1 Overview to Fixed Assets
This chapter contains these topics:
The JD Edwards World Fixed Assets system is flexible. This flexibility is helpful as many companies delay processing fixed asset information until they are ready to compute period depreciation. For example, you can use the Fixed Assets system's automated asset setup to update asset information on a daily, monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
1.1 System Integration
The JD Edwards World Fixed Assets system links to many of the other systems that your company uses within JD Edwards World. System integration helps ensure that asset information and account transactions are consistent. You need to enter fixed asset and account information only once throughout your company. This saves considerable time and money, especially when you need to record numerous and complex business transactions daily, and update or revise asset information, such as depreciation rates and account numbers.
The Fixed Assets system is integrated with the following JD Edwards World systems:
The following graphic shows the integration of the Fixed Assets System with other systems within JD Edwards World.
Figure 1-1 Integration of the Fixed Asset System
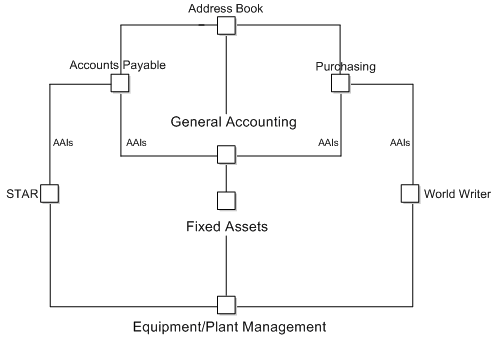
Description of "Figure 1-1 Integration of the Fixed Asset System"
1.2 Fixed Assets Features
The Fixed Assets system includes the following features:
-
Multiple depreciation books and methods
-
Automated asset setup
-
Asset search and location
-
Insurance, financing, and warranty information
-
Asset transfers, splits, and disposals
-
Asset reports (standard and user-defined)
1.2.1 Multiple Depreciation Books and Methods
You can maintain multiple sets of depreciation books for an asset. You can depreciate assets in different ways for different purposes. For example, you might set up the books for an asset to reflect a three-year life for taxation purposes and a five-year life for financial statement purposes. Or, you might have a set of depreciation books for different currencies.
For each set of books that you maintain for an asset, you can assign null depreciation and either a user-defined depreciation method or one of the following 18 predefined depreciation methods:
-
Straight line
-
Sum of the year's digits
-
125% declining balance to cross-over
-
150% declining balance to cross-over
-
Double declining balance to cross-over
-
Fixed percent on declining balance
-
Accelerated cost recovery system (ACRS) standard
-
ACRS optional
-
Units of production
-
Modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS) luxury cars - domestic
-
Fixed percent of luxury cars - foreign
-
MACRS standard
-
MACRS alternative
-
ACRS alternate real property
-
Fixed percent of cost
-
Fixed percent on declining balance to cross-over
-
Alternative minimum tax (AMT) luxury autos
-
Adjusted current earnings (ACE) luxury autos
You can calculate depreciation daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, or annually. You can also base your depreciation calculations on a 4-4-5 fiscal pattern or a 13-period pattern.
Additionally, you can automatically generate depreciation to multiple accounts which share assets using the Depreciation Expense Allocation.
1.2.1.1 User-Defined Depreciation
Although the JD Edwards World Fixed Assets system provides a wide range of depreciation rules, you might need a specific depreciation combination other than those provided with the standard depreciation rules. With user-defined depreciation, you can substitute various depreciation conventions, formulas, and spread patterns to define depreciation methods specific to your company without custom programming. For example, you can copy an existing rule and modify it to create a depreciation method for your specific needs.
You can set up user defined depreciation methods to establish:
-
User-specific depreciation formulas without custom program modifications
-
User-specific depreciation rules and conventions
-
Depreciation methods for specific categories of assets
-
Specific depreciation methods for assets placed in service during certain periods
-
Specific depreciation methods for certain years
1.2.2 Automated Asset Setup
You can use default rules to define default depreciation instructions for individual asset cost accounts by company. When you add newly acquired assets to the Fixed Assets system, the information you establish in default rules is included automatically in the new asset records. You can override the defaults for special cases. Using default rules saves time, especially if you frequently add assets to the system. You can define default values for:
-
Accounting class
-
Equipment class
-
Depreciation accounts
-
Revenue accounts
-
Depreciation information
1.2.3 Asset Search and Location
You can use the system's search capabilities to locate assets based on:
-
Company
-
Equipment status
-
Description
-
Responsible business unit
-
Current location
-
First 10 category codes
You can also track the history of an asset's movement from location to location.
1.2.4 Insurance, Financing, and Warranty Information
You can record and access the insurance information for an asset, such as insurance company, policy number, premium cost, value, and replacement cost. You can also account for leased and mortgaged assets and track monthly payments, purchase options, and contract information.
Additionally, you can ensure that you utilize all services with a warranty, track expirations, costs, and claim information.
1.2.5 Asset Transfers, Splits, and Disposals
You can use the Fixed Assets system to record asset transfers, splits, and disposals in your accounting ledgers.
1.2.6 Fixed Asset Reports
You can print two types of fixed asset reports:
1.3 Fixed Assets Process
The following process is an example outline that follows an asset from its purchase to its disposal, and includes the yearly close. Use this example as a guideline only. Specific steps and procedures vary from company to company.
Figure 1-2 Asset Flow from Purchase to Disposal
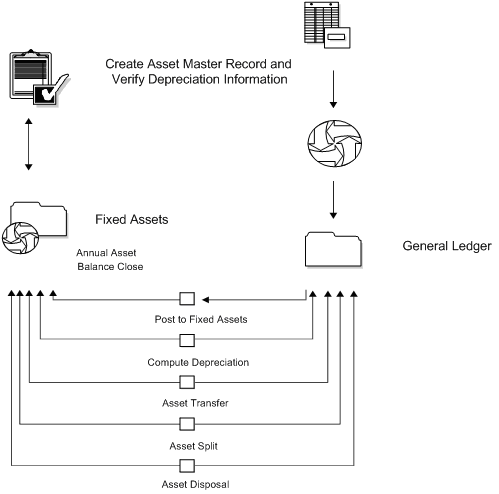
Description of "Figure 1-2 Asset Flow from Purchase to Disposal"
1.4 Fixed Assets Files
The JD Edwards World Fixed Assets system contains both primary and secondary files.
1.4.1 Primary Files
The JD Edwards World Fixed Assets system stores asset and transaction information in three primary files: