1 Introduction to Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager (OAAM) is a key component of Oracle Access Management Suite Plus, delivering risk-aware, context-driven access management across the industry's most complete set of access management services.
This chapter provides a high-level overview of Oracle Adaptive Access Manager 11g with links to more information. This chapter contains the following sections:
1.1 Introduction to Oracle Adaptive Access Manager
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides an innovative, comprehensive feature set to help organizations prevent fraud and misuse. Strengthening standard authentication mechanisms, innovative risk-based challenge methods, intuitive policy administration and integration across the Identity and Access Management Suite and with third party products makes Oracle Adaptive Access Manager uniquely flexible and effective. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides real-time and batch risk analytics to combat fraud and misuse across multiple channels of access. Real-time evaluation of multiple data types helps stop fraud as it occurs. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager makes exposing sensitive data, transactions and business processes to consumers, remote employees or partners via your intranet and extranet safer.
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides an extensive set of capabilities including device fingerprinting, real-time behavioral profiling and risk analytics that can be harnessed across both Web and mobile channels. It also provides risk-based authentication methods including Knowledge Based Authentication (KBA) challenge infrastructure with Answer Logic and OTP Anywhere server-generated one-time passwords, delivered out of band via SMS, email or IM channels. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager also provides out-of-the-box integration with Oracle Identity Management, the industry leading identity management and Web Single Sign-On products, which are integrated with leading enterprise applications.
Functionality can be divided into two major areas as summarized in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1 Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Functionality
| Functionality | Description |
|---|---|
|
Real-time or offline risk analysis |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides functionality to calculate the risk of an access request, an event or a transaction, and determine proper outcomes to prevent fraud and misuse. A portion of the risk evaluation is devoted to verifying a user's identity and determining if the activity is suspicious. Functionality that support risk analysis are:
|
|
End-user facing functionality to prevent fraud |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager protects end users from phishing, pharming, and malware. The virtual authentication devices secure credential data at the entry point; this ensures maximum protection because the credential never resides on a user's computer or anywhere on the Internet where it can be vulnerable to theft. As well, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides interdiction methods including risk-based authentication, blocking and configurable actions to interdict in other systems. Functionality that supports end-user facing security are:
|
With Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, corporations can protect themselves and their online users against potent fraudulent attacks, such as Phishing, Malware, Transaction and Insider Fraud, in a cost-effective manner. Table 1-2 summarizes fraud attack threats and Oracle Adaptive Access Manager defense mechanisms.
Table 1-2 Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Defense Mechanisms
| Threat | Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Offense |
|---|---|
|
Phishing |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager offenses for phishing are:
|
|
Malware |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager offenses for malware are:
|
|
Transaction fraud |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager offenses for transaction fraud are:
|
|
Insider fraud |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager offenses for insider fraud are:
|
1.2 Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Features
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can provide the high levels of security with context-sensitive online authentication and authorization. Thus, situations are evaluated and proactively acted upon based on various types of data.
This section outlines key components/features used for authentication and fraud monitoring and detection.
1.2.1 Autolearning
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager employs a unique mixture of real-time and predictive auto-learning technology to profile behavior and detect anomalies. Because of this, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can recognize high risk activity and proactively take actions to prevent fraud and misuse. Also, as Oracle Adaptive Access Manager is evaluating and learning behaviors in real-time it constantly learns what is typical for each individual user and for users as a whole. In addition to the autolearning, the continuous feedback from experienced fraud and compliance investigators "teach" the OAAM engine what constitutes fraud and misuse. In this way, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager fully harnesses both the human talent in your organization and multiple forms of machine learning to prevent fraud and misuse.
A simple example would be the behavioral profiling and evaluation of access times for a nurse. Nurses often work in a couple of hospitals; they may work different shifts on a rotating schedule, but they will most likely work one shift more than the others in any given month. In such a scenario, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager keeps track of when a nurse is at work accessing the medical records system. If during the same month a nurse has been working mostly night shifts to fill in, then, seeing an access request from her between 10:00 am and 12:00 pm would be an anomaly. This of course does not mean fraud or misuse is occurring, but the risk is elevated, so Oracle Adaptive Access Manager could challenge the nurse for additional identity verification. As the nurse accesses various applications and information during the day shift, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager learns in real-time that this is typical and is therefore low risk.
