| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.7) Part Number E10224-16 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.7) Part Number E10224-16 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter describes how to define composite sensors that provide a method for implementing trackable fields on messages in a SOA composite application. It describes how to define sensors on binding components and on service components that have subscribed to business events. Restrictions are also described.
This chapter includes the following sections:
For information about activity, fault, and variable sensors in a BPEL process, see Chapter 18, "Using Oracle BPEL Process Manager Sensors."
Composite sensors provide a method for implementing trackable fields on messages. Composite sensors enable you to perform the following tasks:
Monitor incoming and outgoing messages.
Specify composite sensor details in the search utility of the Instances page of a SOA composite application in Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control. This action enables you to locate a particular instance.
Specify composite sensors included in the instances of SOA composite applications in the search utility of the Instances page of the SOA Infrastructure in Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control.
Publish JMS data computed from incoming and outgoing messages.
Track composite instances initiated through business event subscriptions.
You define composite sensors on service and reference binding components or on service components that have business event subscriptions in Oracle JDeveloper. This functionality is similar to variable sensors in BPEL processes. During runtime, composite sensor data is persisted in the database.
For information about searching for composite sensors in Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, see Section "Monitoring and Deleting SOA Composite Application Instances at the SOA Infrastructure Level" and Section "Monitoring and Deleting SOA Composite Application Instances from the Application Home Page" of Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management Suite.
Note the following restrictions on the use of composite sensors:
Functions can only be used with the payload. For example, XPath functions such as concat() and others cannot be used with properties.
Any composite sensor that uses expressions always captures values as strings. This action makes the search possible only with the like comparison operator. Also, even if the value is a number, you cannot use other logical operators such as <, >, =, and any combination of these.
Composite sensors only support two types of sensor actions: Enterprise Manager and JMS.
Header-based sensors are only supported for web service bindings.
Sensor actions for Oracle B2B, service data objects (SDOs), web services invocation framework (WSIF), and Oracle Business Activity Monitoring bindings are not supported.
Sensor values can only be one of the following types.
The following scalar types:
STRING
NUMBER
DATE
DATE_TIME
Complex XML elements
When creating an XPath expression for filtering, all functions that return a node set must be explicitly cast as a string:
xpath20:upper-case(string($in.request/inp1:updateOrderStatus/inp1:orderStatus) ) = "PENDING"
Sensors can only be configured on service components that subscribe to business events. The option to configure sensors is not available if there are no subscribed business events associated with the service component.
Sensors cannot be configured on service components that publish business events.
Sensors based on business event headers are not allowed (only payloads are allowed).
PL/SQL subscriptions are not supported.
You add sensors to the following components of a SOA composite application in the SOA Composite Editor:
Service or reference binding components
Service components such as a BPEL process or Oracle Mediator that have subscribed to business events
To add composite sensors:
Use one of the following options to add a composite sensor in the SOA Composite Editor.
Right-click a specific service or reference binding component in the Exposed Services or External References swimlane or a service component that has a subscribed business event. A service component that has a subscribed business event includes the word Subscribed on it.
Select Configure Sensors.
Note:
The service component must already have a subscribed business event for the Configure Sensors option to be displayed.
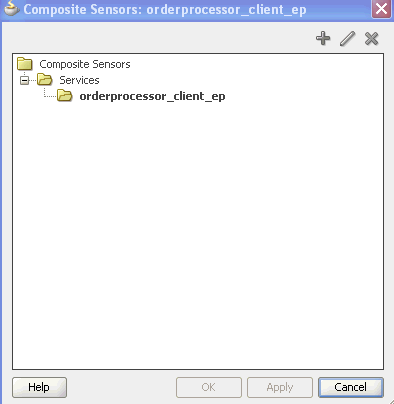
If you selected a binding component, the Composite Sensors dialog displays the details shown in Figure 50-1. For this example, a service binding component is selected.
Figure 50-1 Composite Sensors Dialog for the Selected Binding Component
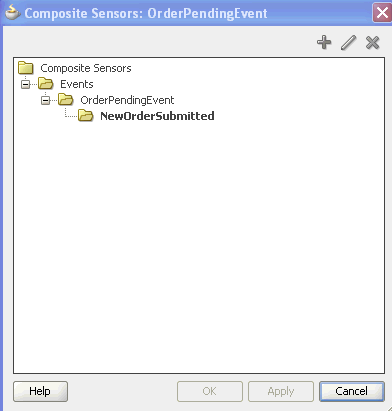
If you selected a service component, the Composite Sensors dialog displays the details shown in Figure 50-2.
Figure 50-2 Composite Sensors Dialog for the Selected Service Component
Select the binding component or service component, and click the Add icon.
or
Click the Composite Sensor icon above the SOA Composite Editor, as shown in Figure 50-3.
The Composite Sensors dialog for the SOA composite application appears, as shown in Figure 50-4. This option displays all the service and reference binding components and service components with subscribed business events in the SOA composite application.
Select the specific service, reference, or business event to which to add a composite sensor, then click the Add icon.
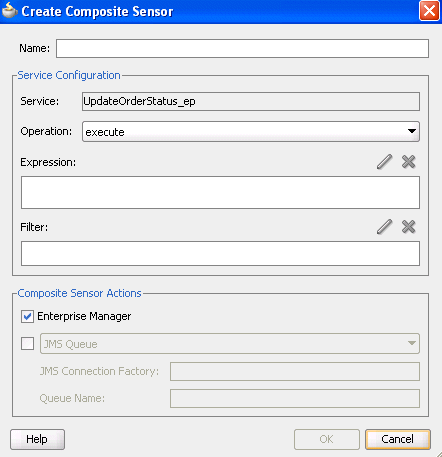
If you selected a binding component such as a service, the Create Composite Sensor dialog appears as shown in Figure 50-5.
Figure 50-5 Create Composite Sensor Dialog for a Service Binding Component
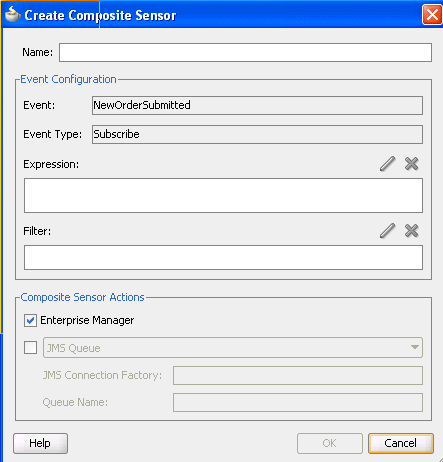
If you selected a service component that has a business event subscription, the Create Composite Sensor dialog appears as shown in Figure 50-6.
Figure 50-6 Create Composite Sensor Dialog for a Service Component
Enter the details shown in Table 50-1.
Table 50-1 Create Composite Sensor Dialog
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Enter a name for the composite sensor. You must enter a name to enable the Edit icon of the Expression field. |
|
Service |
Displays the name of the service. This field is only displayed if you are creating a composite sensor for a service binding component. This field cannot be edited. Service sensors monitor the messages that the service receives from the external world or from another composite application. |
|
Reference |
Displays the name of the reference. This field is only displayed if you are creating a composite sensor for a reference binding component. This field cannot be edited. Reference sensors monitor the messages that the reference sends to the external world or to another composite application. |
|
Operation |
Select the operation for the port type of the service or reference. This field only displays for service or reference binding components. |
|
Event |
Displays the name of the service component. This field is only displayed if you are creating a composite sensor for a service component. This field cannot be edited. Event sensors track composite instances initiated through a business event. You can create multiple sensors per business event. |
|
Event Type |
Displays the Subscribe business event type. This field cannot be edited. The publish business event type is not supported. |
|
Expression |
Click the Edit icon to invoke a dropdown list for selecting the type of expression to create:
|
|
Filter |
Click the Edit icon to invoke the Expression Builder dialog to create an XPath filter for the expression. You must first create an expression to enable this field. For example, you may create an expression for tracking purchase order amounts over $in.inDict/tns:inDict/ns2:KeyValueOfstringstring/ns2:Value > 10000.00 |
|
Composite Sensor Actions |
Displays the supported sensor actions. This feature enables you to store runtime sensor data. You can select both Enterprise Manager and either JMS Queue or JMS Topic.
Notes: The JMS Queue and JMS Topic selections enable the composite sensor data (XML payload) to be used by other consumers, including Oracle Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) and Oracle Complex Event Processing (CEP). Both selections use the native JMS support provided with Oracle WebLogic Server, and not the Oracle SOA Suite JMS adapter described in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Technology Adapters. You can view JMS messages in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. For information about using sensor data with Oracle BAM, see Chapter 53, "Integrating Oracle BAM with SOA Composite Applications." |
Click OK when complete.
For a service or reference binding component, a composite sensor icon displays in the upper right corner, as shown in Figure 50-7.
Figure 50-7 Sensor Icon on Binding Component
For a service component, a composite sensor icon also displays in the upper right corner, as shown in Figure 50-8.
Figure 50-8 Sensor Icon on Service Component

Place your cursor over the composite sensor icon to display details about the composite sensor.
The Select XPath Expression dialog shown in Figure 50-9 enables you to select an element for tracking.
To add a variable:
Expand the tree and select the element to track.
Click OK when complete.
The Expression Builder dialog shown in Figure 50-10 enables you to create an expression for tracking.
To add an expression:
Build an XPath expression of an element to track.
Click OK when complete.
The Select Property dialog shown in Figure 50-11 enables you to select a normalized message header property for tracking.
To add a property:
Select a normalized message header property to track.
Click OK when complete.
For more information about normalized messages, see Appendix H, "Normalized Message Properties."
Note the following details when using duplicate names for composite sensors.
If you create composite sensors with duplicate names, the entire contents of their definitions are compared. Duplicate names are permitted where one or more additional parameters are different (for example, either different configuration types or different expressions, filters, operation names, and so on). Something must be different in the definitions for duplicate names to be permitted.
If you have duplicate sensor definitions, only the last executed sensor value is persisted. Therefore, you can use this type of configuration for mutually exclusive paths (for example, a composite can be invoked through service 1 or service 2). Therefore, you can define the same sensor name on both the services. However, if you define the same names for service 1 and reference 1, only the sensor value from reference 1 (the last executed sensor) is stored.
You typically use multiple sensors with the same name to point to the same logical entity extracted from different sources (for example, Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control displays the final sensor value). Therefore, it would be confusing if the same sensor name is used to extract an email value and a social security value from different sources.
Sensor actions apply to all occurrences of the same sensor name. This situation means the sensor actions on the most recently defined sensor with the same name take precedence.
For the scenario shown in sensor.xml in Example 50-1, the following occurs:
The first two sensors named Service1 are identical. In addition, the configuration type for both is serviceConfig (composite sensors defined on a service binding component). Therefore, the sensors become one entry (the second one is ignored).
The third sensor named Service1 has a different configuration type of eventConfig (a composite sensor defined on a business event). Therefore, this sensor is represented with a separate entry.
The two sensors named PurchaseOrder Id have different configuration types (eventConfig and serviceConfig). Therefore, they are represented with separate entries.
The two sensors named PurchaseOrder have the same configuration type (eventConfig), but different expressions. Therefore, they are represented with separate entries.
Example 50-1 Duplicate Composite Sensors with Multiple Endpoints
<sensors xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/bpel/sensor"> <sensor sensorName="Service1" kind="service" target="undefined" filter=""> <serviceConfig service="OrderPublisher_ep" expression="$in.property.tracking.ecid" operation="execute" outputDataType="string" outputNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"/> </sensor> <sensor sensorName="Service1" kind="service" target="undefined" filter=""> <serviceConfig service="OrderPublisher_ep" expression="$in.property.tracking.ecid" operation="execute" outputDataType="string" outputNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"/> </sensor> <sensor sensorName="Service1" kind="event" target="undefined" filter="" xmlns:po="http://www.mycompany.com/ns/order"> <eventConfig component="EventMediator" expression="$in/po:PurchaseOrder/po:OrderID" event="{http://mycompany.com/events/orders}OrderReceivedEvent" outputDataType="string" outputNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"/> <sensor sensorName="Event1" kind="event" target="undefined" filter=""> <eventConfig component="EventMediator" actionType="Subscribe" expression="$in.property.tracking.ecid" event="{http://mycompany.com/events/orders}OrderReceivedEvent" outputDataType="string" outputNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"/> </sensor> <sensor sensorName="PurchaseOrder Id" kind="event" target="undefined" filter="" xmlns:po="http://www.mycompany.com/ns/order"> <eventConfig component="EventMediator" expression="$in/po:PurchaseOrder/po:OrderID" event="{http://mycompany.com/events/orders}OrderReceivedEvent" outputDataType="string" outputNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"/> </sensor> <sensor sensorName="PurchaseOrder Id" kind="service" target="undefined" filter=""> <serviceConfig service="OrderPublisher_ep" expression="$in.property.tracking.ecid" operation="execute" outputDataType="string" outputNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"/> </sensor> <sensor sensorName="PurchaseOrder" kind="event" target="undefined" filter="" xmlns:po="http://www.mycompany.com/ns/order"> <eventConfig component="EventMediator" expression="$in/po:PurchaseOrder" event="{http://mycompany.com/events/orders}OrderReceivedEvent" outputDataType="PurchaseOrder" outputNamespace="http://mycompany.com/events/orders"/> </sensor> <sensor sensorName="PurchaseOrder" kind="event" target="undefined" filter="" xmlns:po="http://www.mycompany.com/ns/order"> <eventConfig component="EventMediator" expression="$in/po:PurchaseOrder/po:OrderID" event="{http://mycompany.com/events/orders}OrderReceivedEvent" outputDataType="string" outputNamespace="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"/> </sensor> </sensor> </sensors>
During runtime, composite sensor data can be monitored in Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control:
Composite sensor data displays in the flow trace of a SOA composite application.
Composite sensor data can be searched for on the Instances page of a SOA composite application.
Composite sensors can be searched for on the Instances page of the SOA Infrastructure.
For more information about searching for composite sensors in Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, see Section "Monitoring and Deleting SOA Composite Application Instances at the SOA Infrastructure Level" and Section "Monitoring and Deleting SOA Composite Application Instances from the Application Home Page" of Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management Suite.