How DLMP Aggregation Works
In a trunk aggregation, each port is associated with every configured datalink over the aggregation. In a DLMP aggregation, a port is associated with any of the aggregation's configured datalinks.
The following figure shows how a DLMP aggregation works.
Figure 2-4 DLMP Aggregation
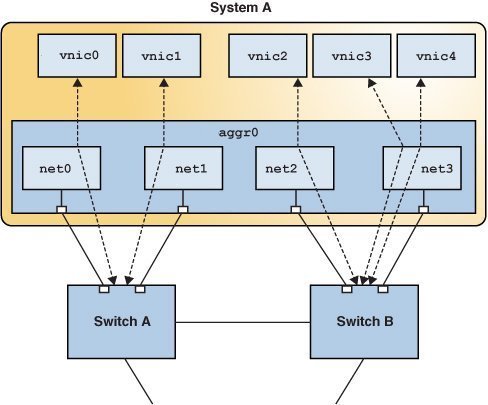
The figure shows System A with link aggregation aggr0. The aggregation consists of four underlying links, from net0 to net3. VNICs vnic0 through vnic4 are also configured over the aggregation. The aggregation is connected to Switch A and Switch B, which in turn connect to other destination systems in the wider network.
VNICs are associated with aggregated ports through the underlying links. For example, in the figure, vnic0 through vnic3 are associated with the aggregated ports through the underlying links net0 through net3. That is, if the number of VNICs and the number of underlying links are equal, then each port is associated with an underlying link.
If the number of VNICs exceeds the number of underlying links, then one port is associated with multiple datalinks. For example, in the figure the total number of VNICs exceeds the number of underlying links. Hence, vnic4 shares a port with vnic3.
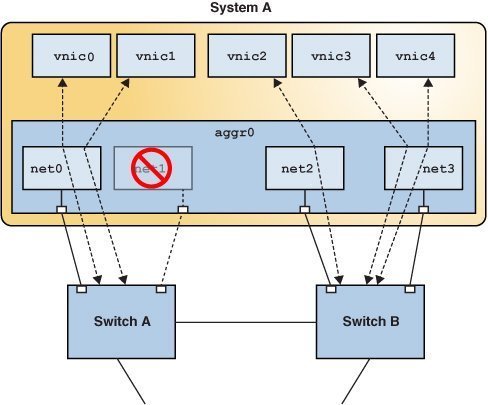
When an aggregated port fails, all the datalinks that use that port are distributed among the other ports, thereby providing network high availability during failover. For example, if net0 fails, then DLMP aggregation shares the remaining port net1, between VNICs. The distribution among the aggregated ports occurs transparently to the user and independently of the external switches connected to the aggregation.
The following figure shows how DLMP aggregation works when a port fails. In the figure, net1 has failed and the link between switch and net1 is down. vnic1 shares a port with vnic0 through net0.
Figure 2-5 DLMP Aggregation When a Port Fails