One of the main goals of automated anti-fraud solutions is to eliminate unnecessary manual processes and remove much of the inconsistency and costs that can occur when humans are directly involved in access evaluations. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager automates not only risk evaluations but also keeps track of changing behaviors so humans do not have to. Based on this dynamic risk evaluation, proactive action can be taken to prevent fraud with various forms of interdiction including blocking and challenge mechanisms. In this way, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager prevents fraud with little or no need for human interaction. However, in instances when human investigators are needed to follow up directly with end users or make final decisions based on additional contextual information, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager seamlessly captures their insights to improve the accuracy of future risk evaluations.
1.2.2 Configurable Risk Engine
The OAAM risk engine utilizes a flexible architecture based on highly configurable components. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager employs three methods of risk evaluation that work in harmony to evaluate risk in real-time. The combination of configurable rules, real-time behavioral profiling and predictive analysis make Oracle Adaptive Access Manager unique in the industry. Administrators can easily create, edit and delete security policies and related objects directly in the business user friendly administration console. Business users can understand and administer OAAM policies and view dashboards and reports in the graphical user interface with little or no dependence on IT resources. Security rules are created by combining any number of configurable rule conditions. Both access and transaction based rules are created from the library of conditions available with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager.
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager also profiles behavior and evaluates risk using a fully transparent and auditable rules based process. This allows high performance, flexibility and complete visibility into how and why specific actions were or were not taken during a session. If Oracle Adaptive Access Manager blocks access for an end user there is a complete audit trail that shows exactly what data was evaluated and the specific evaluations that occurred.
1.2.3 Virtual Authentication Devices
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides a number of rich features that strengthen existing Web application login flows. Regardless of the type of authentication in place, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can improve the level of security. Insider fraud, session hijacking, stolen credentials, and other threats cannot be eliminated by strong, credential based authentication alone. Adding a risk-based challenge layer behind existing authentication can increase the level of security with minimal impact to the user experience.
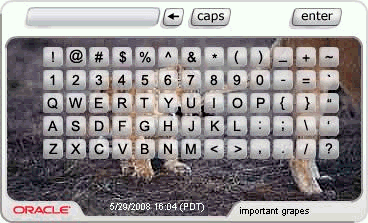
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager's suite of virtual authentication devices combats phishing personalized images and phrases known only to the server and the end user. Through the use of KeyPad and PinPad, security of the user credentials during entry can be assured by not capturing or transmitting the actual credential of the end user. This protects the credential from theft by malware and other similar threats. The virtual authentication devices are server driven; all features are provided without any client-side software or logic that can be compromised by key-loggers and other common malware. Additionally, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager performs device fingerprinting and behavioral profiling on every access to determine the likelihood that the authentication is being attempted by the valid user.
Descriptions of the various text pads in the virtual authentication suite follow.
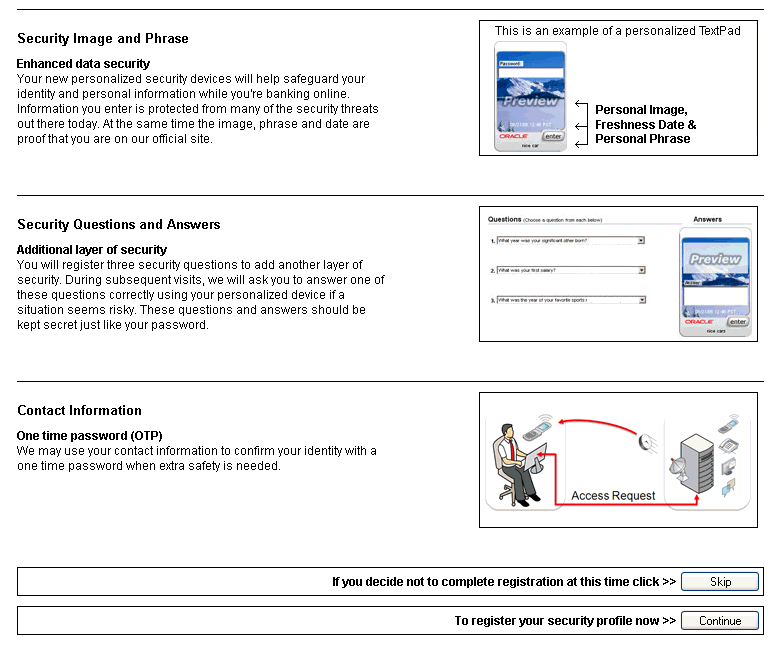
TextPad is a personalized device for entering a password or PIN using a regular keyboard. This method of data entry helps to defend against phishing primarily. TextPad is often deployed as the default for all users in a large deployment. Then, each user individually can upgrade to another device if he wants. The personal image and phrase a user registers and sees every time he logs in to the valid site serves as a shared secret between the user and server. If this shared secret is not presented or presented incorrectly, the users will notice.

