Updates and upgrades to Oracle VM Servers can be automatically performed using a Yum repository. To access patch updates for Oracle VM, you should contact Oracle to purchase an Oracle VM Support contract and gain access to the Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN) which contains updates for Oracle VM. If you have access to ULN you can use this to set up your own Yum repository to use when updating your Oracle VM Servers. Setting up a Yum repository is beyond the scope of this documentation, however you can read about setting one up in an OTN article "Yum Repository Setup" at:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/linux/yum-repository-setup-085606.html
Make sure you subscribe to the Oracle VM Release 3.0.3 channel on ULN when you set up your Yum repository.
If you have a Yum repository configured for Oracle VM Server updates, you add this to Oracle VM Manager and perform the updates from within the Oracle VM Manager user interface.
To add a Yum repository:
Select Server Update Management (YUM) from the Tools menu. The Server Update Management (YUM) dialog box is displayed.
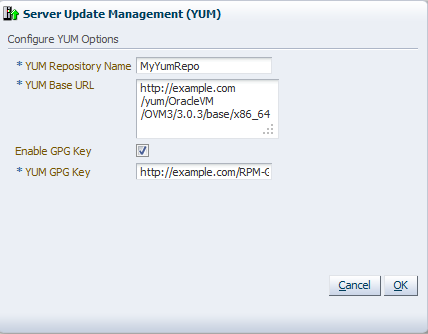
Enter the following information about the Yum repository:
YUM Repository Name: A name for the Yum repository.
YUM Base URL: The URL to access the Yum repository, for example:
http://example.com/yum/OracleVM/OVM3/3.0.3/base/x86_64
NoteThe YUM Base URL should contain the RPMs and the repodata directory created by the createrepo tool. If you are copying the RPMs from the Oracle VM Server ISO media, or loop mounting the ISO file, make sure to include the
Serverdirectory (which includes therepodatadirectory), for example:http://example.com/OVM3/Server/
Enable GPG Key: Whether to use a GPG key for the Yum repository. The GPG key (or GnuPG key) is the key used in the GNU project's implementation of the OpenPGP key management standard. The GPG key is used to check the validity of the Yum repository, and any packages (RPMs) downloaded from the repository.
YUM GPG Key: The GPG key for the Yum repository, for example:
http://example.com/RPM-GPG-KEY-OVM-3.0
The GPG key must be available via one of HTTP, FTP, FILE or HTTPS protocols.
The GPG key for Oracle-signed updates from ULN is pre-installed on Oracle VM Server at /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle. If you want to use this GPG key, enter:
file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle
This field is only enabled when you select Enable GPG Key.
Click OK.
The YUM repository is added and ready to use.
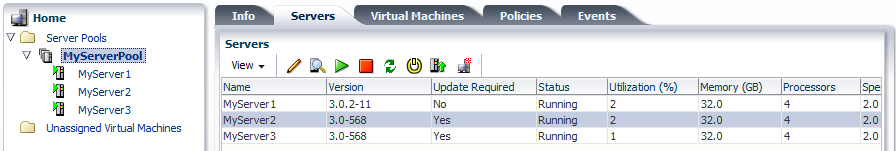
When an Oracle VM Server update is available, an event is posted to the Oracle VM Server and displayed in the Update Required column in the Servers tab. The YUM repository is checked for updates every 6 hours, so there may be a delay between the YUM repository being updated and the notification being displayed in Oracle VM Manager.
To update an Oracle VM Server, the virtual machines on the Oracle VM Server must first be migrated to another Oracle VM Server. You can manually migrate the virtual machines if you prefer, or have the upgrade job perform the virtual machine migration automatically. If the Oracle VM Server is a master Oracle VM Server, the master role is transferred to another Oracle VM Server in the server pool.
To update an Oracle VM Server:
Select the Oracle VM Server in the navigation pane and select Upgrade Server from the Actions menu. Confirm that you want to perform the upgrade. The Oracle VM Server is placed into maintenance mode, and the update performed. Any virtual machines on the Oracle VM Server are automatically migrated to another Oracle VM Server when it is put into maintenance mode. When the update is complete the Oracle VM Server is restarted and remains in maintenance mode.
To have the Oracle VM Server rejoin the server pool as a fully functioning member, edit the Oracle VM Server and take it out of maintenance mode.
For information on manually migrating virtual machines, see Section 7.9.2, “Migrating a Virtual Machine”. For information on taking an Oracle VM Server out of maintenance mode, see Section 6.9.9, “Placing an Oracle VM Server into Maintenance Mode”.