11g Release 6 (11.1.6)
Part Number E16689-06
Home
Contents
Book
List
Contact
Us
|
Oracle® Fusion
Applications Security Guide 11g Release 6 (11.1.6) Part Number E16689-06 |
Home |
Contents |
Book List |
Contact Us |
|
Previous |
Next |
Oracle Fusion Applications Security Business Fit: Explained
Differences in Security Terminology: Explained
FAQs for Security Introduction
Oracle Fusion Applications is secure as delivered.
The security approach consists of tightly coordinating the following aspects of security.
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Function security
Data security
Privacy
Access provisioning and identity management
Segregation of duties policies
Enforcement across tools, technologies, data transformations, and access methods
Enforcement across the information life cycle
The Oracle Fusion Applications security approach supports a reference implementation of roles and security policies that address common business needs. Enterprises address needs specific to their organization by changing or extending the role definitions, role hierarchies, data security, and segregation of duties policies of the reference implementation.
Access to system resources is granted to users through the roles assigned to them, not to the users directly. Roles provide access to functions and data.
The Oracle Fusion Applications security approach includes abstract, job, duty, and data roles. Abstract roles group users without respect to specific jobs, such as all employees or all managers. Job roles group users in adherence to the principle of least privilege by granting access only in support of the duties likely to be performed, such as the job of Accounts Payable Manager. Duty roles define the duties of a job as entitlement to perform a particular action, such as processing payables invoices. Data roles group users who have functional access through a particular job role with access to a particular dimension of data, such as invoices relevant only to their business unit, or based on Human Capital Management (HCM) security profiles, such as employees who work in departments in a particular country, line of business, or division.
Abstract, job, and data roles are implemented as enterprise roles in Oracle Fusion Middleware so they can be shared across the enterprise. Duty roles are implemented as application roles in Oracle Fusion Middleware so they can be defined within applications.
Functions and data are inaccessible to users unless they are provisioned with the roles necessary to gain access. Function security provides users with access to pages in application users interfaces and actions that can be performed there. Data security allows users to see data in those pages. Some data is not secured, in which case access to a user interface page gives unrestricted access to the data that is accessible from that page. For example, some setup data such as Receivables Receipt Method and Payment Method is not secured, and some transaction data such as Receivables Customer Profile is not secured. Archive data such as Receivables Archive is also not secured.
Enterprise roles inherit application roles that provide the enterprise roles with access to application functions and data. Roles are grouped hierarchically to reflect lines of authority and responsibility. The figure shows user access to functions and data determined by roles arranged in hierarchies and provisioned to the user.
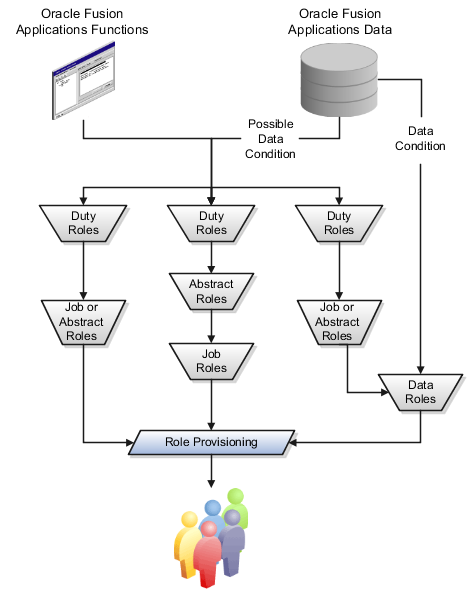
Duty roles carry entitlement to actions on functions and data. An example of a duty role is the Payables Invoice Processing Duty. Job and abstract roles inherit duty roles that determine the access to functions appropriate to the job. For example, the job role Accounts Payable Manager inherits the Payables Invoice Processing Duty.
Data security policies may grant actions on data to enterprise or duty roles. The condition of a data security policy determines if the access is explicit, such as all invoices of a particular business unit, or implicit, such as all invoices in the business unit to which a user is assigned. Job and abstract roles inheriting duty roles for which data security policies are defined grant implicit data access.
Data roles inherit abstract or job roles or both, and are granted explicit access to data. For example, a job role might give view access to the functions needed to access invoices, but a data role that inherits the job role gives view access to the invoices data within a business unit, such as the data role Accounts Payable Manager - US which inherits the job role Accounts Payable Manager for performing accounts payable duties against the US business unit.
Authorization Policy Manager (APM) is available in Oracle Fusion Applications through integration with Oracle Identity Management (OIM). Authorization policy management involves managing duty roles, data role templates, and data security policies, as well as previewing data roles generated based on data role templates.
Privacy encompasses data that should not be available to other individuals and organizations. Where data is possessed by another party, the individual must be able to exercise a substantial degree of control over that data and its use.
Oracle Fusion applications classify data at several levels of sensitivity, and define privacy attributes that participate in data security policies to apply appropriate protections to sensitive data. Oracle Fusion Applications secures the privacy attributes of personally identifiable information (PII) consistently across Oracle Fusion applications, and controls the destination of privacy attributes to the fewest and most highly secured locations possible, such as limiting the attributes that HCM applications share with the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store.
The Oracle Fusion Applications installation process creates an initial user and provisions that user with the administration roles necessary for initial setup.
Oracle Identity Management (OIM) is available in Oracle Fusion Applications through integration with Oracle Fusion Middleware. Identity management in Oracle Fusion Applications involves creating and managing user identities, creating and linking user accounts, managing user access control through user role assignment, managing enterprise roles, and managing OIM workflow approvals and delegated administration.
Through OIM, Oracle Fusion Applications notifies the IT security manager of all of the user requests (user life cycle changes), role provisioning requests, and grants to ensure role administration is always documented, authorized, and auditable.
Provision data roles, when available, and not the job or abstract roles the data roles inherit. In the absence of data roles, provision the abstract or job roles directly.
Segregation of duties (SOD) separates activities such as approving, recording, processing, and reconciling results so an enterprise can more easily prevent or detect unintentional errors and willful fraud.
SOD policies constrain duties across roles so unethical, illegal, or damaging activities are less likely. SOD policies express constraints between role pairs.
Oracle Fusion role definitions respect segregation of duties policies. Oracle Fusion Applications is certified to integrate with Application Access Controls Governor (AACG) in the Oracle Governance, Risk and Compliance Controls (GRCC) suite to ensure effective SOD.
The Oracle Fusion Applications security approach enforces security controls across tools, technology infrastructure, transformations of data, access methods and the information life cycle.
The infrastructures of an Oracle Fusion Applications deployment vary from one tool in the technology stack to another, however the security approach coordinates transactional and analytical security so that all security policies and controls prevail across access methods and data transformations of enterprise information. Oracle Fusion Applications enforce each single statement of security policy through the multiple transformations of data necessary for transactions, dimensional analysis, and search optimization.
Oracle Fusion Applications optionally respect the Information Life Cycle Management policies that your enterprise establishes. Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) and Oracle Database Vault (ODV) protect data in transit and at rest, across the phases of a deployment from installation and setup, to archive and purge, and across databases from development to production.
The security reference implementation consists of roles, policies, and templates for generating data roles.
The security reference implementation consists of the following.
Set of abstract and job roles
Duty roles and role hierarchy for each job role and abstract role
Privileges required to perform each duty defined by a duty role
Data security policies for each job role, abstract role, or data role
Predefined HCM security profiles
Policies that protect personally identifiable information
Mapping of data security policies to fact and dimension to ensure enforcement across tools and access methods
Segregation of duties policies respected in the design of duties for the job role
Segregation of duties conflicts in some job role definitions
Templates for generating data roles and data security policies defined for those data roles
Template of data masking algorithm
An enterprise changes the reference implementation to accommodate its particular business needs, thereby creating the enterprise's security implementation, leaving the reference implementation in place as a baseline. Upgrades preserve enterprise changes.
The security reference implementation can be viewed in the user interfaces where security tasks are performed or in the security reference manual (SRM) for each Oracle Fusion Applications offering.
Security must be implemented to fit the business.
Oracle Fusion Applications supports an extensive predefined business process model (BPM) that is secured by a reference implementation of predefined roles and security policies.
The security reference implementation associates a full range of predefined roles with the business process model (BPM) levels. When assigned to users, the enterprise roles guide and control access to the task flows of the BPM and associated data. At the task level, task flows define the business actions that fulfill the intent of the BPM.
A security reference manual (SRM) for each offering presents all predefined roles, role hierarchies, business objects the roles must access, segregation of duties policies, and jobs that may have conflicting duties according to those policies. The reference implementation also can be viewed using the integrated Authorization Policy Manager (APM) and Oracle Identity Management (OIM) user interface pages to manage security policies, users, and identities.
This roadmap lists the wide range of available information resources that are about or relevant to understanding Oracle Fusion Applications security.
The information resources cover the following areas.
Oracle Fusion Applications
Oracle Fusion Middleware
Application Access Control Governor in the Oracle Governance, Risk and Compliance Controls (GRCC) suite
Oracle Database
Caution
Refer specifically to the Oracle Fusion Applications Edition of the following guides included in this roadmap.
Oracle Fusion Middleware Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Identity Management
Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Authorization Policy Manager
Oracle Fusion Applications installation, deployment, administration, development, and extensibility information supports optimizing the security approach in the application tier. In addition to the resources listed below, each predefined Oracle Fusion Applications offering provides a Security Reference Manual.
Oracle Fusion Middleware provides a foundation of identity management, authorization policy management, and security infrastructure in the middle tier.
Application Access Controls Governor in the Oracle Governance, Risk and Compliance Controls (GRCC) suite provides transaction, preventive, and configuration controls for segregation of duties (SOD).
Oracle Database supports application data security in the data tier. The Oracle Fusion Applications security approach is certified to use a foundation of Oracle Database security features. Information about securing Oracle Database is not relevant for Oracle Cloud implementations. Information about securing Oracle Database is not relevant for Oracle Cloud implementations.
In some cases, terminology used within and outside of Oracle Fusion Applications differs based on vantage point. For example, Oracle Fusion Middleware and Oracle Application Access Control Governor provide a foundation that is integrated with, but external to, the Oracle Fusion Application suite.
The table shows how Oracle Fusion Applications, Oracle Fusion Middleware, Oracle Application Access Control Governor, and some possibly coexistent applications refer to various equivalent elements of security.
Note
Oracle Authorization Policy Manager and Oracle Identity Management are in Oracle Fusion Middleware, and Oracle Application Access Controls Governor is in Governance, Risk, and Compliance Controls.
The equivalencies are true in general and based on the functional meaning of the terms. In the table, an empty cell indicates that no equivalent term exists.
|
Oracle Fusion Applications Security Reference Manuals and other documentation |
Authorization Policy Manager |
Oracle Identity Management |
Oracle Application Access Controls Governor |
Applications coexistent with Oracle Fusion Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
User |
User |
User |
|
PeopleSoft user profile |
|
External user, such as partner or supplier |
User |
External user |
|
|
|
Enterprise role |
External role |
Role |
|
eBusiness Suite responsibility |
|
Abstract role |
External role |
Role |
|
PeopleSoft role |
|
Data role |
External role |
Role |
|
eBusiness Suite responsibility PeopleSoft data permission |
|
Job role |
External role |
Role |
|
eBusiness Suite top level menu PeopleSoft role |
|
Duty role |
Application role |
|
Access control |
eBusiness Suite submenu PeopleSoft role |
|
Privilege |
Entitlement or permission set |
|
Access control |
eBusiness Suite form function PeopleSoft data permission |
|
Entitlement |
|
|
GRC entitlement |
|
|
Segregation of duties policy |
|
|
Access control |
|
|
Database resource |
Database resource |
|
|
Data object |
|
Data security policy |
Data security policy |
|
|
Data security grant |
|
Data security policy |
Entitlement policy |
|
|
|
|
Function security policy |
Resource policy |
|
|
Privilege grant |
|
Function security policy |
Entitlement policy |
|
|
|
|
Condition |
|
|
|
Instance set |
Function security is a statement of what actions you can perform in which user interface pages.
Data security is a statement of what action can be taken against which data.
Function security controls access to user interfaces and actions needed to perform the tasks of a job. For example, an accounts payable manager can view invoices. The Accounts Payable Manager role provisioned to the accounts payable manager authorizes access the functions required to view invoices. Function security is also sometimes called application security and controlled by duty roles.
Data security controls access to data. In this example, the accounts payable manager for the North American Commercial Operation can view invoices in the North American Business Unit. Since invoices are secured objects, and a data role template exists for limiting the Accounts Payable Manager role to the business unit for which the provisioned user is authorized, a data role inherits the job role to limit access to those invoices that are in the North American Business Unit. Objects not secured explicitly with a data role are secured implicitly by the data security policies of the job role.
Both function and data are secured through role-based access control.