PinPad is a lightweight authentication device for entering a numeric PIN.

QuestionPad is a personalized device for entering answers to challenge questions using a regular keyboard. The QuestionPad is capable of incorporating the challenge question into the Question image. Like other Adaptive Strong Authentication devices, QuestionPad also helps in solving the phishing problem.

KeyPad is a personalized graphics keyboard, which can be used to enter alphanumeric and special character that can be enter using a traditional keyboard. KeyPad is ideal for entering passwords and other sensitive data. For example, credit card numbers can be entered.
In Figure 1-1, the user is given the option to register his profile now or to skip registration for a later date.
1.2.4 Device Fingerprinting
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides both proprietary, clientless technologies and an extensible client integration framework for device fingerprinting. Device usage is tracked and profiled to detect elevated levels of risk. OAAM customers can secure both standard browser-based access and mobile browser-based access without additional client software or choose to integrate a custom developed client such as a JAVA applet. For securing access to mobile applications, customers and partners can easily integrate OAAM device fingerprinting capabilities via the Mobile and Social SDK and REST interface. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager generates a unique single-use cookie value mapped to a unique device ID for each user session. The device cookie value is refreshed on each subsequent fingerprinting process with another unique value. The fingerprinting process can be run multiple times during a user's session to allow detection of mid-session changes that could indicate session hijacking. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager monitors a comprehensive list of device attributes. The single-use cookie and multiple attribute evaluations performed by server-side logic and client extensions make OAAM device fingerprinting flexible, easy to deploy and secure.
1.2.5 Knowledge-Based Authentication
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides out-of-the-box secondary authentication in the form of knowledge-based authentication (KBA) questions. The KBA infrastructure handles registration, answers, and the challenge of questions. Since KBA is a secondary authentication method, it is presented after successful primary authentication.

KBA is used to authenticate an individual based on knowledge of personal information, substantiated by a real-time interactive question and answer process. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager's Rules Engine and organizational policies are responsible for determining if it is appropriate to use challenge questions to authenticate the customer.
1.2.6 Answer Logic
Answer Logic increases the usability of Knowledge Based Authentication (KBA) questions by accepting answers that are fundamentally correct but may contain a small typo, abbreviation or misspelling. For example, if abbreviation is enabled in Answer Logic a user is challenged with the question "What street did you live on in high school?" They may answer "1st St." which is fundamentally correct even though when they registered the answer six months ago they entered "First Street". By allowing a configurable variation in the form of correct answers, Answer Logic dramatically increases the usability of registered challenge questions making the balance between security and usability firmly in the control of the enterprise.
1.2.7 OTP Anywhere
OTP Anywhere is a risk-based challenge mechanism consisting of a server generated one time use password delivered to an end user via a configured out of band channel. Supported OTP delivery channels include short message service (SMS), email, and instant messaging. OTP Anywhere can be used to compliment Knowledge Based Authentication (KBA) challenge or instead of KBA. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides an innovative challenge processor framework. This framework can be used to implement custom risk-based challenge solutions combining third party authentication products or services with OAAM real-time risk evaluations. Both KBA and OTP Anywhere actually utilize this same challenge processor framework internally. OTP Anywhere via SMS uses a person's cell phone as a form of second factor, the identity assurance level is elevated without the need for provisioning hardware or software to end users.
1.2.8 Mobile Access Security
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides mobile security features both directly and via the Mobile and Social Access Services component of Oracle Access Management using the ASDK and RESTful web services. Users accessing OAAM protected web applications through a mobile browser will navigate the user interface and flows optimized for the mobile form factor without performing any development. Security policies available with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can dynamically adjust when user access originates from a mobile device.
This improves the range of analysis and accuracy of the risk evaluation, which reduces false positives. For example, IP geolocation velocity rules behave differently if the access request is via a cell connection than it does when using a Wi-Fi connection.
When customers utilize the Mobile and Social (MS) Access Services component of the Oracle Access Management Suite, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides enhanced device fingerprinting, device registration, mobile specific risk analysis, risk-based challenge mechanisms as well as lost and stolen device management. Mobile Access Services allow enterprises to extend their existing access security solution to cover both the web and mobile access channels.
