Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance with Oracle Financials
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Introduction
- Requirements for Financial Compliance
- An Overview of Oracle's Compliance Architecture
- Enterprise Visibility and Security
- Internal Control & Operational Efficiency
- Corporate Governance & GAAP
Introduction
Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance are the issues of reflecting the will of the owners, that is, the investors in the operation and performance of a company. The public, through regulation and law, ratings, and disclosure, has a substantial interest in how companies and management comply with the standards and obligations that they have.
To reflect the investors' will, and to comply with the public's standard, management needs to enforce their decisions and policies on the group. The Japanese word "hoshin" is sometimes applied to the vision of the management. Successful corporate governance and successful implementation of hoshin both require the firm execution of policy and delivery to your business model.
Internal Control is the term used to define the systematic methodology of managing the risk of non-compliance with management policy, error in reporting, and incidental and business losses. Internal Control articulates the risks of error and losses to which you might be exposed, the controls you put in place to mitigate those risks, and your system of monitoring those risks and controls.
The Oracle Financials suite provides you with a comprehensive set of tools for executing the delivery of hoshin throughout your organization. The applications make it easy to incorporate your forecast, track your budget, measure progress, and make sure that the trickle down of your decisions is thorough and complete. You get a clear picture of the state of the group and the ability to pinpoint problem areas. The Oracle Financials suite also provides both inherent and express tools to manage internal control and to comply with legislation and directives requiring compliance assertion.
Regulations and Compliance
The growing complexity and interdependence of the global economy requires accommodating the ever increasing demands of worldwide compliance. Most companies today must comply with multiple regulations such as the following:
-
Financial reporting standards such as International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and United States Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
-
Corporate Governance mandates such as Sarbanes-Oxley, the European Eighth Directive, and other Governance Codes.
-
Privacy laws such as Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) and the European Union's Data and Privacy regulations.
-
Industry-specific regulations such as those negotiated under the Basel II agreement. Other standards are established by standards bodies such as the International Standards Organization or national agencies like the United States Food and Drug Administration.
Note: Though Oracle's governance and compliance architecture incorporates all E-Business Suite Applications, the focus of this chapter is on financial compliance and the financial modules within the suite.
Requirements for Financial Compliance
Good, holistic, governance and compliance require that management have clear visibility across the enterprise, have effective internal controls, and operate efficiently.
Enterprise Wide Visibility
Management asserts that the public accounts are an accurate and fair assessment of financial condition and operational performance and that they can satisfy themselves they are so. To achieve this end, executive managers need to access reliable data behind the financials. They must also be able to align strategies with operational plans to actively monitor day-to-day operations, and to understand the system of internal control.
This is easier to accomplish if:
-
Groups have transparent processes and
-
Signing officers have access to relevant and timely information across the enterprise.
Management needs to have fail-safe, transparent processes, that are integrated across the enterprise and provide relevant data and timely information to senior executives.
Effective Internal Controls
Auditors and management must attest to the effectiveness of their internal controls. Corporations must set up process controls that enable regulatory compliance.
To monitor effectiveness, your policies and processes must be articulated and promulgated. Though the deployment of these processes must be distributed across the firm, it is beneficial to centralize their design and establishment. Once you've identified common business requirements and processes used to meet your organization's compliance mandates, the key is to automate as many of those processes as possible to make them auditable and repeatable. All information about processes and their associated risks and controls must be documented and easily accessible.
Content and records management is another area that compliance court cases and associated electronic discovery have put under the spotlight.
Creating a culture of compliance (an identified element of an effective internal control system) also means that employees must be trained on the company's latest governance and compliance policies and practices. They must also be continually assessed on their understanding of those policies and practices. An enterprise wide learning architecture is critical for training employees and monitoring skills.
High Level of Operational Efficiency
Increased regulation has also translated into tighter deadlines for reporting. By reducing the closing cycle as well as giving executives visibility to business events as they unfold, it makes it easier for executives to:
-
Close the books quickly and then assess and understand their operating performance.
-
Reconcile financial data quickly and accurately, and identify problem areas.
Centralized, low cost, error-reducing processes are a backbone to ensuring consistent, error-free data across the enterprise.
An Overview of Oracle's Compliance Architecture
A proactive compliance program based on sustainable competencies is the best practice in dealing with corporate governance. However, the human and financial costs of responding to each regulatory challenge with unique one off solutions are simply not sustainable.
