4 Getting Started with ADF Mobile Application Development
This chapter describes how to use the Oracle JDeveloper wizards and tools to create a basic ADF Mobile application and also describes the artifacts that are automatically generated when you create an application.
This chapter includes the following sections:
4.1 Introduction to Declarative Development for ADF Mobile Applications
Because ADF Mobile is integrated within the JDeveloper design time, you can create, deploy, and test simple ADF Mobile applications (and most parts of more complex mobile applications) without writing a single line of code.
4.2 Creating an Application Workspace
The ADF Mobile extension provides JDeveloper with the application templates that seed the completed project with basic files. The first steps in building an ADF Mobile application are to assign it a name and to specify a directory where its source files will be saved. By creating an application with the application templates provided by JDeveloper, the workspace is automatically organized into projects, along with the required configuration files.
4.2.1 How to Create a Workspace for an ADF Mobile Application
You create an application using the application creation wizard.
You must download the ADF Mobile application extension. For more information, see Section 3.3, "Setting Up JDeveloper." You may need to download and configure the ADF Mobile application extension for all target platforms.
To create an ADF Mobile application:
-
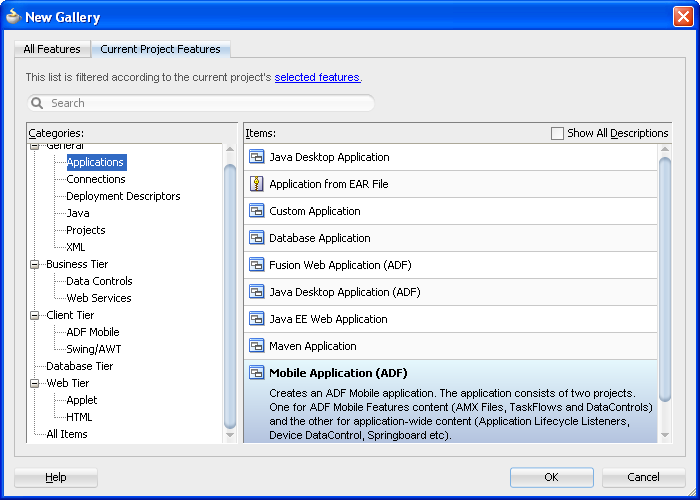
Choose File, then New, and then Mobile Application (ADF), as shown in Figure 4-1.
-
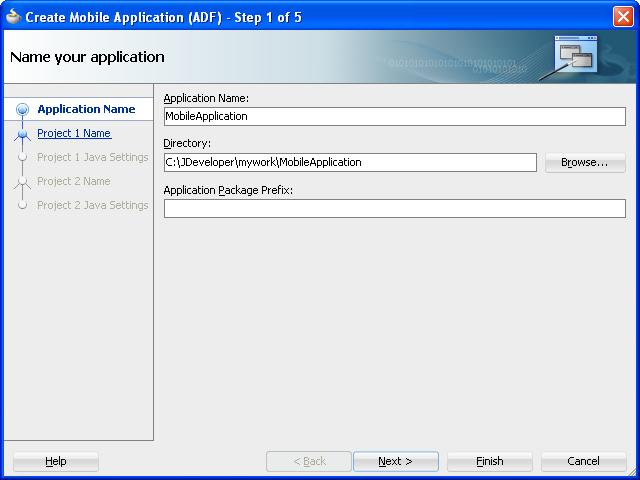
In the Application Name field, enter a name for the application, such as MobileApplication in Figure 4-2. If needed, enter a new location for the project in the Directory field. Ensure that the application package is unique by entering a prefix for it in the Application Package Prefix field. Click Next.
The application is the top-level structure of the ADF Mobile application. It organizes the different tiers of projects that you define in the subsequent pages of this wizard.
-
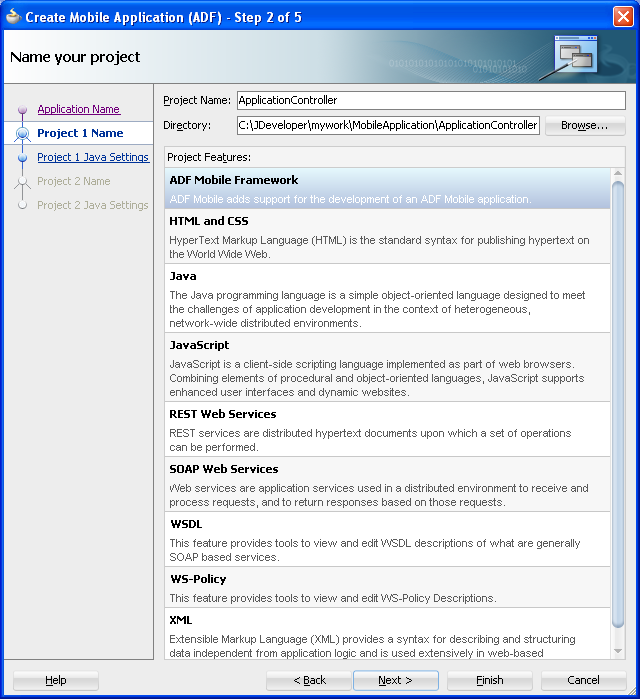
In the Project 1 Name page, change the name and location of the application controller project (if needed), as shown in Figure 4-3. Otherwise, accept the default name of the project, ApplicationController. This Project Feature window of the page lists the technologies available to the application controller project.
This project stores all of the application-wide resources. For more information, see Table 4-1.
-
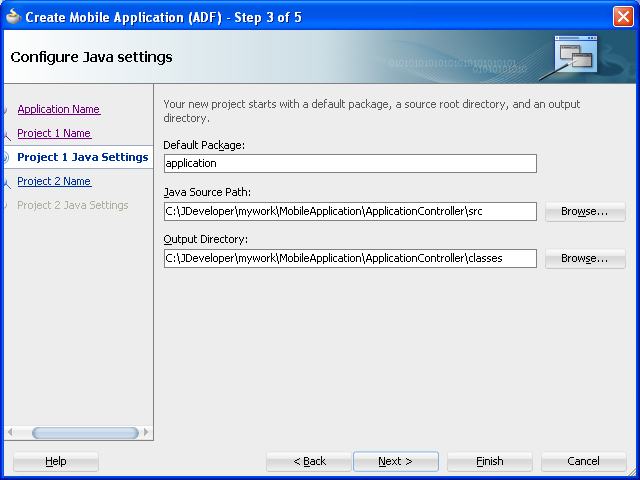
Click Next to the Java Settings page for the application controller project (Project 1 Java Settings, shown in Figure 4-4). Accept, or change, the default package name for the application controller project (
application) and the location for the JavaSOURCEPATHdirectory (src) and the Java output directory (classes). -
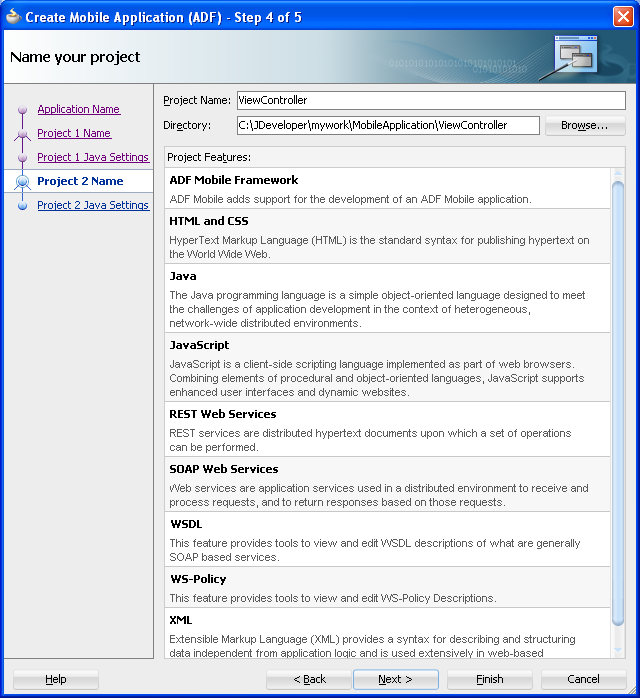
Click Next to traverse to the Project 2 Name page, where you can, if needed, rename the view controller project. The page's Project Features window, shown Figure 4-5, lists the technologies available to the ADF Mobile view controller project. For information on the artifacts created within view controller project, see Table 4-2.