1.2.9 Universal Risk Snapshot
Change control is important in an enterprise deployment, especially concerning mission critical security components. The Universal Risk Snapshot feature allows an administrator in a single operation to save a full copy of all OAAM policies, dependent components, and configurations for backup, disaster recovery and migration. Snapshots can be saved to the database for fast recovery or to a file for migration between environments and external backup. Restoring a snapshot is an automated process that includes visibility into exactly what the delta is and what actions will be taken to resolve conflicts.
1.2.10 Fraud Investigation Tools
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides a streamlined and powerful forensic interface for security analysts and compliance officers. Users can easily evaluate alerts and identify related access requests and transactions to uncover fraud and misuse.
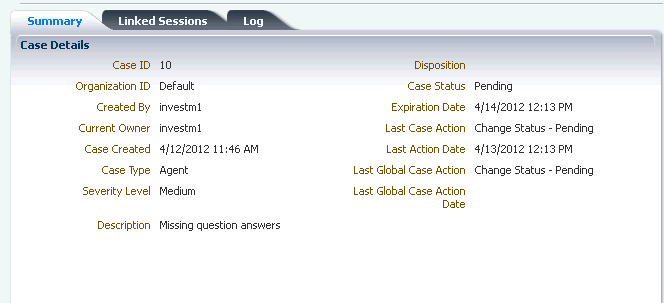
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides case management functionality tailored to forensic investigation. Agents are provided a repository for findings and investigation workflow management. Security analysts and compliance officers' record notes and link suspect sessions to a case as they perform an investigation so all findings are captured for use in legal proceedings and to influence future real-time risk analysis.
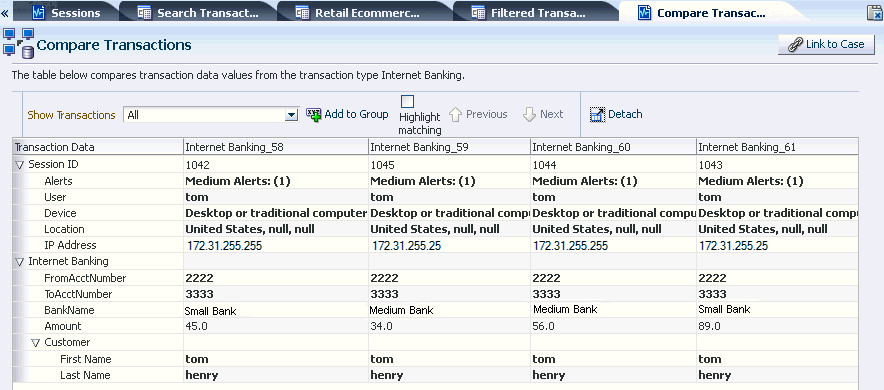
Search and Compare Transactions
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager provides an intuitive interface for security analysts and compliance officers to search and compare transactions that have been subjected to risk analysis. The full data and context of each transaction is available even for encrypted data fields. This allows security and compliance professionals deep visibility into user activity while still protecting the data from administrators or other types of enterprise users. The ability to compare multiple transactions side by side is extremely useful for expanding investigations from known high risk transactions to transactions that may not have initially appeared high risk on their own.
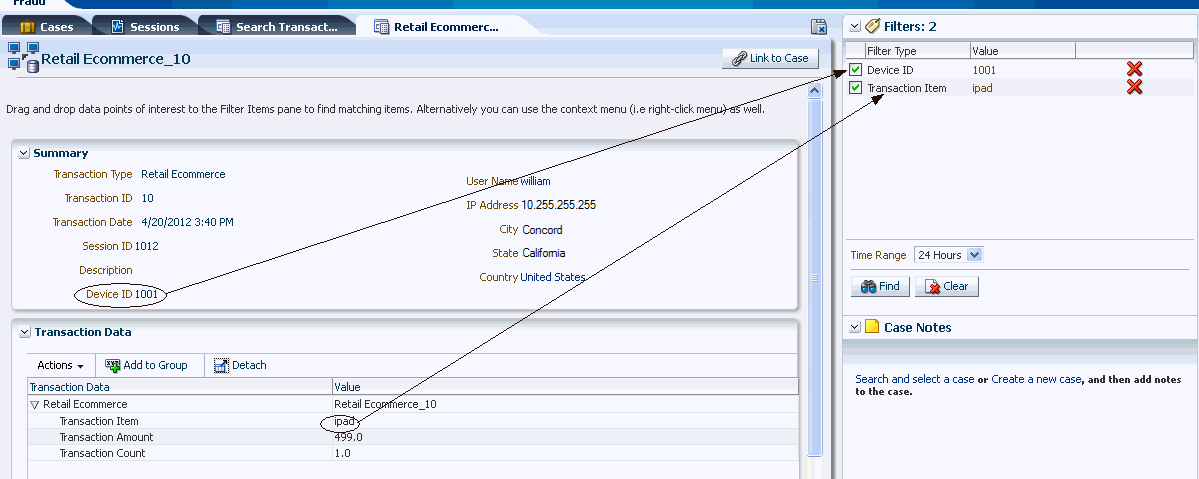
The investigation utility panel provides a persistent interface for common operations security analysts and compliance officers perform multiple times in the process of an investigation. Both quick search and case notes are always available regardless of what other functionality is being used. This ensures that findings from any process can be combined to search for suspect sessions and transactions. Also, the utility panel ensures that any thoughts or findings can be captured in case notes.
