| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Trusted Extensions Label Administration Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Trusted Extensions Label Administration Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library |
1. Labels in Trusted Extensions (Overview)
2. Planning Labels in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
Planning Labels in Trusted Extensions (Task Map)
How to Plan the Encodings File
Encodings Files From Trusted Extensions
Differences Between Simplified GFI Label Encodings Files
Simplified GFI Multilevel Label Encodings File
3. Creating a Label Encodings File (Tasks)
4. Labeling Printer Output (Tasks)
5. Customizing the LOCAL DEFINITIONS Section (Tasks)
6. Planning an Organization's Encodings File (Example)
The label_encodings file is a flat text file. On a system that is configured with Trusted Extensions, the label of the file is ADMIN_HIGH to prevent regular users from reading it. The maximum line length in the label_encodings file is 256 bytes. The file can be edited with any text editor. The security administrator is responsible for the creation and distribution of the label_encodings file.
Note - The label_encodings file can be created or edited on any system. However, the file must be checked and tested on a host that is configured with Trusted Extensions.
Some organizations have a government-furnished label_encodings file that is based on Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) specifications. Other organizations might want to derive their encodings file from one of the files that are provided by Trusted Extensions.
Oracle provides the following sample label_encodings files in the /etc/security/tsol directory. These samples can be modified to meet your site requirements.
Is installed by Trusted Extensions software as the default. This file uses commercial labels, such as Confidential: Need to Know.
Is similar to the example in Appendix A, Encodings File for SecCompany (Example).
The introduction to the appendix describes the label components in the file. Chapter 6, Planning an Organization's Encodings File (Example) describes each step for creating this file.
Is the U.S. government single-level file.
Is Oracle's version of the U.S. government single-level file. The color assignments are different.
Is the U.S. government multilevel file.
Is Oracle's version of the U.S. government multilevel file. The combinations are less restricted, the minimum clearance is higher, the default user label is lower, and the colors are different.
Alternatively, you can build a label_encodings file from scratch. The syntax and structure of the label_encodings file is provided in Encodings File Syntax.
By default, the /etc/security/tsol/label_encodings is installed with the following contents:
ACCREDITATION RANGE: classification= PUB; all compartment combinations valid; classification= SBX; all compartment combinations valid; classification= CNF; all compartment combinations valid except: CNF minimum clearance= PUB; minimum sensitivity label= PUB; minimum protect as classification= PUB;
The ACCREDITATION RANGE definition restricts the user to the following label:
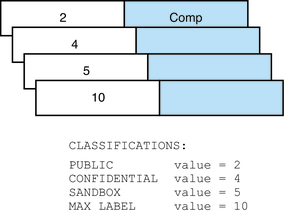
PUBLIC is defined as the lowest classification.
CONFIDENTIAL is defined as a higher classification.
SANDBOX is defined as the highest classification.
PUBLIC is defined as the minimum clearance.
PUBLIC is defined as the minimum sensitivity label.
PUBLIC is defined as the minimum “Protect As” classification.
The Classifications section of the default file is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 2-2 Classifications in the Default label_encodings File
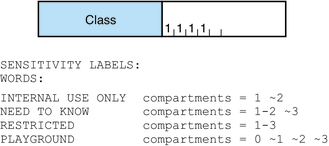
The Compartments section of the file is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 2-3 Compartments in the Default label_encodings File
Oracle provides two government-furnished files, label_encodings.gfi.single and label_encodings.gfi.multi. The label_encodings.gfi.single file is a single-level file, and the label_encodings.gfi.multi file is a multilevel version of the single-level file. The files also differ in the settings in the ACCREDITATION RANGE section. The ACCREDITATION RANGE section describes which classifications and compartments are available to regular users.
Oracle also provides two simplified versions of these files, label_encodings.single and label_encodings.multi. The differences are described in the following sections.
The ACCREDITATION RANGE settings in the label_encodings.multi follow:
ACCREDITATION RANGE: classification= u; all compartment combinations valid; classification= c; all compartment combinations valid; classification= s; all compartment combinations valid; classification= ts; all compartment combinations valid; minimum clearance= c; minimum sensitivity label= u; minimum protect as classification= u;
The ACCREDITATION RANGE definition enables the site to use all the classifications and compartments that are defined in the label_encodings.multi file, as follows:
UNCLASSIFIED, CLASSIFIED, SECRET, and TOP SECRET are defined with all compartment combinations valid.
CLASSIFIED is defined as the minimum clearance.
UNCLASSIFIED is defined as the minimum sensitivity label.
UNCLASSIFIED is defined as the minimum protect as classification.
The ACCREDITATION RANGE settings in the label_encodings.single file follow:
ACCREDITATION RANGE: classification= s; only valid compartment combinations: s a b rel cntry1 minimum clearance= s Able Baker NATIONALITY: CNTRY1; minimum sensitivity label= s A B REL CNTRY1; minimum protect as classification= s;
The ACCREDITATION RANGE definition restricts the user to the following label:
SECRET is defined as the only classification
SECRET A B REL CNTRY1 is defined as the only valid compartment combination
SECRET ABLE BAKER NATIONALITY: CNTRY1 is defined as the minimum clearance
SECRET A B REL CNTRY1 is defined as the minimum sensitivity label
SECRET is defined as the minimum “Protect As” classification
Oracle's implementation of the label_encodings file supports a LOCAL DEFINITIONS section. This section is optional and can be appended to an existing label_encodings file. The word LOCAL in the keyword that starts the section means local to Oracle's implementation.
Options in the LOCAL DEFINITIONS section set label translation options and associate colors with labels. The title bars of application windows display each label against a background of the color that is specified for that label. If an invalid color or no color is specified in the COLOR NAMES option, a default color is supplied. Chapter 5, Customizing the LOCAL DEFINITIONS Section (Tasks) describes how to modify the Oracle extensions for your site.