-
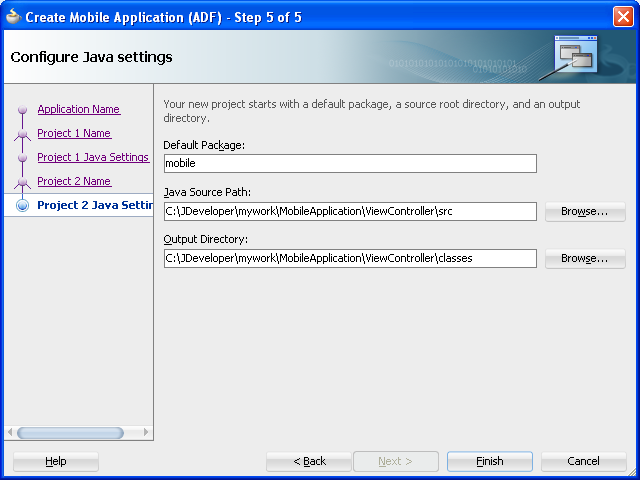
Click Next. In the Java settings page for the view controller project, shown in Figure 4-6, accept (or change) the default package name for the application controller project (
mobile), the location for the project's JavaSOURCEPATHdirectory (src) and the Java output directory (classes). -
Click Finish to complete the creation of the ADF Mobile application and its projects.
Tip:
In addition to creating an ADF Mobile application following the above-mentioned steps, you can open the HelloWorld sample application (located in the PublicSamples.zip file within the jdev_install/jdeveloper/jdev/extensions/oracle.adf.mobile/Samples directory on your development computer) and view the artifacts that JDeveloper generates after you complete the application creation wizard.
4.2.2 What Happens When You Create an ADF Mobile Application
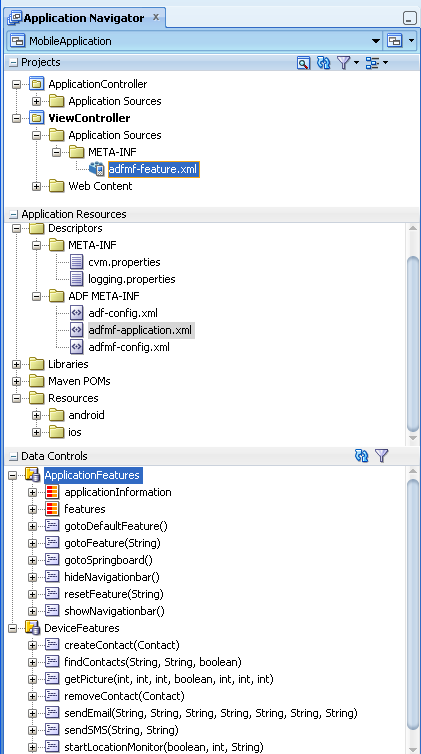
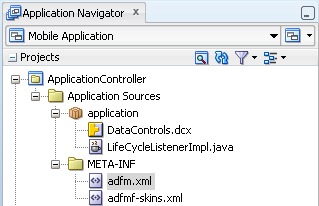
After you create an ADF Mobile application project, JDeveloper adds application-level and project-level artifacts, which you access from the Application Navigator shown in Figure 4-7. These artifacts include two stub descriptor files: one used for configuring the ADF Mobile application itself, such as its name, the application lifecycle listener (LifeCycleListenerImpl.java), the login server connections for the embedded application features, and another that describes which application features comprise the ADF Mobile application. These files, which are called adfmf-application.xml and adfmf-feature.xml, are described in Section 4.2.2.1, "About the Application Controller Project-Level Resources" and Section 4.2.2.2, "About the View Controller Project Resources," respectively.
JDeveloper also creates the DeviceFeatures data control. The Apache Cordova Java API is abstracted through this data control, thus enabling the application features implemented as ADF Mobile AMX to access various services embedded on the device. JDeveloper also creates the ApplicationFeatures data control, which enables you to build a springboard page. By dragging and dropping the operations provided by the DeviceFeatures data control into an ADF Mobile AMX page (which is described in Section 8.5, "Using the DeviceFeatures Data Control"), you add functions to manage the user contacts stored on the device, create and send both e-mail and SMS text messages, ascertain the location of the device, use the device's camera, and retrieve images stored in the device's file system.
4.2.2.1 About the Application Controller Project-Level Resources
JDeveloper generates the files for ADF Mobile application in the application controller project. These files, described in Table 4-1, contain configuration files for describing the metadata of the ADF Mobile application. You access these files from the Application Resources pane of the Application Navigator, shown in Figure 4-8.