1.2.11 Policy Management
Policies and rules can be used by organizations to monitor and manage fraud or to evaluate business elements. The policy and rules are designed to handle patterns or practices, or specific activities that you may run across in the day-to-day operation of your business. Using Oracle Adaptive Access Manager, you can define when the collection of rules is to be executed, the criteria used to detect various scenarios, the group to evaluate, and the appropriate actions to take when the activity is detected.
1.2.12 Dashboard
The Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Dashboard is a unified display of integrated information from multiple components in a user interface that organizes and presents data in a way that is easy to read. The Oracle Adaptive Access Manager dashboard present monitor data versions of key metrics. Administrators can easily see up-to-the-minute data on application activity from a security perspective. The reports that are presented help users visualize and track general trends.
1.2.13 Reports
Reporting is available through Oracle Adaptive Access Manager. A limited license of Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher is included for customizable reporting capabilities.
Oracle Identity Management BI Publisher Reports uses Oracle BI Publisher to query and report on information in Oracle Identity Management product databases. With minimal setup, Oracle Identity Management BI Publisher Reports provides a common method to create, manage, and deliver Oracle Identity Management reports.
The report templates included in Oracle Identity Management BI Publisher Reports are standard Oracle BI Publisher templates—though you can customize each template to change its look and feel. If schema definitions for an Oracle Identity Management product are available, you can use that information to modify and generate your own custom reports.
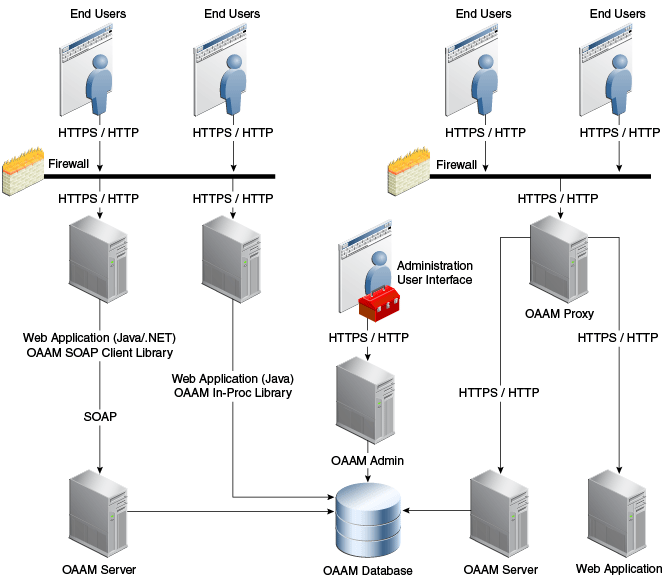
1.3 Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Component Architecture
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager is built on a J2EE-based, multi-tier deployment architecture that separates the platform's presentation, business logic, and data tiers. Because of this separation of tiers, Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can rapidly scale with the performance needs of the customer. The architecture can leverage the most flexible and supported cross-platform J2EE services available: a combination of Java, XML and object technologies. This architecture makes Oracle Adaptive Access Manager a scalable, fault-tolerant solution.
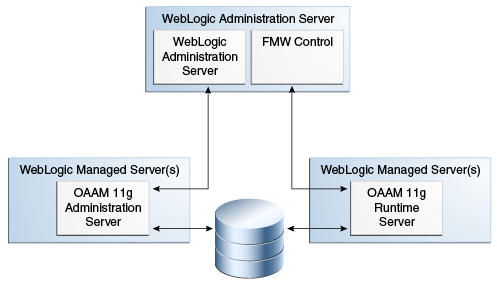
Figure 1-2 shows the single instance architecture for Oracle Adaptive Access Manager.
