5 Overview to Invoice Processing
This chapter contains these topics:
5.1 Objectives
-
To understand the differences between standard invoices and speed invoices
-
To revise unposted and posted invoices
-
To post invoices to the general ledger
-
To understand how to enter and process recurring invoices
-
To locate customer ledger information
5.2 About Invoice Processing
Generally, you create an invoice before you receive payment from the customer. Effective management of invoice processing is fundamental to your accounts receivable department.
Invoice processing consists of:
-
Working with invoice entry controls
-
Understanding fiscal date patterns
-
Working with standard invoices
-
Working with other types of standard invoices
-
Entering speed invoices
-
Reviewing and approving invoices
-
Understanding the post process
-
Posting invoices
-
Revising posted invoices
-
Printing Invoice Journal Information
-
Locating customer ledger information
-
Working with recurring invoices
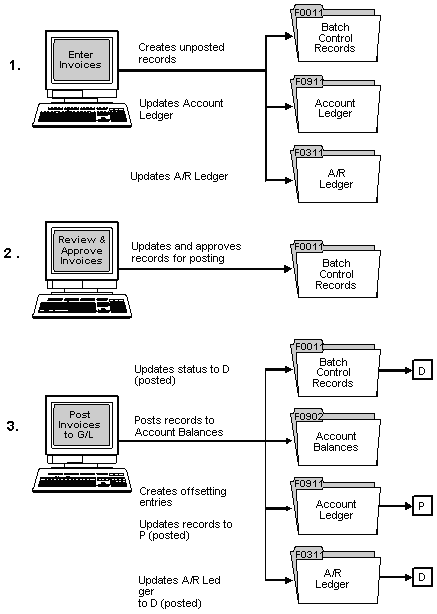
Invoice processing is one example of three-tier processing. All JD Edwards World systems use three-tier processing to manage batches of transactions. The term three-tier refers to three standard steps you perform.
The following graphic illustrates the concept of three-tier processing.
5.2.1 What Are the Types of Invoices?
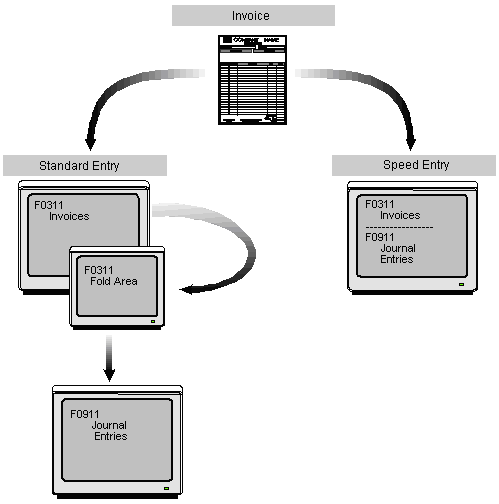
Depending on your needs, you can choose to enter the following types of invoices:
-
Standard invoices. These invoices give you the most flexibility and options.
-
Speed invoices. These invoices give you less flexibility and options than standard invoices. However, they provide a quicker way of entering invoice and accounting information.
5.2.1.1 Which Type of Invoice Should You Enter?
To help determine which type of invoice you should enter, consider the following advantages and disadvantages of standard and speed invoices:
| Invoice Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard invoice advantages | You can:
|
| Standard invoice disadvantages | You cannot:
|
| Speed invoice advantages | You can:
|
| Speed invoice disadvantages | You cannot:
|
5.2.2 When Do You Review and Approve Invoices?
After you enter invoices, you can review and approve them before posting. You can:
-
Review and approve batches
-
Review and revise individual invoices
-
Review and revise associated journal entries
5.2.3 What Happens When You Post Invoices?
After you review and approve invoices, post them to the general ledger. When you submit a batch of invoices for posting, the system:
-
Selects unposted, approved invoices and edits each transaction
-
Posts accepted transactions to the Account Balances table (F0902)
-
Creates automatic offsets to the A/R trade and tax accounts
-
Marks the invoices as posted in the A/R Ledger (F0311) and Account Ledger (F0911) tables
5.2.4 When Do You Set Up a Recurring Invoice?
If you have a customer that you repeatedly bill for a specific amount, such as a service or lease agreement, set up a recurring invoice. You specify the frequency and the number of payments when you enter the original invoice.
5.2.5 What Is Customer Ledger Information?
As part of your A/R activities, you might need to view the transaction history of a customer. Customer ledger information provides:
-
Open amounts remaining on an invoice
-
Pay status and posting status of an invoice
-
Invoice detail and associated journal entry information
-
Account status information
-
Receipt information
When you work with Customer Ledger information, be aware the action code and search type security may affect your ability to inquire upon, add, or change customer information. You must have the appropriate combination of action code/search type security to work with Customer Ledger information.