27 Introduction to Using Oracle Essbase and Associated Components in Oracle Business Intelligence
This chapter explains what you need to know about using Oracle Essbase and associated components when installed with Oracle Business Intelligence. The chapter includes a high-level roadmap; contains information about installation, system administration, service-level maintenance and security, and links to alternative sources of information.
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Section 27.4, "Installing Essbase and Associated Components with Oracle Business Intelligence"
-
Section 27.6, "Managing Essbase System Administration in Oracle Business Intelligence"
-
Section 27.7, "Working with Essbase Cubes in Oracle Business Intelligence"
-
Section 27.8, "Where Can I Learn More Information About Essbase?"
27.1 Overview
You can easily deploy Essbase and associated tools when installing Oracle Business Intelligence and benefit from using shared administration, user management, installation, and configuration support functionality that is also available to Oracle Business Intelligence users.
When you deploy Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence, you can access Essbase multidimensional databases that provide multidimensional analysis, enabling rapid development of custom analytic applications. Essbase enables you to develop and manage analytic applications that model complex scenarios, forecast business trends, and perform "what-if" analyses. Essbase supports fast query response times using pre-aggregated dimensions, for large numbers of users, for large data sets, and for complex business models. Essbase can be configured to use with a range of data sources.
Several tools and components are installed alongside Essbase when installed with Oracle Business Intelligence. These include Financial Reporting, Calculation Manager and Essbase Studio. These tools can be used to interact with Essbase installed through Oracle Business Intelligence.
This chapter includes information about installing, configuring, managing and securing Essbase and associated tools installed through Oracle Business Intelligence as well as creating, securing, and accessing Essbase databases using Oracle Business Intelligence.
This chapter does not describe using Essbase and associated tools when installed with the EPM System Installer. For information about using Essbase and associated tools when installed with the EPM System Installer, see the EPM System deployment documentation, located on the "Deployment and Installation" tab in the EPM System Documentation Library.
For information on which guide to refer to for information about Essbase and associated tools, when installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, see Section 27.3, "Performing Tasks on Essbase and Associated Tools in Oracle Business Intelligence Compared to Performing the Same Tasks in EPM and Information on Which Guides to Consult."
27.2 High-Level Roadmap for Working with Essbase and Associated Tools in Oracle Business Intelligence
Read this section before you start working with Essbase and associated tools in Oracle Business Intelligence. This high-level roadmap explains the tasks to perform and what choices are available. This section also indicates when to refer to the Oracle Business Intelligence documentation or the EPM System documentation.
To understand about working with Essbase and associated tools in Oracle Business Intelligence:
-
Read the rest of this chapter for an overview of Essbase concepts and configuration tasks.
-
Install Essbase as described in Section 27.4, "Installing Essbase and Associated Components with Oracle Business Intelligence."
Select the Essbase Suite option to install and configure Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence.
-
Perform essential security tasks as described in Section 27.5, "Configuring Security for Essbase and Associated Tools in Oracle Business Intelligence."
Essbase uses the Oracle Fusion Middleware security model, which Oracle Business Intelligence also uses. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
-
Perform essential system administration tasks as described in Section 27.6, "Managing Essbase System Administration in Oracle Business Intelligence."
Perform these tasks after installing Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence to ensure that Essbase is correctly configured.
-
Create, manage and use Essbase cubes as described in Section 27.7, "Working with Essbase Cubes in Oracle Business Intelligence."
27.3 Performing Tasks on Essbase and Associated Tools in Oracle Business Intelligence Compared to Performing the Same Tasks in EPM and Information on Which Guides to Consult
When you install Essbase and associated tools as components of Oracle Business Intelligence, you do not perform a full Enterprise Performance Management System installation. Therefore, instructions for completing certain tasks can be different to those documented in the EPM documentation. When Essbase and associated tools are installed as components of Oracle Business Intelligence, they are configured to work with the same Oracle Fusion Middleware components as Oracle Business Intelligence rather than the EPM infrastructure components. Specifically, Hyperion Shared Services (HSS) are not installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, so you can ignore any references to HSS in the EPM documentation.
Use Table 27-1 to help you decide what to use to perform certain tasks in Oracle Business Intelligence compared to EPM systems, and which guides to reference.
Table 27-1 How to Perform Essbase-Related Tasks in Oracle Business Intelligence or EPM Systems and Which Guides to Reference?
| Essbase-Related Tasks Performed in Oracle BI and EPM Systems | How to Perform Essbase-Related Tasks in an Oracle BI System and Which Guides to Reference | How to Perform Essbase-Related Tasks in an EPM System and Which Guides to Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Authentication |
When using Essbase and associated tools installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, use Fusion Middleware Control. Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
When using an EPM system, use HSS, MaxL, and EAS. Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Authorization |
When using Essbase and associated tools installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, use Fusion Middleware Control. Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
When using an EPM system, use HSS, MaxL, and EAS. Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Data Security (Provisioning) |
When using Essbase and associated tools installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, use Fusion Middleware Control and Security. Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. Note: Filters are provisioned from the Oracle Fusion Middleware Policy Store, but the actual filter definitions are still in the Essbase .SEC file. |
When using an EPM system, use HSS. Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Data Security (Filter Definitions) |
When using Essbase installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, use EAS and MaxL. Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. Note: The detail of data security filter definitions and defining filters can be found in the EPM guides where references to HSS can be ignored. |
When using an EPM system, use HSS and MaxL and EAS. Refer to EPM guides. |
|
System Configuration |
When using Essbase and associated tools installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, use Fusion Middleware Control, essbase.cfg (and opmn.xml). Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
When using an EPM system, use a text editor and MaxL, essbase.cfg (and opmn.xml). Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Backup and Recovery |
When using Essbase and associated tools installed with Oracle Business Intelligence use Fusion Middleware Control. Refer to Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide and Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Migration (Test to Production) |
When using Essbase installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, use Oracle Fusion Middleware and EAS. Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
When using an EPM system, use EAS web application. Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Essbase cubes |
When using Essbase and associated tools installed with Oracle Business Intelligence use EAS or Essbase Studio. Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Capacity |
N/A, Uses Active/Passive model (one cluster only). Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
Use N Clusters 1, 2, 3, 4 agents. Uses the Active/Active model. Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Availability |
Use Fusion Middleware Control. Uses - Active/Passive model. Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
Refer to EPM guides. Uses Active/Active model. |
|
Essbase Studio |
Refer to EPM guides when using Essbase Studio functionality. |
Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Financial Reporting |
Enables: - Print |
Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Calculation Manager |
Refer to EPM guides, but ignore the prerequisite to install HSS. |
Refer to EPM guides. |
|
Workspace |
Cannot register EPM Apps. Enables you to use: Refer to Oracle Business Intelligence guides. |
Refer to EPM guides. |
|
APIs |
There are some restrictions imposed on Essbase APIs meaning that certain functionality is not available. See this guide for more details: Oracle Platform Security Services APIs are available. |
Refer to EPM guides. |
27.4 Installing Essbase and Associated Components with Oracle Business Intelligence
You can install Essbase and associated components when you install Oracle Business Intelligence. When you install these components with Oracle Business Intelligence, Essbase databases become available to Oracle Business Intelligence users, and you can manage Essbase components using a combination of Oracle Business Intelligence tools and Essbase EPM System tools. For information about which version of Essbase is installed, go to the Certifications page in Oracle Support and check the product details for appropriate releases of Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition with Oracle Essbase at:
Note:
You cannot add Essbase to an existing Oracle Business Intelligence installation although you can still use Essbase as a data source. There is no upgrade path for adding Essbase to Oracle Business Intelligence Release 11.1.1.6 or earlier. The only way to install Essbase and associated components with Oracle Business Intelligence is to perform a new Oracle Business Intelligence installation and select the Essbase component.
This topic contains the following sections:
-
Section 27.4.3, "Selecting the Essbase Suite Option During Install"
-
Section 27.4.4, "Updating the Essbase Studio Catalog - Post Installation Task"
27.4.1 Installing Essbase and Associated Components in a New Installation of Oracle Business Intelligence
You install Essbase and associated components with Oracle Business Intelligence by selecting the Essbase Suite option in the Oracle Business Intelligence Installer. Following installation, Essbase components (Essbase Studio, Essbase Administration Services, Financial Reporting, Calculation Manager, and Workspace) are available, and Oracle BI EE security is deployed.
You must install Essbase and associated components in a new Oracle Business Intelligence installation and cannot add Essbase to an existing Oracle Business Intelligence installation. The Essbase server is installed as an Oracle Business Intelligence system component, on single or multiple hosts.
Figure 27-1 shows the Oracle Business Intelligence domain architecture after performing an Enterprise Install (with Essbase Suite), on multiple hosts.
Figure 27-1 Domain Architecture for an Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Install Including Essbase Components (on two Hosts)
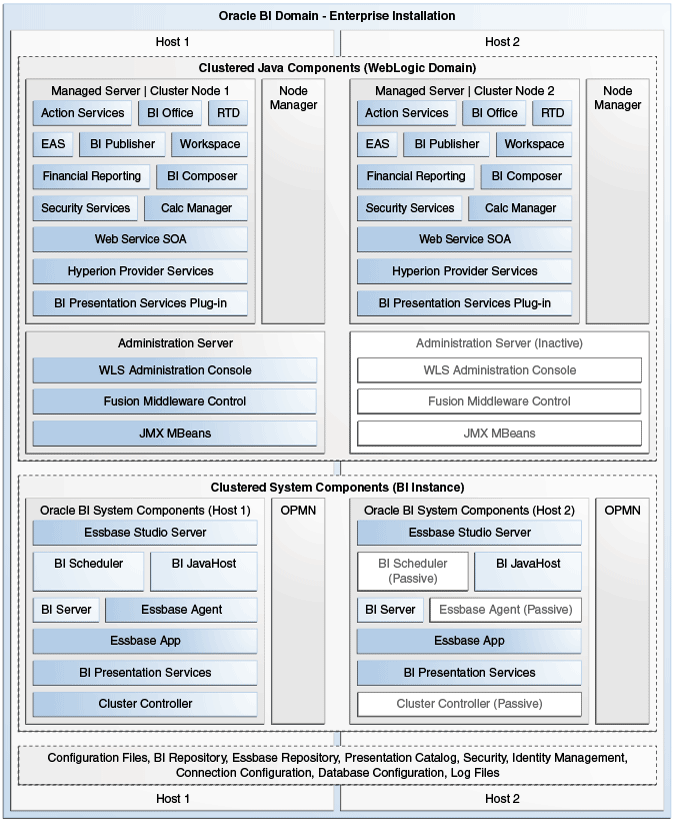
Key to Essbase-related components in Figure 27-1:
Essbase-related Java components are deployed as one or more Java EE applications and are described in the following list:
-
EAS (Essbase Administration Services) — This Essbase component is an administration tool for Essbase. Administration Services consists of a Java middle-tier server, called Essbase Administration Server, and a Java client console, called Administration Services Console.
-
Financial Reporting — This EPM component enables book-quality financial management and reporting targeted at meeting the unique requirements of the Finance department or any functional area that requires very highly formatted multidimensional reporting. Financial Reporting can use Hyperion Financial Management, Hyperion Planning and Essbase as data sources.
-
Calc Manager (Calculation Manager) — This EPM component provides the ability to develop and administer calculation rules for Planning and Essbase. You access Calculation Manager from within Workspace.
-
Hyperion Provider Services (APS) — This Essbase component is a dedicated data-source provider to Essbase for Java API, Smart View, and XMLA clients.
-
Workspace — When deployed with Oracle Business Intelligence, this EPM component provides a user interface for viewing and interacting with content created using Oracle Business Intelligence, Financial Reporting and Calculation Manager.
Essbase-related system components are deployed as one or more server processes and are described in the following list:
-
Essbase Studio Server — This Essbase component is the server process used by Essbase Studio.
Essbase Studio Console provides simplified cube construction by delivering a single environment for performing tasks related to data modeling, cube designing, and analytic application construction.
-
Essbase Agent — This Essbase component manages a collection of application Essbase servers. It stops and starts the application Essbase servers. It also provides a lookup point for access to Essbase applications.
-
Essbase App — This Essbase component represents an Essbase application, each of which contains one or more multi-dimensional databases.
The Oracle Business Intelligence components shown in Figure 27-1, are described in Section 1.3, "What Is the Oracle Business Intelligence System Logical Architecture?"
27.4.2 Selecting the Install Type
You can select to install Essbase Suite either as part of an Oracle Business Intelligence Simple Install type, as part of an Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Install type, or as part of an Oracle Business Intelligence Software Only Install type.
This topic contains the following sections:
For more information, see "Installation Types" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence.
27.4.2.1 Why Use the Oracle Business Intelligence Simple Install Type to Install Essbase and Associated Components?
The Oracle Business Intelligence Simple Install type creates and configures a WebLogic Server domain, and deploys Essbase JEE components to an Administration Server. Managed Servers are not created for this install type.
You use the Simple Install type, for example, to install Essbase and associated components with Oracle Business Intelligence on a laptop, so that you can demonstrate or test functionality.
If you select Essbase Suite during the installation process, then the Simple Install type deploys Essbase JEE components to the server and creates a single Essbase cluster called EssbaseCluster-1.
Users with the BIAdministrator role can create applications and cubes in this cluster. Sample Essbase applications and cubes are not created. You can use existing Essbase sample applications. For more information, see Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.html
Essbase Agent and Studio system components are created and configured to use ports within the Oracle Business Intelligence port range.
SSL is not enabled or configured by default.
27.4.2.2 Why Use the Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Install Type to Install Essbase and Associated Components?
The Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Install type separates applications and their administration.
The Enterprise Install type creates and configures a single WebLogic Server Domain that contains a cluster with two WebLogic Servers, an Administration Server, and a Managed Server. If you select Essbase Suite during the install, then Essbase JEE components and Oracle Business Intelligence JEE components are installed on Managed Servers. For information, see Section 27.4.3, "Selecting the Essbase Suite Option During Install."
You use the Enterprise Install type to scale out the domain to additional Managed Servers, increasing the availability of Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence to handle machine failures. You must use this install type if you subsequently want to scale out to another server. For more information, see Section 27.6.2, "Maintaining High Availability of Essbase Components in Oracle Business Intelligence." Note that the Enterprise Install type creates a single cluster that uses a single agent, such that only one agent is active at any one time, and the other agent is passive. You cannot change component selection before, during, or after scale out.
27.4.2.3 Why Use the Oracle Business Intelligence Software Only Install Type to Install Essbase and Associated Components?
The Software Only Install type installs software binary files in an existing Middleware home for later configuration.
There are no specific Essbase-related reasons why you use the Software Only Install type. However, you can use this install type, for example, to make WebLogic Server domain changes before deploying Oracle Business Intelligence into the domain. The Software Only install type is required for enterprise deployment configurations.
27.4.3 Selecting the Essbase Suite Option During Install
Selecting the Essbase Suite option during the install does the following:
-
Installs the following Essbase-related JEE applications and services into the local Oracle BI EE Managed Server in an Enterprise Install, and into the Administration Server in a Simple Install:
-
Workspace (EPM application with limited functionality)
-
Calculation Manager (EPM application also known as Allocations Manager)
-
Essbase Administration Services (Web application)
-
Hyperion Provider Services (APS)
-
-
Installs the following Essbase server processes:
-
Essbase Studio Server
-
Essbase Agent
-
Essbase App
-
-
Enables you to download the following Essbase-related client applications from the Download BI Desktop Tools option, which is available in the Get Started area of the Home page for Oracle BI EE:
-
Essbase Administration Services Console
-
Essbase Studio Console
-
Financial Reporting Studio (EPM application)
-
Smart View for Office (EPM application)
For more information, see "Downloading BI Desktop Tools" in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
-
-
Enables users to log in to the following Essbase command line tools:
-
ESSCMD
-
ESSMSH (MaxL)
-
Studio Server Command Line
-
-
Enables users to log in through the following supported Essbase API languages:
-
JAPI
-
VB API
-
C-API
Note:
Client applications and API languages that are not included in this section are not supported with Essbase and related components installed with Oracle Business Intelligence.
-
27.4.4 Updating the Essbase Studio Catalog - Post Installation Task
This task initializes essential environment variable updates that enable Essbase Studio catalog to be used for the latest release.
After you have installed Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence, you must create and run a script, and then use the Essbase Studio command line tool to update the Essbase Studio catalog to use in the latest release.
To update the Essbase Studio catalog:
-
Ensure that Essbase Server is running.
In Fusion Middleware Control, the Essbase Server process is displayed as essbaseserver1 when you expand Essbase Agents in the Processes page of the Availability tab.
For more information, see Section 27.6.1, "Starting and Stopping Essbase Components."
-
Create a script called startCommandLineClient.bat (or .sh), for starting the Essbase Studio command line client, as follows:
-
Copy the file startCommandLineClient.bat template (or .sh), from the following location:
ORACLE_HOME/products/Essbase/EssbaseStudio/Server/scripts.template/startCommandLineClient.bat (or .sh) and make the file executable.
-
Paste the file startCommandLineClient.bat (or .sh) into the following location:
ORACLE_INSTANCE/EssbaseStudio/essbasestudio1/bin
-
Open the file startCommandLineClient.bat (or .sh) in a text editor, and replace the two lines involving setEnv.sh and the setJavaRuntime.sh with variables ORACLE_HOME and JAVA_HOME as shown in the following example extract from the file:
#!/bin/sh # Set environment variables ${JAVA_HOME} and ${ORACLE_HOME} ORACLE_HOME=mw_home/OracleBI1 JAVA_HOME=mw_home/OracleBI1/jdk "${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java" -Xmx128m $JAVA_OPTIONS -jar "${ORACLE_HOME}/products/Essbase/EssbaseStudio/Server/client.jar" if [ $? != 0 ]; then echo "" echo "Press Enter to finish the client session" read fi -
Save the file.
-
Change the permissions on ${ORACLE_HOME}/products/Essbase/EssbaseStudio/Server/client.jar to ensure read access is possible.
-
-
Run the script by entering the following command:
startCommandLineClient.bat (or .sh)A command window called the CPL Shell displays.
-
At the command prompt, enter a valid Essbase Studio host name, administrator user name, and password.
Note:
The administrator user must have Essbase Studio administrator privileges to use the 'reinit' command.
-
At the command prompt, enter the following command:
reinit -
Enter
exitto close the CPL Shell when the reinit command completes.The Essbase Studio catalog is now ready for use.
27.4.5 Limitations for Using Client Tools when Essbase Is Installed with Oracle Business Intelligence
There are limitations for using the following Essbase tools when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence:
-
Essbase Administration Services
This tool enables you to perform many of the tasks for Oracle Business Intelligence Essbase that are also possible with Oracle EPM System Essbase.
You must not attempt to perform any security administration using Essbase Administration Services. For more information about setting up security, see Section 27.5, "Configuring Security for Essbase and Associated Tools in Oracle Business Intelligence."
-
MaxL command line interface
The MaxL command line supports most of the tasks for Oracle Business Intelligence Essbase that are also possible with Oracle EPM System Essbase.
Note that you cannot use the MaxL command line to provision security.
27.4.6 Essbase Features Not Supported when Essbase Is Installed with Oracle Business Intelligence
When Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, you do not get a full Enterprise Performance Management installation, and the following Essbase features are not supported:
-
Permission grants are not supported at the database level. For example, if you have two multidimensional databases that are used by an application, then permission grants apply equally to the multidimensional databases in an application.
-
Multiple clusters are not supported.
-
The Active-Active failover process is not supported. You can have only one machine or cluster active at a time, and you cannot load balance across computers or clusters.
-
The audit report showing what users, groups and application roles can do in Essbase, when Essbase is installed as part of an Enterprise Performance Management System, is not available in this release. However, you can use Fusion Middleware Control to view the Essbase permissions assigned to application roles.
-
There might be other Enterprise Performance Management features that are not supported when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence. To avoid misunderstandings, do not use EPM System or Essbase documentation (when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence), unless directed to do so in this chapter.
27.5 Configuring Security for Essbase and Associated Tools in Oracle Business Intelligence
This section explains typical Essbase-related security configuration when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence. You might also refer to this section if you maintain Essbase security in an existing installation of Oracle Business Intelligence.
The Oracle Business Intelligence Installer configures Essbase components to use Oracle Fusion Middleware security for authentication and authorization. You can secure an Essbase environment to provide equivalent functionality to Essbase secured through Hyperion Shared Services. Exceptions to this are documented in the Oracle Business Intelligence Certification Matrix.
Essbase components installed using the Oracle Business Intelligence installer cannot use Native Essbase or Hyperion Shared Services (HSS) security. However, when you install Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence, the Common Security Service (CSS) token-based identity assertion continues to be available and enables Oracle Business Intelligence to connect to Essbase data sources (both Essbase installed with Oracle Business Intelligence and Essbase installed with EPM) with the credentials of the end user. For this mechanism to work with an Essbase data source external to the Oracle Business Intelligence installation, you must follow the documentation. Also note that if multiple Essbase data sources are being used by Oracle Business Intelligence and there is a requirement to use this mechanism, all Essbase data sources must use the same shared secret for producing CSS tokens. For more information, see Section 11.6, "Configuring Oracle Business Intelligence to Use Hyperion SSO Tokens when Communicating with Essbase, Hyperion Financial Management, and EPM Workspace."
The Oracle Business Intelligence installer pre-configures core users, groups, application roles, credentials, permissions, and privileges for Essbase. There is no automated migration of security artifacts from Essbase installed with the EPM System Installer to Essbase installed with Oracle Business Intelligence. You must configure the equivalent authentication and authorization mechanism for Essbase when it is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence.
This topic describes configuring security when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence and contains the following sections:
-
Section 27.5.1, "Prerequisites for Configuring Security on Essbase and Associated Tools"
-
Section 27.5.2, "Common Security Tasks for Essbase and Oracle Business Intelligence"
-
Section 27.5.3, "Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools"
-
Section 27.5.4, "Configuring Data-Level Security Using Essbase Filters"
-
Section 27.5.5, "Configuring Access to Essbase Calculations"
-
Section 27.5.6, "Changing Essbase Ports in Oracle Business Intelligence"
-
Section 27.5.8, "Resource Permissions Reference for Essbase and Associated Tools"
27.5.1 Prerequisites for Configuring Security on Essbase and Associated Tools
Before you configure Essbase-related security in Oracle Business Intelligence, you must:
-
Familiarize yourself with Essbase-related security in Oracle Business Intelligence by reading the whole of Section 27.5, "Configuring Security for Essbase and Associated Tools in Oracle Business Intelligence."
-
Learn about configuring Oracle Business Intelligence security.
For information, see "Detailed List of Steps for Setting Up Security In Oracle Business Intelligence" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
27.5.2 Common Security Tasks for Essbase and Oracle Business Intelligence
Table 27-2 describes common security tasks that you perform for Essbase and Oracle Business Intelligence.
Table 27-2 Common Security Tasks for Essbase and Oracle Business Intelligence
| Security Task | More Information |
|---|---|
|
Configure authentication and authorization |
Essbase and associated tools integrate with the Oracle Business Intelligence security service and Oracle Fusion Middleware security mechanisms in order to provide authentication and authorization. Note: Essbase (and associated clients) deployed with Oracle Business Intelligence cannot use initialization block authentication/authorization or any mechanism that requires this approach (for example, Oracle eBusiness Suite security). For more information, see "Introduction to Security in Oracle Business Intelligence" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition. |
|
Deploy Single Sign-On |
Single Sign-On (SSO) capability for Essbase web applications uses the same Oracle Fusion Middleware security mechanisms as Oracle Business Intelligence. For more information, see "Enabling SSO Authentication" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition. Note: If you do not want to deploy Oracle Business Intelligence in a SSO environment, then no additional configuration steps are required to deploy the default configuration. |
|
Manage permissions on Essbase-related tools and artifacts |
Permissions to use tools such as Financial Reporting Studio or Essbase Administration Services console are granted through the Oracle Fusion Middleware Policy Store. Permissions to administer or use artifacts such as Essbase databases or filters are also granted through the Oracle Fusion Middleware Policy Store. |
For complete information on managing the default Oracle Business Intelligence security, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
27.5.3 Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools
You enable users to perform specific actions in Essbase and associated tools (for example, read and write, use calculations, use filters, use specific filters) by granting resource permission definitions to application roles. Appropriate resource permissions must be defined first (for more information, see Section 27.5.4, "Configuring Data-Level Security Using Essbase Filters" and Section 27.5.5, "Configuring Access to Essbase Calculations"). Resource permissions contain definitions of Essbase actions that a user can perform in an Essbase application. Essbase actions are derived from Essbase resource types, which are linked to resource permissions.
Resources are hierarchical; therefore global, cluster, and application level resources are listed.
Note:
The Essbase actions described here are not the same as actions in Oracle Business Intelligence.
The installation process grants default Essbase resource permissions to existing application roles in Oracle Business Intelligence.
For more details about the default Essbase resource permissions configured by default when you install Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence, see Section 27.5.8, "Resource Permissions Reference for Essbase and Associated Tools."
Note:
The BIConsumer application role is granted to all users, and has oracle.essbase.server /EssbaseCluster-1 access and oracle.essbase.application /EssbaseCluster-1 user_filter.This gives all users access to Essbase by default.
Note:
Resource permissions are stored by default in a file-based shared policy store, but you can reassociate them to an OID LDAP shared policy store. For more information, see "Using Alternative Authentication Providers" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
Note:
Parent roles inherit permission grants through child group or role members. Permission grants are cumulative; for example, a user who has a grant of oracle.essbase (filter) through an application role but not granted through another role, is still considered to have the oracle.essbase (filter) role.
To grant resource permissions to users and application roles:
-
If you are granting resource permission definitions to Essbase filters or Essbase calculations, then the filters or calculations must already exist. If they do not exist, then follow one of these links:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control.
For information, see Section 2.2.2, "Logging into Fusion Middleware Control to Manage Oracle Business Intelligence."
-
Select Business Intelligence then coreapplication.
-
From the Business Intelligence Instance menu (or right-click coreapplication), select Security and Application Policies.
-
Select the obi Application Stripe.
-
Select a Principal Type and click Search to display a list of application roles.
Best practice is to assign permissions to application roles.
This search returns only principals that already have policies or permissions assigned. If you have a new application role that does not have any permissions yet, then you must click Create or Create Like.
Note:
Non-Essbase permissions might also be displayed for the selected principal.
-
Click Create to display the Create Application Grant page.
-
Click Add in the Grantee section, to add an application role.
-
Select Application Role from the Type list and click the search arrow.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Add in the Permissions section to display the Add Permission page.
-
Click Resource Types and select an appropriate resource type from the list.
For example, select oracle.essbase.application.
-
Click the search arrow button to confirm your selection.
Note:
There is no synchronization between the filters or applications created in EAS and the list returned in the policy store. Therefore, you must manually enter the Resource Name in the following steps the first time that you provision a particular resource (server, application, filter or calculation).
-
Click Continue to display the Add Permission page.
-
Enter appropriate information into the Resource Name and Resource Type fields.
For example, to configure access permissions to use any filters within the Demo application, enter the following information:
Resource Type - oracle.essbase.application
Resource Name - /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo
Permission Actions - use_filter
For more examples of what to enter in the Resource Type, Resource Name, and Permission Actions fields when you grant resource permissions to filters or calculations, see the following:
-
Section 27.5.4.2, "Configuring Resource Permission Definitions for Essbase Filters"
-
Section 27.5.5.2, "Configuring Resource Permission Definitions for Essbase Calculations"
Note:
You can also manually enter permission actions for the resource into the Permission Actions field. Essbase actions are hierarchical, such that actions higher in the list include the lower members. For example, selecting read grants read and restart permissions to the /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo Essbase application.
-
-
Click Select.
-
Click OK.
27.5.4 Configuring Data-Level Security Using Essbase Filters
Data-level security enables you to restrict the dimensional data that users see in Essbase multidimensional databases. You secure data-level access for Oracle Business Intelligence users by configuring resource permission definitions on Essbase filters and granting them to application roles. For more information, see Section 27.5.3, "Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools."
This topic contains the following sections:
-
Section 27.5.4.2, "Configuring Resource Permission Definitions for Essbase Filters"
-
Section 27.5.4.3, "Securing Data Access with Essbase Filters"
-
Section 27.5.4.4, "When Are Filter Access Permission Grant Changes Consumed?"
27.5.4.1 What Are Essbase Filters?
An Essbase filter is an Essbase resource that provides an access control mechanism for dimensional data. For example, a filter might restrict a user to view or update data only for a specific geographical region or a specific product.
Essbase filters are stored in the local file system in a .SEC file.
Table 27-3 describes filter access permissions for dimensional members.
Table 27-3 Essbase Filter Access Permissions for Dimensional Members
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
|
No Access or None |
No inherent access to data values unless access is granted globally |
|
Read |
Ability to read data values |
|
Write |
Ability to read and update data values |
|
Meta read |
Ability to read metadata (dimension and member names) |
You create Essbase filters using Essbase Administration Services (and the MaxL command line), which also enables you to:
-
View dimensions and their members.
-
List filter operations.
-
Validate filters at design time.
For more information, see Oracle Essbase Administration Services Online Help and Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.html
You can ignore any references to Hyperion Shared Services (HSS) in Enterprise Performance Management documentation.
27.5.4.2 Configuring Resource Permission Definitions for Essbase Filters
Resource permission definitions combine with Essbase filters in the policy store, and you grant them to an application role. This enables users associated with an application role to secure the data that is defined by one or more combinations of resource permission definitions for Essbase filters.
Before you can grant resource permission definitions for Essbase filters to an application role (see Section 27.5.3, "Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools"), the appropriate resource permission definitions must first exist in the policy store. Use the examples in this section to understand how to configure resource permission definitions so that users can use Essbase filters.
An application role requires at least two policy store permission grants to access to a specific filter. You must give an application role permission to use filters within a specific scope.
For detailed information about permissions, see Section 27.5.8, "Resource Permissions Reference for Essbase and Associated Tools."
Use the following examples to understand how to configure resource permission definitions for Essbase filters:
Example 1 - Configuring resource permissions to enable the use of filters within the Demo application:
This example configures resource permission definitions to enable the use of filters within the Demo application. In this example you must ensure that one of the following resource permission definitions exists in the policy store. For example:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_filter
where:
-
oracle.essbase.application, - is the resource type (in this case, an application)
-
/EssbaseCluster-1, - is the cluster name
-
use_filter - is the action permission (in this case it enables the use of filters)
In this example, the use_filter action permission configures the oracle.essbase.application resource type such that a user associated with this definition in the policy store can use filters in any application in EssbaseCluster-1 (including the Demo application).
OR
-
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo, use_filter
In this example, the use_filter action permission configures the oracle.essbase.application resource type such that a user associated with this definition in the policy store can use filters in the Demo application in the EssbaseCluster-1.
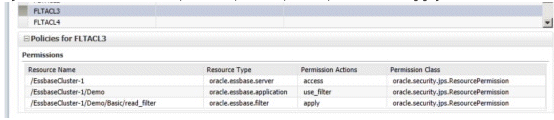
Example 2 - Configuring resource permissions for specific filters:
This example configures resource permission definitions that enable the use of a specific filter. You must specify additional resource permission definitions that name the filter in scope of the first grant.
For example, to restrict a user's dimensional access in a database called Basic to members defined by the filter called read_filter, the following resource permission definitions are required:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_filter
OR
-
oracle.essbase.application, ./EssbaseCluster-1/Demo, use_filter
AND
-
oracle.essbase.filter, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo/Basic/read_filter, apply
In this example, the read_filter action permission configures the oracle.essbase.application resource type such that a user that is associated with this definition in the policy store is restricted to read filters in the Basic database in the Demo application in the EssbaseCluster-1.
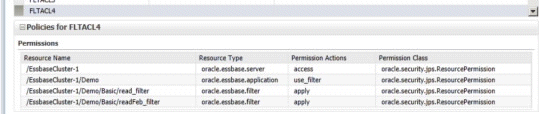
Example 3 - Configuring resource permissions for multiple filters:
This example activates multiple filters with multiple resource permission definitions to restrict a user's dimensional access in database Basic to members that are defined either by filters "read_filter" or "readFeb_filter." The following resource permission definitions are required:
Note:
. This differs from EPM installations where users and groups are limited to a single active filter.
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_filter
OR
-
oracle.essbase.application, ./EssbaseCluster-1/Demo, use_filter
AND
-
oracle.essbase.filter, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo/Basic/read_filter, apply
AND
-
oracle.essbase.filter, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo/Basic/readFeb_filter apply
Example 4 - Configuring resource permissions for filters to extend or restrict data access at database level:
This example uses an active filter to extend or restrict data access at the database level.
For example, a user that is associated with the following resource permission definitions cannot read from Demo where noAccess1 restricts access to all dimensions:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo, read
-
oracle.essbase.filter,/EssbaseCluster-1/Demo/Basic/noAccess1, apply
27.5.4.3 Securing Data Access with Essbase Filters
You secure data access by granting Essbase filters to an application role. An Essbase filter resource permission definition secures data access for the grantee at the database level.
To secure data access for a user with Essbase filters:
-
If a specific filter does not exist, then create it using Essbase Administration Services Console or the MaxL command line.
For more information, see Oracle Essbase Administration Services Online Help and Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.html -
Grant filter resource permission definitions to an application role using Fusion Middleware Control.
For more information, see Section 27.5.3, "Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools."
You can also do this programmatically using Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST). For more information, see "Managing Application Policies with OPSS Scripts" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Application Security Guide.
Note:
The following Enterprise Performance Management restriction does not apply when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence:
For EPM-installed systems, there can be only one filter per multidimensional database per user or application role. If a user or application role is directly provisioned with a second filter, then the first is revoked. Multiple filters can be provisioned indirectly when a user is a member of multiple application roles that each have a provisioned filter.
Filter resource permission definitions are determined when you connect to a specific Essbase multidimensional database. Filter resource permission definitions pass to the Essbase Agent during authentication. If the user is authenticated successfully, then the list of filters for that user is updated in a locally stored .SEC file.
27.5.4.4 When Are Filter Access Permission Grant Changes Consumed?
The filter access permissions for a user are determined at login time and are consumed when the Essbase database is selected (SetActive). Authorization changes are not noticed by existing sessions; a user must log in again to consume changes in authorization policy.
27.5.4.5 How Do Filter Permission Grants Differ Between Oracle Business Intelligence and EPM?
You grant filter resource permissions differently when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence compared to when Essbase is installed as part of an EPM System as follows:
-
When Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence
You grant filter resource permission definitions to an application role, or assign the admin permission to the application role.
-
When Essbase is installed as part of an EPM System
You grant filter resource permissions to a group, or assign the admin permission to the group.
Essbase installed with Oracle Business Intelligence grants a user the union of all permissions that are granted directly or through groups and application roles. Unlike an EPM system, with Oracle Business Intelligence there is no restriction that, for example, the oracle.essbase.application filter action must be granted using the same group as the filters. In Oracle Business Intelligence, you can have conflicting roles. See Table 27-4 to understand the consequences of these grants.
Table 27-4 Example Showing How Permission Grants Can Differ Between EPM and Oracle Business Intelligence
| Application Role (Group) | Application Grant | Filter Grant |
|---|---|---|
|
A |
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo, use_filter |
oracle.essbase.filter, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo/Basic/read_filter, apply |
|
B |
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo, use_filter |
oracle.essbase.filter, /EssbaseCluster-1/Demo/Basic/readFeb_filter, apply |
In Table 27-4, user JDoe is a member of groups A and B, and so when querying Basic, JDoe has access to rows defined by read_filter and readFeb_filter. If group A has the application grant removed in an EPM System installation, then users of group A no longer have access to any filters. However, when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, user JDoe continues to have access to rows from both filters because JDoe also inherits the permissions from membership of group B.
27.5.5 Configuring Access to Essbase Calculations
Essbase calculations enable you to apply mathematical formula to data in Essbase multidimensional databases. You enable users to access Essbase calculations by configuring resource permission definitions for Essbase calculations and granting them to application roles. For more information, see Section 27.5.3, "Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools."
This topic contains the following sections:
-
Section 27.5.5.2, "Configuring Resource Permission Definitions for Essbase Calculations"
-
Section 27.5.5.3, "Enabling Users to Access Essbase Calculations"
27.5.5.1 What Are Essbase Calculations?
An Essbase calculation enables a user to define and apply complex formulas to dimensional members. You can name calculations and save them in files at the application or database level; these are called calculation scripts. Calculations can also be interactively created and run; these are called inline calculations. Finally, every database has a default calculation defined in the outline.
Calculation scripts are stored in the local file system, and their definitions can be complex and require tool support. For example, you can use Essbase Administration Services (EAS) and Calculation Manager, which provide the ability to:
-
View dimensions and their members.
-
List calculation operations.
MaxL can also be used for calculation definition.
27.5.5.2 Configuring Resource Permission Definitions for Essbase Calculations
Before you can grant an application role permission to use Essbase calculations (see Section 27.5.3, "Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools"), appropriate resource permission definitions must exist in the policy store. Use the examples in this section to understand how to configure resource permission definitions so that users can use Essbase calculations.
For more information about resource permissions, see Section 27.5.8, "Resource Permissions Reference for Essbase and Associated Tools."
Example 1 - To configure resource permission definitions to use default and inline calculations in /cluster/App1:
This example configures resource permission definitions to use default and inline calculations in /EssbaseCluster-1/App1. The following resource permission definition must exist in the policy store. For example:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_calculation
In this example an application resource permission grants the use_calculation permission to all applications in the cluster.
OR
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1, use_calculation
In this example an application resource permission grants the use_calculation permission to applications in App1.
Example 2 - To configure resource permission definitions to use all calculations in /cluster/App1:
This example configures resource permission definitions to use all calculation scripts in /EssbaseCluster-1/App1, you must ensure that the following permissions exist in the policy store. For example:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_calculation
OR
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1, use_calculation
AND
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1, all
This calculation permission grants access permissions to use to all calculation scripts in App1.
Example 3 - Configuring resource permission definitions to use all calculations in the cluster:
This example configures resource permission definitions to use all calculations in the cluster, you must ensure that both of the following permissions exist in the policy store. For example:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_calculation
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1, all
Example 4 - Configuring resource permission definitions to use calculation scripts forcastQ1 and forcastQ2:
This example configures resource permission definitions to use specific calculation scripts in the cluster (for example, forcastQ1 and forcastQ2), you must ensure that the following permissions exist in the policy store. For example:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_calculation
OR
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1, use_calculation
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1/Db1/forcastQ1, execute
AND
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1/Db1/forcastQ2, execute
Note:
A grant to a specific calculation script revokes cluster or application level access to all calculations. Consider specific grants to calculations scripts as restrictions.
For example:
A user with the following grants has access only to the forcastQ1 calculation script:
-
oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, use_calculation
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1, all
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1/Db1/forcastQ1, execute
Note:
The presence of an oracle.essbase.calculation grant does not imply oracle.essbase.application calculate access. For example:
The user does not have access to any calculation, outline, inline, or script with any of following grants if there is no oracle.essbase.application calculate grant:
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1, all
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1, all
-
oracle.essbase.calculation, /EssbaseCluster-1/App1/Db1/forcastQ1, execute
27.5.5.3 Enabling Users to Access Essbase Calculations
You enable a user to access Essbase calculations by granting one or more Essbase calculation access permissions to an application role that is associated with the user. By default, users with the calculate permission can execute the default and inline calculations on all databases.
To enable users to access Essbase calculations:
-
If the calculation script does not exist, then create and activate it using Essbase Administration Services Console or the MaxL command line.
For more information, see Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide and Oracle Essbase Administration Services Online Help:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.html -
Grant the Essbase calculation access permission to an application role using Fusion Middleware Control.
For more information, see Section 27.5.3, "Enabling Users to Perform Specific Actions in Essbase and Associated Tools."
27.5.6 Changing Essbase Ports in Oracle Business Intelligence
You can change the port on which the local WebLogic Server runs; for example, if the Essbase installation with Oracle Business Intelligence uses a port that is required for a third-party product. The network administrator might want to limit the available port range.
Oracle Business Intelligence (including Essbase) system component port ranges are shown in Fusion Middleware Control in the Scalability page, Capacity Management tab. For more information, see Section 5.5, "Using Fusion Middleware Control to Scale System Components." To explicitly specify an Essbase Server port range or an Essbase Agent port number, you manually edit the appropriate entries SERVERPORTBEGIN, SERVERPORTEND, or AGENTPORT in the essbase.cfg file.
To manually update the Essbase Server port range or Essbase Agent port number outside of Fusion Middleware Control:
-
Open the essbase.cfg file for editing.
The essbase.cfg file is located in:
ORACLE_INSTANCE/Essbase/essbaseserver1/bin/essbase.cfg
-
Update the following entries as required:
For example:
AGENTPORT 9799
SERVERPORTBEGIN 9000
SERVERPORTEND 9499
For more information about these ports, see Table 27-1 and Oracle Essbase Technical Reference Guide:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.html -
Save the essbase.cfg file.
-
Restart WebLogic Server
Note:
Essbase standalone clients that contact the BI Security Service use a new port address at the next startup. Essbase Web applications that run in the same WebLogic Server might not require restarting to continue to communicate with the co-located BI Security Service.
27.5.7 Allocating Essbase Studio (JSE) Ports
Essbase Studio port is not managed by Oracle Business Intelligence.
The value of Essbase Studio port is specified by the value of the entry transport.port (for example transport.port=5300) in the server.properties file. The server.properties file is located in:
<INSTANCE>/EssbaseStudio/essbasestudio1/bin/server.properties
27.5.8 Resource Permissions Reference for Essbase and Associated Tools
This section provides reference information about the resource permissions for Essbase and associated tools that are configured by default when you install Essbase with Oracle Business Intelligence.
To access Essbase-related functionality, a user (or group, or application role that the user belongs to), needs to be granted one or more resource permissions. Essbase-related resource permissions are defined by resource type, name, and actions and are held in the Policy Store as part of the Oracle Fusion Middleware security model. For more information, see "Managing the Policy Store" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Application Security Guide.
-
Resource Type
Includes a named group of permissions.
-
Resource Name
Specifies the scope for which a permission applies.
-
Action
Defines what operation the permission allows the grantee to perform.
You manage Essbase-related resource permissions using Fusion Middleware Control. However, you can also use APIs in Oracle Platform Security Services using JMX or Oracle WebLogic Scripting Tool.
Note:
When Essbase and associated tools are installed with Oracle Business Intelligence, the functionality described in this chapter replaces that provided by Hyperion Shared Services for provisioning users.
This topic contains the following sections:
-
Section 27.5.8.1, "What Resource Types Apply to Essbase and Associated Tools?"
-
Section 27.5.8.2, "What Resource Names Apply to Essbase and Associated Tools?"
-
Section 27.5.8.3, "What Actions Apply to Essbase and Associated Tools?"
27.5.8.1 What Resource Types Apply to Essbase and Associated Tools?
Resource types are named groups of permissions that can be associated with specific actions. There are several levels of authority in the Essbase server with a resource type for each. Resource types are used by Fusion Middleware Control to limit the list of applicable Essbase-related actions when selecting a new grant.
Table 27-5 lists the Essbase-related resource types that are supported in Oracle Business Intelligence.
Table 27-5 Essbase-Related Resource Types Supported in Oracle Business Intelligence
| Resource Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
oracle.essbase.server |
Global, cluster, and server level permissions. |
|
oracle.essbase.application |
Application level permissions required to use filters and calculations. |
|
oracle.essbase.filter |
Filter access control. |
|
oracle.essbase.calculation |
Calculation script access control. |
|
oracle.essbasestudio |
Essbase Studio permissions. |
|
oracle.fr |
Financial Reporting permissions. |
|
oracle.calcmanager |
Calculation Manager permissions. |
27.5.8.2 What Resource Names Apply to Essbase and Associated Tools?
Each resource type has a set of resources and actions that can be authorized. Essbase-related resource names are either specific objects or scopes in which objects are contained.
For oracle.essbasestudio, oracle.fr and oracle.calcmanager resource types, the resource name is always a global scope of '/'.
For oracle.essbase.server and oracle.essbase.application resource types, resource names are scopes. They are hierarchical and as such any scope in Table 27-6 includes the set of scopes contained within it.
Table 27-6 lists the supported Essbase scopes.
Table 27-6 Essbase Scopes Supported
| Name | Scope |
|---|---|
|
/ |
Global, all clusters, all applications, all cubes. |
|
/cluster |
All applications within a logical cluster. |
|
/cluster/application |
Specific application and its cubes. |
Table 27-7 lists the supported oracle.essbase.filter scopes.
Table 27-7 Essbase Filter Scopes Supported
| Name | Scope |
|---|---|
|
/cluster/application/database/filtername |
Access to a specific, named filter. |
Table 27-8 lists the supported Essbase calculation scopes.
Table 27-8 Essbase Calculation Scopes Supported
| Name | Scope |
|---|---|
|
/cluster/ |
All calculation scripts at cluster level: any applications, any cubes. |
|
/cluster/application |
All calculation scripts at application level: any cube within the named application |
|
/cluster/application/database/scriptname |
Access to a specific named calculation script. |
27.5.8.3 What Actions Apply to Essbase and Associated Tools?
Essbase-related actions (permissions) represent operations that a user can perform on Essbase or an associated tool.
Actions granted to oracle.essbase.server or oracle.essbase.application resource types are hierarchical, such that any action listed includes the set of permissions listed beneath it.
For example, granting oracle.essbase.application, /EssbaseCluster-1, read enables the grantee to read multidimensional databases and to restart the applications in EssbaseCluster-1.
Actions on other Essbase-related resource types are not hierarchical and need to be individually granted.
The series of tables below give details on the actions available with each Essbase-related resource type.
Table 27-9 lists the supported oracle.essbase.server actions.
Table 27-9 Essbase Server Actions Supported With Oracle Business Intelligence
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
administer |
Full access to administer the server, applications, and databases. |
|
create |
Ability to create and delete applications and databases within applications. Includes Application Manager and Database Manager permissions for the applications and databases created by this user. |
|
access |
Ability to log in to Essbase. Note: This is deprecated and the existence of any server or application permission now suffices. |
Note:
A user that creates an application has permission to manage that application within the same session. The same user requires an explicit grant to manage the application in subsequent sessions.
Table 27-10 lists supported oracle.essbase.application actions.
Table 27-10 Essbase Application Actions Supported With Oracle Business Intelligence
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
manage_application |
Ability to create, delete, and modify databases and application settings within the particular application. Includes Database Manager permissions for databases within the application. |
|
manage_database |
Ability to manage databases (for example, to change the database properties or cache settings), database artifacts, locks, and sessions within the assigned application. |
|
use_calculation |
Ability to execute calculations, update, and read data values based on the assigned scope, using any assigned calculations and filter. |
|
write |
Ability to update and read data values based on the assigned scope, using any assigned filter. |
|
read |
Ability to read data values. |
|
use_filter |
Ability to access specific data and metadata according to the restrictions of a filter. |
|
restart |
Ability to start and stop an application or database. |
Table 27-11 lists supported oracle.essbase.filter actions.
Table 27-11 Essbase Filter Actions Supported With Oracle Business Intelligence
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
apply |
Apply the filter identified by the resource name. |
Table 27-12 lists supported oracle.essbase.calculation actions.
Table 27-12 Essbase Calculation Actions Supported With Oracle Business Intelligence
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
all |
Enables the user to execute any calculation that is contained in the scope referenced by the resource name. |
|
execute |
Enables the user to execute the calculation script that is identified by the resource name. |
Table 27-13 lists supported oracle.fr actions.
Table 27-13 Essbase Financial Reporting Actions Supported With Oracle Business Intelligence
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
accessReporting |
Enables the user to access reports. |
|
administerReporting |
Enables the user to administer reports. |
|
editReport |
Enables the user to edit reports. |
|
scheduleBatch |
Enables the user to schedule reports. |
|
editBook |
Enables the user to edit books. |
|
editBatch |
Enables the user to edit batch. |
Table 27-14 lists supported oracle.essbasestudio actions.
Table 27-14 Essbase Studio Actions Supported With Oracle Business Intelligence
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
cpadmin |
Administrator, performs all Essbase Studio tasks, including model creation, cube deployment and executing drill-through reports. |
|
cpdsadmin |
Data Source Administrator, performs all tasks related to data source, connection creation and maintenance, executes drill-through reports. |
|
cpdm |
Data Modeler, performs all tasks related to metadata element creation and maintenance, deploys cubes, executes drill-through reports. |
|
viewer |
Viewer, views all Essbase Studio data sources and metadata elements, executes drill-through reports. |
Table 27-15 lists supported oracle.calcmanager actions.
Table 27-15 Essbase Calc Manager Actions Supported With Oracle Business Intelligence
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
admin |
Treated as an administrator. Can perform all activities. |
|
designer |
Can edit, delete, modify, and deploy their own rules and view rules that were created by others. |
Table 27-16 lists permissions granted to Oracle Business Intelligence application roles.
Table 27-16 Essbase Permissions Granted to Oracle Business Intelligence Application Roles
| Role Name | Resource Permission | Role Members |
|---|---|---|
|
BIAdministrator |
oracle.essbase.server, /, administrator oracle.fr,/,administerReporting oracle.calcmanager,/,admin |
BIAdministrators group |
|
BIAuthor |
oracle.calcmanager,/,designer oracle.essbasestudio,/,cpadmin oracle.fr,/,editBatch,editBook,editReport,scheduleBatch |
BIAuthors group BIAdministrator application role |
|
BIConsumer |
oracle.essbase.server,/,access,use_filter oracle.fr,/,accessReporting oracle.essbasestudio,/,viewer |
BIConsumers group BIAuthor application role |
|
AuthenticatedUser |
not applicable |
BIConsumer |
This application role hierarchy and permission grants are defaults only and the administrator user can change them in Fusion Middleware Control.
AuthenticatedUser is a member of BIConsumer by default. This means that any successfully authenticated user has BIConsumer role permissions.
27.6 Managing Essbase System Administration in Oracle Business Intelligence
You manage Essbase system administration in Oracle Business Intelligence by starting and stopping Essbase Agents, enabling and viewing log files, setting logging levels, migrating Essbase configuration between domains, monitoring Essbase metrics, and backing up and recovering Essbase data.
This topic contains the following sections:
-
Section 27.6.3, "Diagnostics - Enabling Essbase Logging, Setting Log Levels, and Viewing Log Files"
-
Section 27.6.4, "Migrating Essbase Configuration Between Domains"
For information about managing system administration in Oracle Business Intelligence, see Chapter 1, "Introduction to Oracle Business Intelligence System Administration."
27.6.1 Starting and Stopping Essbase Components
You can monitor status, and start and stop Essbase Agents, Essbase Administration Services, and Provider Services using Fusion Middleware Control. For more information, see Chapter 4, "Starting and Stopping Oracle Business Intelligence."
Note:
Chapter 4 does not include specific references to Essbase components. You see Essbase components displayed in Fusion Middleware Control, and you can start and stop them using the same steps as those that are described for Oracle Business Intelligence components.
To start or stop the Essbase Server using Fusion Middleware Control:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control.
For information, see Section 2.2.2, "Logging into Fusion Middleware Control to Manage Oracle Business Intelligence."
-
Select Business Intelligence then coreapplication.
-
Display the Processes page in the Availability tab.
-
For example, expand Essbase Agents and select essbaseserver1 in the Processes section.
This enables you to start or stop just the Essbase Server process.
-
Click Stop Selected to stop the selected process, or click Start Selected to start the selected process.
Note:
You can use the Stop All, and Start All buttons to stop and start all Oracle Business Intelligence processes, which includes the Essbase Server process. You cannot stop and start Essbase Studio using Fusion Middleware Control. You must use the command line.
27.6.2 Maintaining High Availability of Essbase Components in Oracle Business Intelligence
High availability for Essbase in Oracle Business Intelligence is automatically maintained using an active-passive fault tolerance model, and failover is managed by Oracle Process Management and Notification (OPMN) service and Fusion Middleware Control.
-
Section 27.6.2.1, "Scaling Out Essbase to Support High Availability"
-
Section 27.6.2.2, "Configuring a Secondary Instance of the Essbase System Component"
-
Section 27.6.2.3, "What Is the Essbase Active-Passive Topology?"
27.6.2.1 Scaling Out Essbase to Support High Availability
You scale out Essbase onto additional computers, when using an Enterprise Install (see Section 27.4.2.2), to support high availability between computers.
Scale-out is achieved in a similar way to existing Oracle BI EE components, using the Oracle Business Intelligence Installer to scale out and using Fusion Middleware Control to configure the secondary Essbase component.
To scale out Essbase to support high availability:
-
Scale out the existing Enterprise installation.
For more information, see "Enterprise Install to Scale Out Existing Installations" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence.
-
Configure the secondary Essbase component created during scale-out, so that it is distributed for high availability.
Proceed to Section 27.6.2.2, "Configuring a Secondary Instance of the Essbase System Component."
27.6.2.2 Configuring a Secondary Instance of the Essbase System Component
The Oracle Essbase Agent is a single component that operates in active/passive mode. Configure a secondary instance of this component so that it is distributed for high availability.
To configure a secondary instance of Essbase system component:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control at http://mycompany.example:7001/em.
-
Expand the Business Intelligence node.
-
Click coreapplication.
-
Click Availability, then click Failover.
-
Click Lock and Edit Configuration to activate the Primary/Secondary Configuration section of the Availability tab.
-
Specify the Secondary Host/Instance for Essbase Agent.
-
In the Essbase Agents section, ensure that the Shared Folder Path is set to:
MW_HOME/INSTANCE/Essbase/essbaseserver1.Note: You must manually copy the contents of the
/MW_HOME/INSTANCE/Essbase/essbaseserver1directory to the shared folder path. -
Click Apply.
Under Potential Single Points of Failure, you see No problems - all components have a backup.
-
Click Activate Changes.
-
Click Restart to apply recent changes.
-
Click Restart under Manage System.
-
Click Yes in the confirmation dialog.
27.6.2.3 What Is the Essbase Active-Passive Topology?
The active Essbase server uses the local BI Security Service. If the local service becomes unavailable (for example, if the WebLogic Managed Server has been stopped), then the active Essbase Server stops and the passive Essbase Server is started. This provides service availability, but loses existing sessions.
The two-node active-passive topology applies to the Essbase Server and Agent plus the mid-tier Essbase Administration Services, Analytic Provider Services, and Essbase Studio Server components.
For information, see "Oracle Essbase High Availability Concepts", "Configuring Oracle Essbase Clustering", and "Oracle Hyperion Provider Services Component Architecture" in Oracle Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide.
27.6.2.4 Managing Essbase Capacity
You manage Essbase capacity within Oracle Business Intelligence by monitoring Essbase components and service levels using Fusion Middleware Control to answer the following questions:
-
How do I know that Essbase components are running?
For information, see Section 2.2.3, "Using Fusion Middleware Control to Manage Oracle Business Intelligence System Components."
-
How do I know if my system is overloaded?
For information, see Section 7.1, "Monitoring Service Levels."
27.6.3 Diagnostics - Enabling Essbase Logging, Setting Log Levels, and Viewing Log Files
You enable logging to diagnose configuration problems. You set log levels and view Essbase log files using Fusion Middleware Control.
For more information, see:
-
Section 8.2.1, "Using Fusion Middleware Control to View Log Information, Error Messages, and Alerts"
-
Section 8.2.2, "Configuring Log File Rotation Policy and Specifying Log Levels"
To view Essbase log files in Fusion Middleware Control:
-
Log in to Fusion Middleware Control.
For information, see Section 2.2.2, "Logging into Fusion Middleware Control to Manage Oracle Business Intelligence."
-
Select coreapplication.
-
Display the Log Messages page in the Diagnostics tab.
-
Click Essbase Log in the View/Search Log Files section.
This displays log information for the target essbaseserver1 of target type Essbase Server.
-
Click Target Log Files to display a table of all the Essbase logs found.
Essbase log files are located in the following directory:
MW_HOME/INSTANCE/diagnostics/logs/Essbase/essbaseserverN/essbase/ESSBASE_ODI
Essbase Shared Services Log Files
Essbase shared services log files are located in the following directory:
MW_HOME/INSTANCE/diagnostics/logs/Essbase/essbaseserverN/essbase/SharedServices
There may also be older logs of this type in this directory. For example, "SharedServices_Security_Client-280.log.
Essbase application log files are not displayed in Fusion Middleware Control, but are located in the following directory:
MW_HOME/INSTANCE/diagnostics/logs/essbaseserverN/essbase/app/<application name>/<application name>_ODL.log
Essbase Agent Log Configuration Files
Essbase Agent log configuration files are located in the following directory:
ORACLE_INSTANCE/Essbase/essbaseserverN/bin/logging.xml
Use the following EssbaseAgentODLLogger file for general logs and oracle.EPMCSS for the security provider.
Example of a Log Configuration File for EPM Workspace
All log configuration files conform to the Oracle Diagnostic Log (ODL) standard, although they can differ slightly in appearance.
Example 27-1 is an excerpt of the logging.xml configuration file for EPM Workspace, which includes log file settings for the ConsoleHandler and ODLHandlerFactory components.
Example 27-1 EPM Workspace Diagnostic Log Configuration File Format
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
- <logging_configuration>
- <log_handlers>
<log_handler name="console-handler" class="oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ConsoleHandler" level="WARNING:32" formatter="oracle.core.ojdl.weblogic.ConsoleFormatter" />
- <log_handler name="odl-handler" class="oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory" filter="oracle.dfw.incident.IncidentDetectionLogFilter">
<property name="path" value="${domain.home}/servers/${weblogic.Name}/logs/${weblogic.Name}-diagnostic.log" />
<property name="maxFileSize" value="10485760" />
<property name="maxLogSize" value="104857600" />
<property name="encoding" value="UTF-8" />
<property name="useThreadName" value="true" />
<property name="supplementalAttributes" value="J2EE_APP.name,J2EE_MODULE.name,WEBSERVICE.name,WEBSERVICE_PORT.name,composite_instance_id,component_instance_id,composite_name,component_name" />
</log_handler>
<log_handler name="wls-domain" class="oracle.core.ojdl.weblogic.DomainLogHandler" level="WARNING" />
- <log_handler name="owsm-message-handler" class="oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory">
<property name="path" value="${domain.home}/servers/${weblogic.Name}/logs/owsm/msglogging" />
<property name="maxFileSize" value="10485760" />
<property name="maxLogSize" value="104857600" />
<property name="encoding" value="UTF-8" />
<property name="supplementalAttributes" value="J2EE_APP.name,J2EE_MODULE.name,WEBSERVICE.name,WEBSERVICE_PORT.name" />
</log_handler>
- <log_handler name="em-log-handler" class="oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory" level="NOTIFICATION:32" filter="oracle.dfw.incident.IncidentDetectionLogFilter">
<property name="path" value="${domain.home}/servers/${weblogic.Name}/sysman/log/emoms.log" />
<property name="format" value="ODL-Text" />
<property name="useThreadName" value="true" />
<property name="maxFileSize" value="5242880" />
<property name="maxLogSize" value="52428800" />
<property name="encoding" value="UTF-8" />
</log_handler>
- <log_handler name="em-trc-handler" class="oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory" level="TRACE:32">
<property name="logreader:" value="off" />
<property name="path" value="${domain.home}/servers/${weblogic.Name}/sysman/log/emoms.trc" />
<property name="format" value="ODL-Text" />
<property name="useThreadName" value="true" />
<property name="locale" value="en" />
<property name="maxFileSize" value="5242880" />
<property name="maxLogSize" value="52428800" />
<property name="encoding" value="UTF-8" />
</log_handler>
...
...
<loggers>
- <logger name="" level="WARNING:1">
<handler name="odl-handler" />
<handler name="wls-domain" />
<handler name="console-handler" />
</logger>
<logger name="oracle" level="NOTIFICATION:1" />
<logger name="oracle.adf" />
<logger name="oracle.adf.desktopintegration" />
<logger name="oracle.adf.faces" />
<logger name="oracle.adf.controller" />
<logger name="oracle.adfinternal" />
<logger name="oracle.adfinternal.controller" />
<logger name="oracle.jbo" />
...
...<server>
27.6.4 Migrating Essbase Configuration Between Domains
For information about migrating an Essbase configuration between domains for an Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System installation, see "Moving Oracle Hyperion Enterprise Performance Management System to a Target Environment" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
27.6.5 Monitoring Essbase Metrics
You monitor Essbase metrics using Fusion Middleware Control.
For more information, see Section 7.1, "Monitoring Service Levels."
27.6.6 Backup and Recovery of Essbase Data
This section describes backing up and recovering Essbase data when Essbase is installed with Oracle Business Intelligence.
For information about backing up and recovering Essbase data, see:
-
Oracle Business Intelligence and Essbase - When installed using the Oracle Business Intelligence installer, see "Backup and Recovery Recommendations for Oracle Essbase" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
-
EPM System products - When installed using the EPM System Installer, see Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System Backup and Recovery Guide at:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.html
27.7 Working with Essbase Cubes in Oracle Business Intelligence
This section introduces working with Essbase cubes in Oracle Business Intelligence:
-
Section 27.7.1, "Creating Essbase Cubes in Oracle Business Intelligence"
-
Section 27.7.2, "Importing Metadata from Essbase Data Sources"
-
Section 27.7.4, "Configuring Database Objects and Connection Pools"
-
Section 27.7.5, "Enabling Single Sign-On for Essbase Data Sources"
27.7.1 Creating Essbase Cubes in Oracle Business Intelligence
You must create Essbase cubes to use in Oracle Business Intelligence before users can create, schedule, or run analyses against Essbase data sources.
A user with the BIAdministrator application role (with the permission oracle.essbasse.server, administer), creates the Essbase applications and databases. A user with the BIAuthor application role can then create the Essbase metadata (or outline) for Oracle Business Intelligence (the BIAdministrator application role inherits the BIAuthor application role by default).
To create Essbase cubes in Oracle Business Intelligence:
Oracle recommends that you create Essbase cubes using the Essbase Administration Services Console.
-
Use the following URL to display the Essbase Administration Services Console login page:
http://<computer_name>:<port>/easconsole
Alternatively, to use the Essbase Studio client application, download it from the Download BI Desktop Tools option, in the Get Started area of the Home page for Oracle BI EE. For more information, see "Downloading BI Desktop Tools" in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
-
Complete this step if you want to deploy Essbase sample applications.
The Essbase Server installation includes sample applications that are designed to familiarize you with Essbase features. The sample applications are not available when you first use Essbase Administration Services Console. For more information, see "Setting Up Sample Applications" in Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.htmlYou deploy the sample applications by unzipping them into the ARBORPATH (data directory) folder, for example:
MW_HOME/instance/instance1/Essbase/essbaseserver1
-
To create Essbase cubes, see Table 27-1, Oracle Essbase Administration Services Online Help and Oracle Essbase Studio Users Guide:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.html
Note:
Users must be assigned the application role that has the resource permission to perform tasks in Essbase Studio. Essbase Studio Roles are not the same as Fusion Middleware application roles.
Note:
A user that creates an application has permission to manage that application within the same session. The same user requires an explicit grant to manage the application in subsequent sessions.
Proceed to Section 27.7.2, "Importing Metadata from Essbase Data Sources."
27.7.2 Importing Metadata from Essbase Data Sources
You import Essbase cube metadata from an Essbase data source into the Oracle BI metadata repository to enable you to extract and display data in Oracle Business Intelligence analyses and dashboards. Use the Hyperion Provider Services (APS) connection to Essbase in preference to a direct connection.
Use the Hyperion Provider Services (APS) connection to Essbase in preference to a direct connection.
To connect to APS, you specify the following in the Oracle BI Administration Tool when importing Essbase data:
http://mycomputer.example:7001/aps/Essbase?ClusterName=Cluster-1
The port number is the Managed Server port where APS is running, or the Administration Server port in the case where a Simple Install is being used.
For more information, see "Importing Metadata from Multidimensional Data Sources" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Metadata Repository Builder's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
Note:
When Essbase metadata changes, you must reimport the metadata.
27.7.3 Working with Essbase Data Sources
After you have imported metadata from Essbase data sources, the cube metadata is mapped by default to the Physical layer of the Oracle BI repository. To understand the tasks that you can perform to model the data in different ways, see "Working with Essbase Data Sources" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Metadata Repository Builder's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
When working with Essbase, you must disable the BI Server Query cache. For more information, see Section 7.5, "Configuring Query Caching."
27.7.4 Configuring Database Objects and Connection Pools
If you must adjust database or connection pool settings or create a database object or connection pool manually, then see "Setting Up Database Objects and Connection Pools" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Metadata Repository Builder's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
27.7.5 Enabling Single Sign-On for Essbase Data Sources
To enable SSO for Essbase data sources installed using the Oracle Business Intelligence installer, you select SSO in the General tab of the connection pool object that corresponds to the Essbase data source in the Oracle BI repository. Also select the Virtual Private Database option in the corresponding database object to protect cache entries.
For more information, see "Multidimensional Connection Pool Properties in the General Tab" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Metadata Repository Builder's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
27.7.6 Creating, Scheduling, and Running Analyses and Reports Where Essbase Is the Data Source
A user with the BI Author application role can create, schedule, and run analyses and reports where Essbase is the data source, where filters are applied using the identity of the end user, and where SSO is configured.
For more information about:
-
Creating, scheduling, and running Oracle Business Intelligence analyses, see:
Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition
-
Creating and running BI Publisher reports, see:
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher
27.8 Where Can I Learn More Information About Essbase?
Use the following links to learn more about Essbase in Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System.
-
For all Essbase and EPM documentation, use the Performance Management Documentation page:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/performance-management/documentation/index.htmlThis page also contains links to EPM System Supported Platform Matrices, My Oracle Support, and other information resources.
Drill down to view specific documents for a release.
-
For information about meeting system requirements and understanding release compatibility, use Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System Certification Matrix:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/ias/downloads/fusion-certification-100350.html