The runtime components including the rules engine and end user interface flows are contained in one managed server while the administration console functionality is separated out into its own managed server. The administration console contains the customer service and security analyst case management functionality which must always be available to employees in potentially large call centers with high call volumes.
Depending on the deployment method used the topology changes slightly. Native application integration deployments embed the runtime components so the administration console is the only additional managed server added to the deployment. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager is also completely stateless and fully supports clustered deployments to meet high performance requirements. As well, all high availability features of the Oracle database are supported for use with Oracle Adaptive Access Manager.
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager consists of the following two components:
-
OAAM_ADMIN: This component is used for administration and configuration of OAAM_SERVER application. This component is developed using the Oracle JAVA ADF Framework the Identity Management shell and deployed as Web applications in a J2EE container. It is packaged as an EAR file.
-
OAAM_SERVER: This component contains the OAAM Admin and OAAM Server sub-components within a single web application. The OAAM_SERVER component is packaged as an EAR file and is composed of servlets and JSPs in addition to Java classes. The subcomponents of OAAM_SERVER are described below by layer:
-
Presentation Layer: typically a Web application serving JSPs, servlets, and so on. The presentation layer provides the strong authenticator functionality; it uses the interfaces provided by the business layer (SOAP or Java native) to access its services.
-
Business Logic Layer: this layer contains the core application logic that implements the risk analyzing engine. This layer provides Java and SOAP interfaces for the presentation layer. When the Java interface is used, the business logic layer and presentation layer can be part of a single web application. With the SOAP interface, these layers are deployed as different applications.
-
Data Access Layer: contains data access components to connect to the supported relational databases. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager uses Oracle's TopLink, which provides a powerful and flexible framework for storing Java objects in a relational database.
-
Table 1-2 illustrates the distribution of Oracle Adaptive Access Manager components.
Note:
If batch processing is used, there is another Managed Server in addition to the ones shown in the illustration, which is the OAAM Offline server.1.4 Deployment Options
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager supports a number of deployment options to meet the specific needs of practically any deployment. The decision of which deployment type to employ is usually determined based on the use cases required and the applications being protected.
Table 1-3 describes the types of OAAM deployments.
Table 1-3 Oracle Adaptive Access Manager Deployment Options
| Deployment | Description |
|---|---|
|
Single Sign-On Integration |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager has an out of the box integration with Oracle Access Management Access Manager to provide advanced login security including the virtual devices, device fingerprinting, real-time risk analysis and risk-based challenge. New to 11g there are two versions of the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager and Access Manager integration, basic and advanced. The "basic" integration embeds Oracle Adaptive Access Manager into the Access Manager runtime server. It includes many of the login security use cases available from Oracle Adaptive Access Manager and reduces the footprint. To gain advanced features and extensibility customers can deploy using the "advanced" integration. Features such as OTP anywhere, challenge processor framework, shared library framework and secure self-service password management flows require the advanced integration option. Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can also be integrated with third party single sign-on products via systems integrators if required. |
|
Universal Installation Option Reverse Proxy |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can be deployed using an Apache module to intercept login requests and provide advanced login security. The flows available are the same as for the advanced single sign-on integration option. The main benefit of the Oracle Universal Installation Option (UIO) deployment is that it requires little or no integration with protected applications and SSO is not required. |
|
Native Application Integration |
Oracle Adaptive Access Manager can be natively integrated with an application to provide extreme high performance and highly customizable security. A native integration embeds OAAM in-process inside the protected applications. The application invokes the Oracle Adaptive Access Manager APIs directly to access risk and challenge flows. |
|
Web Services Application Integration |
Customers who have advanced requirements similar to native integration but who prefer to use SOAP web services instead of Java API integration directly can choose this option. |
|
Java Message Service Queue Integration |
Customers with access monitoring requirements involving multiple applications and data sources now have the ability to take a proactive security and compliance posture. Using the provided Java Message Service Queue (JMSQ) customers can implement near real-time risk analysis to actively identify suspected fraud or misuse. |
1.5 System Requirements and Certification
Refer to the system requirements and certification documentation for information about hardware and software requirements, platforms, databases, and other information. Both of these documents are available on Oracle Technology Network (OTN).
You can access OTN at
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork
The system requirements document covers information such as hardware and software requirements, minimum disk space and memory requirements, and required system libraries, packages, or patches:
The certification document covers supported installation types, platforms, operating systems, databases, JDKs, directory servers, and third-party products: