1 Offline Mediation Controller System Administration Overview
This chapter provides an overview of Oracle Communications Offline Mediation Controller and basic administration tasks.
About Offline Mediation Controller
Offline Mediation Controller is a mediation application designed for multi-service, IP, VoIP, and 3G wireless networks. It delivers pre-integrated mediation solutions that provide all network-to-OSS data collection, aggregation, and correlation required for billing, service-level agreement (SLA) management, and performance management.
In addition, Offline Mediation Controller:
-
Enables rapid implementation with decreased cost and risk through pre-integrated solutions
-
Delivers a convergent mediation solution for multi-vendor, multi-service networks
-
Supports the differentiation of service offerings to attract and retain customers
-
Drives information consistency across applications, ensuring that customer invoices match performance and SLA reports
-
Offers scalability and reliability to prevent revenue losses caused by missing data
-
Offers a Cartridge Development Kit (CDK) that enables the development of nodes to support new network elements (NEs), billing systems, and other operational support systems (OSS).
-
Supports secure communication between the mediation components and role based user management.
About the Offline Mediation Controller Architecture
Offline Mediation Controller provides a flexible and scalable architecture for the collection, aggregation, enhancement, and distribution of network data. It can accommodate multiple collection requirements and distribute the data to billing systems.
Offline Mediation Controller consists of several components that work together to process network data. Table 1-1 describes each component.
Table 1-1 Offline Mediation Controller Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
Functional nodes |
Software modules that collect and perform specific tasks on network data. The basic node types are: collection cartridge (CC), enhancement processor (EP), aggregation processor (AP), and distribution cartridge (DC). You connect a series of nodes to form a node chain. |
|
Node chains |
Series of functional nodes in which the output from each node (except the DC) becomes the input for another node. |
|
Mediation hosts |
Servers on which the functional nodes run. |
|
Node manager |
Background process that manages the nodes on the mediation host. |
|
Local data manager |
Background process that moves data between processing nodes on the same mediation host. |
|
Remote data manager |
Background process that moves data from a functional node on one mediation host to a functional node on another mediation host. |
|
Administration client |
GUI that administers the Offline Mediation Controller system. |
|
Administration server |
Background process that communicates between Administration Client and the functional nodes. |
|
Oracle Unified Directory server |
Stores user account data that Offline Mediation Controller uses to authenticate user login attempts. |
|
SNMP trap host |
IP host designated to receive SNMP trap messages from Offline Mediation Controller. |
Figure 1-1 shows the relationship of the Offline Mediation Controller components.
Figure 1-1 Offline Mediation Controller System
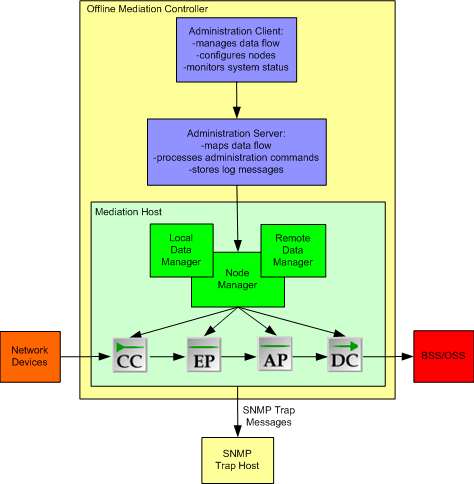
Description of ''Figure 1-1 Offline Mediation Controller System''
About the Standard Offline Mediation Controller Features
Offline Mediation Controller offers the following standard features:
-
Distributed data components: Allows components to be distributed in the network, providing greater flexibility and scalability.
-
Multiple data sources: Allows data collection from multiple data sources of different types, located on different NEs.
-
Node-based design: Allows simple and direct monitoring of the Offline Mediation Controller processes. The nodes are chained together so the output from one node becomes the input to another node.
-
Flexible distribution formats: Distributes data in a wide variety of user-selected data types.
-
Network Accounting Record (NAR) distribution and routing modes: You can achieve greater flexibility, selectivity, and load balancing by using one or more of the following distribution modes: multicast, directed, round-robin, and modulus.
-
Ability to run multiple Administration Servers: Allows redundant control of Offline Mediation Controller systems and prevents an Administration Server from being the single point of failure in such systems. If you use more than one Administration Server, they must run on separate mediation servers.
-
Ability to run multiple Node Managers on the same mediation server: Allows you to manage a mediation server from different administration domains.
-
System utilization notification: You can configure Node Manager to supervise disk and CPU usage and send warnings to Administration Client when disk utilization reaches specified thresholds.
-
File-based EP: Finds a key attribute (or a set of key attributes) in an incoming NAR and matches this value against an entry in a simple lookup table. The EP can then retrieve any information contained in the entry and add it to the incoming NAR.
-
LDAP EP: Accesses information from an LDAP directory and use the retrieved information to modify incoming NARs.
-
Security protected GUI access: Access to Administration Client has two security levels based on user roles: administrator and general user. The administrator has total access on the Offline Mediation Controller system and can create general users. General users have restricted access to the Offline Mediation Controller system. See "About Users in Offline Mediation Controller" for more information.
-
FTP push/pull capabilities: If an NE does not have the capability to send data to the Offline Mediation Controller system, many CCs are able to pull data directly from the NE. Also, if a billing system does not have the capability to fetch the output data from the Offline Mediation Controller system, many DCs are able to push their output files to the billing system.
-
Infrastructure for sharing configuration information: A centralized shared data dictionary (a persistent storage mechanism) that contains attributes from applicable service solutions that can appear in the system, along with additional information about those attributes. The data dictionary is used as a reference tool when modifying node behavior using NPL.
Note:
The data dictionary is not used for the Wireless service solution. -
Drag-and-drop GUI: Administration Client provides a graphical display of all the nodes in the system and shows connectivity between the nodes. Administration Client also provides a window of available node types that can be used to create new nodes for various service solutions.
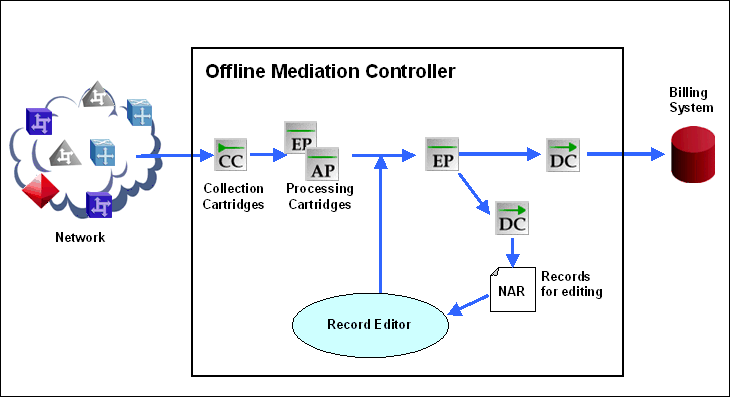
About the Record Editor
The Offline Mediation Controller Record Editor allows you to edit NARs and submit them to the node chain to be processed and distributed to downstream applications.
Figure 1-2 displays the role of the Record Editor.
Records in Offline Mediation Controller are stored and processed in a NAR format. When processing is complete, NARs are converted to an external format and distributed to one or more downstream OSS applications, such as a Billing Centre.
Overview of Offline Mediation Controller Administration Tasks
The Offline Mediation Controller system administrator is responsible for the day-to-day tasks of maintaining and managing Offline Mediation Controller, its users, its components, and its database.
The system administrator performs the following tasks:
-
Configuring the Offline Mediation Controller system. See "Configuring Offline Mediation Controller".
-
Managing Offline Mediation Controller security. See "Managing Offline Mediation Controller Security".
-
Backing up and restoring data. See "Backing Up and Restoring Offline Mediation Controller".