Oracle delivers a complete information architecture that can support sustainable compliance by combining control based business and compliance applications, content and records management, and security technologies. The architecture provides for complete visibility into financial results, business performance, and underlying controls. Enterprises can confidently and cost effectively comply with their compliance and governance mandates, from financial reporting regulations such as Sarbanes-Oxley, to industry specific mandates.
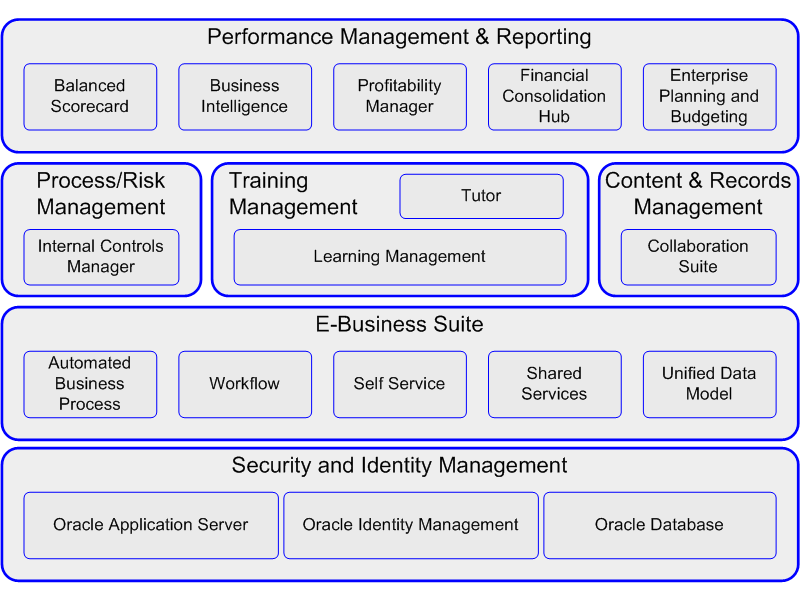
The following diagram provides a high level overview of Oracle's Compliance Architecture and captures the visibility, control, and efficiency constructs discussed above. The diagram illustrates the four layers of technology stacks:
-
Performance Management and Reporting: Balanced Scorecard, Business Intelligence, Profitability Manager, Financial Consolidation Hub, Enterprise Planning and Budgeting
-
Process/Risk Management: Internal Controls Manager
Training Management: Tutor, Learning Management
Content and Records Management: Collaboration Suite
-
E-Business Suite: Automated Business Process, Workflow, Self Service, Shared Services, Unified Data Model
-
Security and Identity Management: Oracle Application Server, Oracle Identify Management, Oracle Database
Oracle supports this architecture with multiple components that are integrated with each other. The integration simplifies your entire information technology and security infrastructure as well as a large segment of your process efforts in the following two ways:
-
Standardized information technology systems, applications, and business processes streamline much of the compliance effort. You can now maximize control through automated processes and embedded controls.
-
Improves compliancy and operations visibility through a single source of high quality information. You can run your entire business on a single, global data repository and have a concise and accurate picture of regulatory compliance and enterprise performance.
Operational efficiencies are a direct benefit of these initiatives.
Enterprise Visibility and Security
Data and Security Management
Security and integrity of data is a top priority for executive signing officers. Fragmented systems, multiple general ledgers, and transaction system interfaces are barriers to meeting governance and compliance mandates. Standardizing on a single instance helps break down information silos by eliminating duplicate systems and application interfaces, ensuring data accuracy, reliability, and auditability.
Oracle Database/ Application Server
The Oracle Database meets the need for a single source of truth through access control and authentication features required to protect data in a single, consolidated database repository. The Oracle Application Server and middleware platform is designed to leverage service-oriented and grid computing and complements the database security structure.
For example, the Oracle Database delivers advanced audit capabilities through extensible, policy-based auditing features. These features can provide data logs that are useful for analysis in a compliance investigation. Organizations can also define specific audit policies that alert administrators to misuse of legitimate data access rights and generate a record of them.
Oracle Identity Management
While the security fundamentals of authentication, access control, and audit are built into the Oracle Database and Application Server, many organizations still struggle with distinct user and authorization repositories. The security policy infrastructure associated with the Oracle Database and middleware platforms can be further leveraged by Oracle Identity Management.
Oracle Identity Management delivers centralized, policy driven user management and security administration for distributed deployments. Compliance related tasks such as password management and enabling delegated administration are also easily facilitated.
-
User Account Management - allows for identity creation and management services through delegated administration, user self-service, integrated workflow, and role-based access control to manage user access to applications and data. This feature allows for the separation of duties common to many regulations today.
-
User Authentication and Authorization - manages the authentication mechanism employed. This service utilizes authentication devices such as tokens, smartcards, and biometric devices to increase assurance that users are who they state themselves to be.
Users can be provisioned directly in the Identity Management repository or synchronized with a third party repository and assigned a security clearance level. This capability simplifies administration by providing a central, enterprise-wide repository that allows security and privacy policies to be shared. These policies authorize access to specific applications based on attributes of the user, their organization, and any other information that an administrator may wish to employ.
-
Access and Entitlement Reporting and Auditing - provides for aggregated audit capabilities across numerous applications with pre-built reports that offer a demonstrable means to show compliance.
Internal Control & Operational Efficiency
Automated Processes & Controls in the E-Business Suite
Sarbanes-Oxley requires tighter deadlines and prompt disclosure. The more automated your business processes, the more reliable and timely is the data captured by those processes. The Oracle E-Business Suite is engineered to work together as an integrated system wherein you can pass information from one application to another without incurring incremental integration costs or inducing mapping error.
You can set up alerts to automate exception management and notifications. Alerts can specify database exception conditions for continuous or scheduled monitoring of all E-Business suite applications. This improves your ability to research and resolve issues on a proactive basis.
The applications also offer a rich set of built-in automated internal controls that enable companies to enforce their business rules in every transaction. Such controls can be utilized to implement and enforce policies that meet the evolving requirements of multinational regulations. Examples include:
-
Cross-validation rules for journal processing to prevent inaccurate journals and entries of invalid account combinations.
-
2-, 3-, and 4-way matching in the purchasing and payables domain.
-
Sequential numbering of invoices and journal entries.
-
The ability to set quantity and price tolerance limits during invoice processing.
Controls embedded in the system make it easy for them to be integrated into the day to day activities of the firm. This helps you to ensure compliance across your global organization. Application controls are also significantly easier to test and validate than manual controls and hence reduce the scope of audit activities.
Oracle Workflow and BPEL
Oracle Workflow and Oracle BPEL Process Manager are modeling tools in the Oracle E-Business Suite that allow users to design internal business processes and approval hierarchies and store them in a central repository.
Companies can use Workflow to support a wide variety of compliance mandates, designing processes that are both auditable and repeatable, while enforcing pre-set approvals and limits. Workflows are embedded into the applications thus enabling your organization to streamline inter user approvals and information flows. You can configure these flows according to your business rules while validating the information transferred. Such flows expedite business processes across the enterprise.
Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) provides enterprises with an industry standard for business process orchestration and execution. Oracle BPEL Process Manager enables organizations to model and deploy business processes based on the BPEL standard.
Self Service Solutions
By utilizing a self-service paradigm where end user requests are by and large facilitated by those same users, you can reduce administrative tasks and the time and effort involved in recording and tracking business events. Manual processes are eliminated and bottlenecks are streamlined. Overall, extending automation to the end user via self-service increases the efficiency of your business information and raises data integrity.
Within the Oracle E-Business Suite, a number of self-service applications automate and connect internal processes such as:
-
Expense Reports and Time Cards
-
Employee Information
-
Purchasing Processing
-
Competency Management
Using the suite, self-service automation is also extended to customers and suppliers to interact with items such as:
-
Orders
-
Invoices
-
Payments
-
Requisitions and Auctions
-
Inquiries and Disputes
Oracle self-service applications such as iSupplier Portal, Internet Expenses, and iProcurement increase the efficiency of information. These applications take advantage of embedded workflows that allow you to streamline inter-user approvals and participate in review processes.
Shared Service Centers
The Oracle E-Business Suite is a functionally complete suite of integrated applications. The applications support the centralization and integration of business operations through shared service centers.
We've discussed shared services and shared service centers in the Worldwide Operations chapter. An important impact of the deployment of shared service centers is that the number of control points in a process and the number of variations of a process are greatly reduced, dramatically mitigating the risk of process error. The consolidation of data and processes in shared service centers also mitigates against the risk of error and of poor decision making.
The benefits of shared services are not just for multinationals. Medium sized firms can reap benefits from their efficiencies. The Oracle E-Business Suite allows you to be both locally and corporately compliant while increasing efficiencies through shared service centers. Examples of functional areas where shared service centers make most sense include procurement, disbursement, collections, order management, and Human Resources.
Standardized business practices ensure that all parts of the organization conform to practices that are consistent with corporate objectives:
-
Establish global processes and accessibility to data.
-
Hasten incorporation of new business units.
-
Establish the right balance of centralized and decentralized functions.
-
Standardize and automate processes with self-service.
-
Focus on core competencies.
Standardized Processes
It is advantageous for companies to standardize their business processes across organizations and geographic regions. Common process methodologies provide benefits of economies of scale and learning, control, and comparability.
A good example of the move to standardization is Oracle and its subsidiaries. When Oracle decided to move to a single instance of financial data, the company had more than 90 independent businesses around the world. Each business had different processes none of which were linked to each other. As a first step to run the enterprise as a single unit and avoid redundancy, Oracle took on the responsibility of standardizing those processes.
In order to do this, the company established a fictional subsidiary called Monaco and then articulated the idealized procedures that this subsidiary deployed. These idealized procedures were then subject to review by Oracle's European, American, and Asia Pacific management. Through those reviews, the processes were refined to a standard procedure. Though the processes have been edited and revised many times, they are now all standardized, global procedures.
Consider the way an employee submits expenses and receipts for reimbursement. At Oracle, the methodologies, user interfaces, receipt submissions, and reimbursements are now the same anywhere in the world. The employee submits the expenses electronically and sends the paper documentation to a shared service center from where treasury funds the reimbursement. In addition, we also meet unique local requirements such as recovering overseas taxes paid by American travelers.
Similar standardization has been applied to almost all processes including:
-
Revenue and expense recognition
-
Human Resources processing
-
Procurement
-
Order Management
-
Sales and service
Finally, formally designed standardized reports from a central reporting organization are utilized to complete the business cycles.
Oracle Internal Controls Manager
Oracle Internal Controls Manager is a comprehensive tool for executives, controllers, and auditors to address regulations that require organizations to maintain internal financial controls and monitor ongoing compliance. The solution integrates with other enterprise business systems, Oracle and non-Oracle, to monitor key control points. It also includes specific audit features such as one designed expressly to look at segregation of duties. Oracle Internal Controls Manager is based on Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) and COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and related Technology) standards.
Note: The following sections provide an overview of the salient features available in Oracle Internal Controls Manager. For detailed information on these features, see the Oracle Internal Controls Manager Implementation Guide.
Tip for Existing Oracle Financials User
-
In Release 12, Oracle Internal Controls Manager provides preventative controls such as the segregation of duties feature and a DBI dashboard for control managers.
Process - Risk - Control Library
One of the biggest challenges to compliance is identifying and defining a company's business processes, linking documentation to those processes, then identifying the risks and controls associated with those processes. The COSO framework for internal controls and the COBIT framework for Information Technology controls are often used to identify the process- risk- control matrix in a firm. Once these risks and controls are identified, regulations require testing, certification, and ongoing monitoring of the controls.
Oracle Internal Controls Manager can be used to automate and streamline all the processes associated with its internal control environment. Processes, risks, and control activities are now stored in the Oracle Internal Controls Manager risk library, enabling a firm to have a 360 degree view of risks associated with each control activity as well as the individuals within the organization who have responsibility over that control.
Process Approvals and Change Management
The verification of business processes in an organization is a major portion of the internal audit function. These processes (both manual and automated) are subject to change due to a variety of reasons such as a rapidly changing environment, legislation, and changes in other processes. Since the changes can adversely impact process risk exposure as well as the internal controls set up on the process, process changes must be subject to a review and approval mechanism.
Further, the internal audit department must assess the process change to ascertain whether it introduces additional control risks. Risks to internal controls can be captured through a review of the changes to key risks, controls, and business settings. It is therefore critical to be able to view version information and historical data for business processes. Oracle Internal Controls Manager provides a rich functionality in this domain and uses an intuitive workbench to provide features and benefits including the following:
-
Processes and process revisions are created in a "Draft" status and must be approved before the process or its revision can be used in the system. Change notifications are sent to all concerned personnel (for example, process owners) and recipients of these notifications can review the modified processes prior to giving their approval.
-
The application maintains a detailed revision history for all processes (including non standard processes) in the entity. Auditors have the ability to view a complete audit trail of changes taking place in the organization and the risk library.
-
Before approving a process change, you can compare the revised process with its prior version to determine whether the change is acceptable. This comparison is crucial in determining the impact of changes and deviations on associated processes. Through a hierarchy viewer, you can also see which associated business processes are impacted by the change.
Integration with Oracle Scripting
To help in making assessments, you can associate a survey written with the Oracle Scripting tool to an "Assessment" in Oracle Internal Controls Manager. Oracle Scripting is a powerful web based tool for soliciting, managing, and analyzing stakeholder feedback through surveys. In any organization, surveys created with Oracle Scripting can help in providing an effective control environment and the results can be used to make macro level risk assessments.
Oracle Scripting is comprised of several components including a Script Author and a Survey Administration console. The Script Author is used to build "survey scripts" that can be deployed throughout the enterprise. With the Survey Administration console, you can establish and maintain survey campaign information as well as generate reports for analyzing survey data.
Segregation of Duties Constraints
Oracle Internal Controls Manager can be used to check whether users in an enterprise have access to responsibilities and functions that are incompatible with each other.
The Segregation of Duties feature in Oracle Internal Controls Manager is based on access to "Responsibilities" and "Functions" in the Oracle E-Business Suite.
Note: Responsibilities define application privileges by allowing users access to only those Oracle Applications functions and data appropriate to their roles in the organization.
Note: Functions are a security feature in Oracle Applications that are used to control access to specific application features. Each function typically corresponds to an application feature such as a page, button, tab, or menu.
You now have the ability to identify any specific combination of incompatible responsibilities or functions in an organization as a constraint. The application can report occurrences where an individual possesses access to two or more of these incompatible tasks and thereby violates the constraint.
When a constraint violation is found, you can initiate a request for management to take action by modifying the duties of those users with incompatible tasks.
Process and Organization Certification
Corporate management systems typically imply the existence of processes that are employed to implement the objectives of management. For these management systems to be effective, it is critical that the business processes supporting them are regarded as reliable. Companies therefore need to establish an ongoing monitoring of business processes while evaluating and improving their effectiveness.
You can accomplish this objective in Oracle Internal Controls Manager through the periodic certification of processes and organizations in the enterprise. Certification requires process owners to provide assurance that their organization's processes are in compliance with the standard(s) utilized as the basis of its management system. It includes a series of rigorous audits and other activities to provide assurance that the organization's management system is adequate and effective.
Successful completion of an audit and any related follow-up activities which may be required results in the process being "certified". The certification attests to the process meeting the requirements of the applicable standard.
Financial Statement Certification
Financial statements are comprised of financial items. Each financial item is an account or consolidation of accounts and an integral part of the processes that affect it. It is imperative that the processes behind financial items be recognized and incorporated into the financial audit. Financial audits therefore include both test of details of balances as well as audits of the processes that affect those balances.
In addition, governmental regulation in several countries, for example Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in the United States, requires that the principal officers of a firm certify the information contained in the firm's quarterly and annual reports. Management must now attest to the effectiveness of internal controls over financial reporting.
To this end, monitoring of the controls in the various processes impacting the financial statement takes on increased importance and companies need to establish this ongoing monitoring as part of the financial audit. Successful completion of an audit of these processes and any related follow-up activities which may be required, results in the financial item being "certified."
With the financial statement certification functionality in Oracle Internal Controls Manager, signing officers now have a structured way of ensuring that the internal controls related to every account and financial item is working. The adequacy of internal controls within business processes affecting financial statements is brought about from two different inputs:
-
For each financial item, the results from internal audit evaluations of the processes affecting that item are presented in a consolidated fashion to financial "signing" officers.
-
Also brought into context are the results of the relevant process certifications by the process owners.
These inputs present adequate perspective for the signing officer to evaluate the processes behind the numbers and decide whether adequate controls are in place.
Executives can use the dashboard in Oracle Internal Controls Manager to see how they stand at any given time in the 404 certification process, as defined by financial statement line items and their associated business processes. The dashboard displays when process owner have evaluated and signed off on the effectiveness of internal controls associated with a specific business process. Having such a detailed and granular level of accountability supports the compliance process.
Application Controls Management
The Oracle E-Business Suite offers a comprehensive set of automated application controls in the form of setup parameters. These application controls are critical to the overall control environment because any changes to them can have an adverse effect on the organization's processes including those that influence the reliability and integrity of financial reporting.
The Application Controls Monitoring is an integrated, out of the box Information Technology (IT) controls management feature within Oracle Internal Controls Manager. It enables companies to effectively and efficiently manage their IT environment by monitoring the application control parameters within the Oracle E-Business Suite. IT managers and IT auditors can now track changes to application controls in several applications within the suite.
This type of monitoring supports a number of high level control objectives within the COBIT framework such as maintaining application software, managing changes, ensuring systems security, and managing configuration. IT auditors and managers can use this functionality to support COBIT by monitoring and enforcing set parameters within the Oracle E-Business Suite.
Oracle Learning Management
In addition to the deployment of enterprise wide policies and procedures, the success of any compliance program also depends on the employee knowledge of those policies and procedures. Legal mandates require that firms actively manage ethics and compliance programs and communicate appropriate standards throughout the organization. Oracle Learning Management is a powerful tool to institutionalize policies and procedures through online education and training. It can also be used to confirm employee knowledge of the company's various business and ethics programs.
Oracle Learning Management is an enterprise learning management system that enables you to manage, deliver, and track training in a consistent fashion across the firm and on a worldwide basis. Learners interact with content, instructors, and peers at their own pace. Managers can automate key business flows - from courseware order processing to training delivery and from performance appraisals to training assessments.
Oracle Tutor
Documented end user procedures are a proven way to communicate job performance expectations to employees. While documented procedures alone cannot enforce corporate governance, they can help tremendously – especially when such procedures are standardized across the enterprise and supported by cohesive business applications. Increasing visibility and control over all your business practices through documentation is critical for ongoing Sarbanes-Oxley attestation audits.
Oracle Tutor enables companies to create, distribute, and maintain their business procedures and corporate governance documentation. The application features a native Microsoft Word based format, web enabled remote access, and company wide deployment.
Oracle Collaboration Suite
Several regulations require companies to retain and manage their electronic content with a particular emphasis on electronic communications. While each of these regulations has its own individual characteristics and requirements for evidence discovery, a set of common requirements can be identified:
-
Rapid, reliable access to all content (for example, electronic documents, e-mail, instant messages, physical documents)
-
Retention and disposition management
-
Secure access control
-
Content analysis and classification
Few companies have formal records retention policies in place, despite the fact that intelligent discovery, retrieval, and search capabilities are very important to compliance. Many firms also lack e-mail archiving policies and programs. Lack of formal, enterprise-wide processes and solutions for records and document management is not only risky, but ultimately drives up the cost of compliance for companies that rely on manual processes and point solutions.
Oracle Collaboration Suite offers a unique architecture for effectively retaining, auditing, archiving, and supervising electronic communications. Built on Oracle's unified data model, Oracle Content Services (within the Collaboration Suite) can effectively archive both structured and unstructured content including electronic documents, e-mails, and web content. All your firm's communications therefore reside in a single system, allowing management to implement record retention policies consistently across the organization as well as find documents easily and cost effectively.
Corporate Governance & GAAP
A large part of the corporate governance task is ensuring that external reporting and statutory reporting meet the standards imposed by your Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and your subsidiaries' statutory regulators.
Requirements for Multiple Representations
Transactions are regulated by a surprising amount of regulation and legislation. They have their base in public company regulation, company registration legislation, corporation tax rules, value added tax and sales tax rules, overt legislation, and similar jurisdictions.
Localizations Support
In addition to using ledgers and subledger accounting, Oracle supports national regulations in multiple ways.
Many national compliance issues are now built into the product itself and you do not need any further tools to support it. Newer legislation which is not yet absorbed into the core product may be available through country specific patches. Finally, when a requirement is brand new and still under analysis, you may implement a customized solution through a consulting engagement.