roles must access, segregation of duties policies, and jobs that may have conflicting duties according to those policies. The reference implementation also can be viewed using the integrated Authorization Policy Manager (APM) and Oracle Identity Management (OIM) user interface pages to manage security policies, users, and identities.
The Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation provides predefined roles assigned to a business process model of activities and tasks.
For example, the IT Security Manager role is assigned to the Manage Job Roles task in the Implement Function Security Controls activity, which belongs to the Manage IT Security detailed business process of the Information Technology Management business process. In Oracle Fusion Applications, you perform the Manage Job Roles task using Oracle Identity Management (OIM).
The Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation provides predefined policies for data security, function security, segregation of duties, and implementation life cycle management. An enterprise sets policies for authorization, authentication, and privacy.
The predefined security policies of the security reference implementation form the foundation of Oracle Fusion Applications security and can be inspected and confirmed to be suitable or the basis for further implementation with the Application Authorization Policy Manager.
Predefined segregation of duties policies prevent errors and fraud caused by giving a user control over two or more phases of secured business transactions or operations, such as custody, authorization or approval, and recording or reporting of related transactions affecting an asset.
Predefined information life cycle management policies secure data from live database, through backup, archive, and purge.
Predefined authorization policies are the function and data security of the security reference implementation. The policies define permissions for an entity to perform some action, such as view, update, or personalize, against some resource, such as a task flow. The permissions are grouped as privileges, which comprise the entitlement granted to duty roles. Access Control Rule and grants of entitlement together identify the actions allowed on an entity by a resource.
Authentication policies certify the trustworthiness of an identity. Oracle Identity Management (OIM) stores passwords in encrypted form in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). OIM can delegate authentication to Oracle Access Manager.
Predefined privacy policies protect sensitive information about an identity.
The security reference implementation does not include predefined provisioning rules or auditing rules.
In Oracle Fusion General Ledger, accounting flexfield segment security rules secure balancing segment values.
At a high level, the security implementation life cycle follows the same phases as other aspects of information technology.
A planning phase allows for understanding the security requirements of your enterprise and mapping those to Oracle Fusion Applications security as reflected in the reference implementation. The implementation phase fulfills those requirements and a deployment phase puts your Oracle Fusion Applications implementation into secured production with your users, customers, and partners. The maintenance phase addresses security upgrades and modifications as your enterprise and Oracle Fusion Applications evolve.
Patches to the security reference implementation preserve your changes to the implementation. Patching the security reference implementation preserves enterprise security changes of the reference implementation because your enterprise' security implementation is a copy of the reference implementation with changes.
Oracle Fusion Applications security provides four types of roles: abstract, job, duty, and data.
The reference implementation contains predefined abstract, job, and duty roles in hierarchies that streamline provisioning access to users.
Abstract roles
Job roles
Duty roles
Data roles
Role hierarchies
For example, a worker may be provisioned with the Employee abstract role. In addition, the worker may be an accounts payable manager for the US business unit. Since the reference implementation provides for a data role to be generated based on the Financials Common Module Template for Business Unit Security role template, the worker is also provisioned with the Accounts Payable Manager - US data role. That data role inherits the Accounts Payables Manager job role in a role hierarchy, which includes descendent duty roles that an accounts payable manager requires to perform the duties of the job.
Note
Abstract, job, and data roles are enterprise roles in Oracle Fusion Applications. Oracle Fusion Middleware products such as Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) and Authorization Policy Manager (APM) refer to enterprise roles as external roles. Duty roles are implemented as application roles in APM and scoped to individual Oracle Fusion Applications.
An abstract role is a type of enterprise role that is not specific to a particular job.. The reference implementation contains predefined abstract roles, such as Employee or Contingent Worker.
Abstract roles inherit duty roles as a means of accessing application functions and data that users require to perform the tasks associated with the duties of work not specific to a particular job.
Provision abstract roles directly to users.
Some Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA) abstract roles provide the job roles that inherit them with access to reports and analytics.
Job roles are a type of enterprise role, called an external role in OIM and APM. The reference implementation contains predefined job roles.
Job roles inherit duty roles as a means of accessing application functions that users require to perform the tasks associated with the duties of the job. Job roles are not assigned entitlement to access functions directly. You change job roles by changing their hierarchy of inherited abstract and duty roles. Job roles may inherit other job roles, abstract roles, and duty roles.
The job roles in the reference implementation grant no explicit access to data. To grant access to specific data for a job role, you can define a data role.
You can provision job roles directly to users, and would do so if no data roles are available that inherit the job role. Job roles may grant access to data implicitly through data security policies defined for the duty roles that the job role inherits.
Important
As a security guideline, if data roles are associated with a job role, provision the data role to the user instead of the job role.
Duty roles are a type of application role. The reference implementation contains predefined duty roles. For example, the Accounts Payable Manager job role inherits the Approving Payables Invoices Duty role. For example, the Human Resource Specialist job role inherits the Worker Administration Duty role.
Duty roles provide access to the application functions that users require to perform the tasks associated with the duty. The access is defined as entitlement, which consist of privileges.
Duty roles are the building blocks of role based access control and cannot be changed. For reasons of security life cycle management, Oracle Fusion Applications implementations should use the predefined duty roles and not add custom duty roles unless you are adding custom application functions that require a new or modified duty role.
All predefined duty roles respect the segregation of duties constraints defined in the reference implementation.
Note
Duties or tasks carried by Oracle Fusion Applications enterprise roles may be incompatible according to the segregation of duties policies of the reference implementation, but any single duty role is free from an inherent segregation of duties violation.
Data roles are a type of enterprise role, called an external role in OIM and APM. The reference implementation does not contain predefined data roles. Data roles are specific to an enterprise. Data role templates in the reference implementation provide predefined structures for defining data roles.
The data roles that product family implementation users define for the enterprise carry explicit data access grants and may inherit abstract, duty or job roles. Provisioning a user with a data role augments the inherited abstract, duty or job roles with entitlement to access data. The access is explicit because the grant is defined based on the needs and data of the enterprise. For example, Accounts Payable Manager - US Business Unit data role is given explicit access to the US accounts payable data and inherits the job role Accounts Payable Manager. US Business Unit represents data determined by your enterprise and is not part of the Oracle Fusion reference implementation.
Provision data roles directly to users. As a security guideline, provision a data role, rather than also provisioning a job role that the data role inherits.
Data roles can be defined as a hierarchy of data roles.
Role hierarchies are structured to reflect your enterprise.
Job roles inherit duty roles. For example, the Accounts Payable Specialist job role inherits the Invoice Reviewer Duty and Invoice Receiver Duty roles.
Job roles can inherit one or more other job roles. For example, the Chief Financial Officer job role inherits the Controller job role, and the Applications Implementation Consultant role inherits the Application Administrator roles of the product families, such as the Human Capital Management Application Administrator job role required for core HCM setup.
Job roles can inherit abstract roles, such as the Accounts Payable Specialist and Accounts Payable Manager job roles inheriting the Employee abstract role, and a Warehouse Manager inheriting the Contingent Worker abstract role.
Important
To give enterprises the flexibility to decide if, for example, a job role is filled by employees or contingent workers, the reference implementation contains no predefined role hierarchies in which a job role inherits an abstract role.
Most job roles do not grant access to data. To provide data access for such job roles, you must generate data roles using the data role templates provided by the reference implementation. The data roles you generate inherit the base job role.
Abstract roles can inherit one or more other abstract roles. The Employee abstract role inherits the Procurement Requester abstract role.
Abstract roles can inherit one or more other duty roles. The Employee role inherits the Worker Duty role.
Abstract roles make use of implicit data security and generally are not inherited by data roles. For example, user context determines which data the Employee abstract role can access.
The predefined roles and role hierarchies are listed in the Oracle Fusion Applications Security Reference Manual for each offering.
In the security reference implementation, function security policies entitle a role to access a function in Oracle Fusion Applications unconditionally.
Predefined function security consists of roles and security policies. Details of the security reference implementation can be viewed in security reference manuals (SRM) for each offering and in the Authorization Policy Management.
Functions are secured with the following standard approaches.
Role-based access control
Set of job roles
Duty roles and role hierarchy for each job and abstract role
Access entitlement granted to each duty role
Segregation of duties policies
If the roles of your enterprise fall outside the scope of the security reference implementation, you may need to extend your Oracle Fusion Applications and predefined function security with new job and duty roles.
The duties that define jobs consist of access to those application functions that are used to perform the duty.
Predefined function security policies give grants of entitlement to access functions for the purpose of carrying out the actions associated with a duty. Duties are segregated to prevent combining grants in a duty role that should be separated across multiple roles, such as approving, recording, processing, and reconciling results.
The predefined security reference implementation is a general case representing security guidelines. Your enterprise may require additional roles with specific constraints on accessing application functions.
For example, your enterprise is a bank with a bank manager job role. Create this new job role as a new group in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) identity store by performing the Manage Job Roles or Create Job Roles tasks in Oracle Identity Management (OIM). Define the job role to inherit the duties of a bank manager, as defined by the available predefined duty roles. Create the role hierarchy of duty roles for the new job role using the Manage Duties task in Authorization Policy Manager (APM)..
If your enterprise is a pharmaceutical company, you may have users who must perform clinical trial administration duties. If the applications that a user must access to administer a clinical trial are already part of Oracle Fusion Applications, a new duty can be created in Authorization Policy Manager with entitlement to the resource code or functions users need to access for performing clinical trial administration duties. The new duty role is then associated with an enterprise role, which is represented by a group in LDAP and thereby made available for provisioning to users.
The security reference implementation can be viewed in the user interfaces where security tasks are performed or in the security reference implementation manual (SRM) for each Oracle Fusion Applications offering.
The reference implementation contains a set of data security policies that can be inspected and confirmed to be suitable or a basis for further implementation using the Authorization Policy Manager (APM).
The security implementation of an enterprise is likely a subset of the reference implementation, with the enterprise specifics of duty roles, data security policies, and HCM security profiles provided by the enterprise.
The business objects registered as secure in the reference implementation are database tables and views.
Granting or revoking object entitlement to a particular user or group of users on an object instance or set of instances extends the base Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation without requiring customization of the applications that access the data.
The data security policies in the reference implementation entitle the grantee (a role) to access instance sets of data based on SQL predicates in a WHERE clause.
Tip
When extending the reference implementation with additional data security policies, identify instance sets of data representing the business objects that need to be secured, rather than specific instances or all instances of the business objects.
Predefined data security policies are stored in the data security policy store, managed in the Authorization Policy Manager (APM), and described in the Oracle Fusion Applications Security Reference Manual for each offering. A data security policy for a duty role describes an entitlement granted to any job role that includes that duty role.
Warning
Review but do not modify HCM data security policies in APM except as a custom implementation. Use the HCM Manage Data Role And Security Profiles task to generate the necessary data security policies and data roles.
The reference implementation only enforces a portion of the data security policies in business intelligence that is considered most critical to risk management without negatively affecting performance. For performance reasons it is not practical to secure every level in every dimension. Your enterprise may have a different risk tolerance than assumed by the security reference implementation.
The security reference implementation includes some predefined HCM security profiles for initial usability. For example, a predefined HCM security profile allows line managers to see the people that report to them.
The IT security manager uses HCM security profiles to define the sets of HCM data that can be accessed by the roles that are provisioned to users
The security reference implementation includes no predefined data roles to ensure a fully secured initial Oracle Fusion Applications environment.
The security reference implementation includes data role templates that you can use to generate a set of data roles with entitlement to perform predefined business functions within data dimensions such as business unit. Oracle Fusion Payables invoicing and expense management are examples of predefined business functions. Accounts Payable Manager - US is a data role you might generate from a predefined data role template for payables invoicing if you set up a business unit called US.
HCM provides a mechanism for generating HCM related data roles.
Segregation of duties (SOD) is a special case of function security enforcement. A segregation of duties conflict occurs when a single user is provisioned with a role or role hierarchy that authorizes transactions or operations resulting in the possibility of intentional or inadvertent fraud.
The predefined SOD policies result in duty separation with no inherent violations. For example, an SOD policy prevents a user from entitlement to create both payables invoices and payables payments.
However, the most common duties associated with some job and abstract roles could conflict with the predefined segregation of duties. A predefined role hierarchy or job or abstract role may include such common duties that are incompatible according to a segregation of duties policy. For example, the predefined Accounts Payable Supervisor job role includes the incompatible duties: Payables Invoice Creation Duty and Payables Payment Creation Duty.
Every single predefined duty role is free from an inherent segregation of duties violation. For example, no duty role violates the SOD policy that prevents a user from entitlement to both create payables invoices and payables payments.
Jobs in the reference implementation may contain violations against the implemented policies and require intervention depending on your risk tolerance, even if you define no additional jobs or SOD policies.
Provisioning enforces segregation of duties policies. For example, provisioning a role to a user that inherits a duty role with entitlement to create payables invoices enforces the segregation of duties policy applied to that duty role and ensures the user is not also entitled to create a payables payment. When a role inherits several duty rules that together introduce a conflict, the role is provisioned with a violation being raised in the Application Access Controls Governor (AACG). If two roles are provisioned to a user and introduce a segregation of duties violation, the violation is raised in AACG.
Note
SOD policies are not enforced at the time of role definition.
Aspects of segregation of duties policies in the security reference implementation involve the following.
Application Access Controls Governor (AACG)
Conflicts defined in segregation of duties policies
Violations of the conflicts defined in segregation of duties policies
AACG is a component of the Governance, Risk, and Compliance Controls (GRCC) suite of products where segregation of duties policies are defined.
Define SOD controls at any level of access such as in the definition of an entitlement or role.
Simulate what-if SOD scenarios to understand the effect of proposed SOD control changes.
Use the library of built-in SOD controls provided as a security guideline.
Your risk tolerance determines how many duties to segregate. The greater the segregation, the greater the cost to the enterprise in complexity at implementation and during maintenance. Balance the cost of segregation with the reduction of risk based on your business needs.
An intra-role conflict occurs when a segregation of duties policy expresses constraints within the construct of a single role (entitlement and duties) that creates violations.
Tip
As a security guideline, use only the predefined duty roles, unless you have added new applications functions. The predefined duty roles fully represent the functions and data that must be accessed by application users and contain all appropriate entitlement. The predefined duty roles are inherently without segregation of duty violations of the constraints used by the Application Access Controls Governor.
A segregation of duties violation occurs when a policy is defined that allows a segregation of duties conflict to occur.
Notifications report conflicts to the requester of the transaction that raised the violation. Oracle Identity Management (OIM) shows the status of role requests indicating if a segregation of duties violation has occurred.
For information on configuring audit policies, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Administrator's Guide.
For more information on managing segregation of duties, see the Oracle Application Access Controls Governor Implementation Guide and Oracle Application Access Controls Governor User's Guide.
In general, the security reference implementation is designed to require only small deltas to adjust the Oracle Fusion Applications security approach for a specific enterprise.
Most commonly, the security reference implementation is extended with the following.
Roles for vertical industries such as pharmaceuticals
Data Roles
Role hierarchies that leverage predefined roles or make use of newly created roles
The predefined duty roles and entitlement represent all functions in Oracle Fusion Applications and do not require extension except where custom application development introduces new functions. Custom functions require custom entitlement definitions. Custom tables and objects may also require protections. Objects extended or created by an enterprise are preserved during upgrade and patching.
As a security guideline, use the predefined security reference implementation.
The predefined security reference implementation does not include data roles, but does provide extensive data role templates that create data roles based on your enterprise setup. The roles and role hierarchies of the predefined security reference implementation may not adequately secure the function and data of a vertical industry enterprise or a custom deployment of applications.
Assess the security reference implementation during planning. The security reference implementation can be viewed in the user interfaces where security tasks are performed or in the security reference manual (SRM) for each Oracle Fusion Applications offering.
As a security guideline, copy an existing role and make changes to the copy as a way to modify an existing role to better fit your enterprise, or create a new role for your enterprise.
Modifications include the following actions
Changing a predefined enterprise role or creating a new enterprise role modeled on the existing one, and applying modifications to the new role
Adding a data role by using a predefined data role template
The IT Security Manager and IT Security Administrator roles are authorized to add new roles.
To change a predefined enterprise role by making a copy and modifying the copy use the Authorization Policy Manager.
Create a new job role, which creates a new group in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store.
Map the duties to the new job role in the role hierarchy.
Define data security policies referencing the new job role.
New job roles or copies of seeded job roles modified to fit your enterprise should be distinct by including new data security policies.
As a security guideline, if the new role is a data role, generate the data role using the predefined data role templates or Human Capital Management (HCM) data role management. To add a data role by using a predefined data role templates, use the Authorization Policy Manager.
Creating a new data role template to accommodate the data needs of your enterprise is a custom activity.
As a security guideline, , create a new job role that contains a hierarchy of roles modeled on an existing role hierarchy, but with the desired modifications.
To modify an existing role hierarchy, use the Authorization Policy Manager.
You can extend the Oracle Fusion Applications security implementation with provisioning rules, such as automatic role provisioning rules in HCM and Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
The scope of the security reference implementation typically exceeds the needs of a real world enterprise. For example, every feature in a Oracle Fusion Application deployment corresponds to one or more duty roles predefined to use the feature. When your enterprise does not use every feature, it does not need to provision every predefined duty role.
The common decisions made to match an enterprise to the security reference implementation include the following:
Do the predefined job roles match the equivalent job roles in your enterprise?
Do the jobs in your enterprise exist in the security reference implementation?
Do the duties performed by the jobs in your enterprise match the duties in the security reference implementation?
In the figure, various tasks correspond to the decisions you make about changing the security reference implementation.
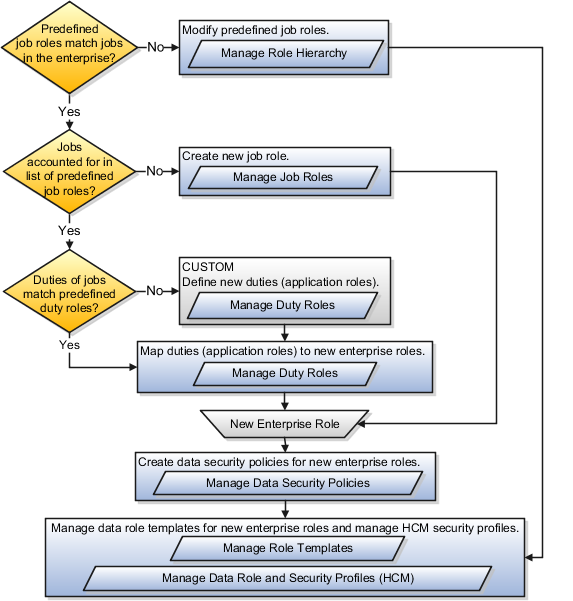
The following figure shows some examples of changes that may be required to match the security reference implementation job roles to the job roles of your enterprise.
Add duty roles to a predefined job role hierarchy.
Remove duty roles from a predefined job role hierarchy to include as a new, separate job role.
Create a new job role with a hierarchy of predefined duty roles.

All functions and actions in Oracle Fusion Applications that need to be secured are covered by the reference implementation. In some cases, especially with function customizations, a new duty role may be needed.
Changes to data security require changing data security policies and the data roles templates.
The security reference implementation remains an intact reference that is always up to date with the latest security patches. Oracle Fusion Applications manages the changes you make to the reference implementation as a copy. Your functional setup of the mapping between features and duty roles determines what roles are present and what updates are applied to your deployment. Change management and reconciliation keep your deployment up to date with the reference implementation.
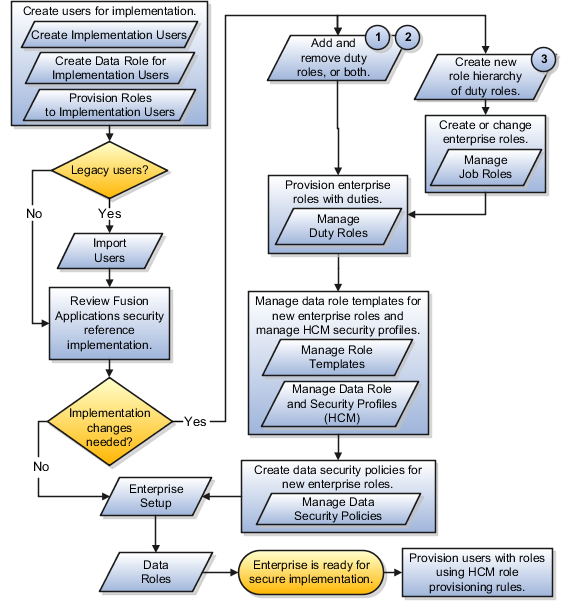
The following figure shows three types of changes within the process for implementing Oracle Fusion Applications security. Managing data role templates for new enterprise roles and managing Human Capital Management (HCM) security profiles specifies the conditions needed by role changes in the reference implementation. Creating data security policies for new enterprise roles establishes access controls where no data roles are available.
Note
Data roles are automatically generated based on enterprise set up and the predefined data role templates, and manually created using the HCM Manage Data Role and Security Profiles task.
The figure shows the security implementation flow from creating users for implementation to provisioning users with roles so they can implement the deployment for their enterprise. Most of the tasks in the flow after creating users for implementations and before setting up the enterprise are optional. In particular, you only need to manage data role templates and data security policies if you have data security needs not addressed by the security reference implementation.
The security reference implementation can be viewed in the user interfaces where security tasks are performed or in the security reference implementation manual (SRM) for each Oracle Fusion Applications offering.
For information on securing new business objects in Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Application Composer and securing new business objects in an extended application, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Extensibility Guide.
An action that is conditionally or unconditionally granted to a user or role to access functions and data. In most contexts, entitlement is equivalent to privilege.
Entitlement provides the means necessary to access or act upon business objects, including Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA) objects. There is a one-to-one mapping between an operation and entitlement. For example, the Create Purchase Order operation is granted as a privilege to a role with entitlement to approve a purchase order.
In function security, entitlement is a set of privileges. Each privilege enables a single action, such as Enter Payable Invoice. A single action consists of permissions on the resources relevant to the action.
In data security, entitlement is conditionally granted to a role on a named set of data. For example, a Payables Accountant is entitled to delete an invoice with invoice_id=100. The entitlement includes the privilege that allows the accountant to read this invoice with the delete function enabled.
Governance Risk and Compliance Controls (GRCC) entitlement is a set of permissions defined in the Oracle Application Access Controls Governor (AACG) to participate in segregation of duties policies.