The application controller project, which contains the application-wide resources, provides the presentation layer of the ADF Mobile application in that it includes metadata files for configuring how the application will display on a mobile device. This project dictates the security for the ADF Mobile application and can include the application's login page, an application-wide resource. The application controller project is essentially a consumer of the view controller project, which defines the application features and their content. For more information, see Section 4.2.2.2, "About the View Controller Project Resources."
Tip:
Place code that supports application-wide functionality, such as an application-level lifecycle listener, in the application controller project.
Table 4-1 Mobile Application-Level Artifacts Accessed Through Application Resources
| Artifact(s) | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
For example:
|
A stub XML application descriptor file that enables you to define the ADF Mobile application. Similar to the application descriptors for ADF Fusion Web applications, this file enables you to define the content for an application, its navigation behavior, and its user authentication requirements. For more information, see Section 5.2, "About the Mobile Application Configuration File." |
|
|
For example:
|
Use to configure the default skin used for ADF Mobile applications. For more information, see Section 5.12, "Skinning ADF Mobile Applications." |
|
Application images |
For example:
|
A set of images required for the deployment of iOS and Android applications. These include PNG images for application icons and splash screens. Deployment to an iOS-powered device, such as an iPhone, requires a set of images in varying sizes. The default iOS images provided with the project include:
To override these images, see Section 17.2.4.3, "Adding a Custom Image to an iOS Application." |
|
|
For example:
|
The |
|
|
For example:
|
Enables you to set the application error logging, such as the logging level and logging console. For more information, see Section 19.4, "Using and Configuring Logging." |
|
|
For example:
|
The configuration file for the Java virtual machine, JVM 1.4. Use this file to configure the application startup and heap space allotment, as well as Java and JavaScript debugging options. For more information, see Section 19.3.4, "How to Enable Debugging of Java Code and JavaScript." |
|
|
For example:
|
Used to configure application-level settings, including the Configuration Service parameters. For more information, see the "adf-config.xml" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. See also Chapter 10, "Administering Web Services." |
|
|
For example:
|
The repository for all of the connections defined in the ADF Mobile application. See also the "Lookup Defined in the connections.xml File" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. |
Within the application controller project itself, shown in Figure 4-9, JDeveloper creates the following artifacts, listed in Table 4-2.
Table 4-2 Application Controller Artifacts
| Artifact(s) | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
For example:
|
The default application lifecycle listener (ALCL) for the ADF Mobile application. For more information, see Section 5.7, "About Lifecycle Event Listeners." |
|
|
For example:
|
Defines the available skins and also enables you to define new skins. For more information, see Section 5.12, "Skinning ADF Mobile Applications." |
|
|
For example:
|
Maintains the paths (and relative paths) for the |
|
|
For example:
|
The data controls registry. For information on using the DeviceFeature data control, which leverages the services of the device, see Section 8, "Using Bindings and Creating Data Controls." For information on the ApplicationFeatures data control, which enables you to create a springboard page that calls the embedded application features, see Section 5.5.5, "What You May Need to Know About Custom Springboard Application Features with ADF Mobile AMX Content." For more information see the "Configuring the ADF Binding Filter" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework. |
4.2.2.2 About the View Controller Project Resources
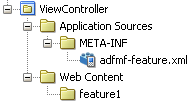
The view controller project (which is generated with the default name, ViewController, as illustrated in Figure 4-10) houses the resources for the application features. Unlike the application controller project described in Section 4.2.2.1, "About the Application Controller Project-Level Resources," the view controller project's metadata files describe the resources at the application feature-level, in particular the various application features that can be aggregated into an ADF Mobile application so that they can display on a mobile device within the springboard of the ADF Mobile application itself or its navigation bar at runtime. Further, the application feature metadata files describe whether the application feature is comprised of HTML or ADF Mobile AMX pages. In addition, the view controller project can include these application pages as well as application feature-level resources, such as icon images to represent the application feature on the springboard and navigation bar defined for the ADF Mobile application.
Tip:
Store code specific to an application feature within the view controller project. Use the application controller project as the location for code shared across application features, particularly those defined in separate view controller projects.
The view controller project can be decoupled from the application controller project and deployed as an archive file for reuse in other mobile applications as described in Section 5.13, "Working with Feature Archive Files." In rare cases, an application controller project can consume more than one view controller project.
Note:
Adding an ADF Mobile view controller project as a dependency of another ADF Mobile view controller project, or as a dependency of an ADF Mobile application controller project, prevents the deployment of an ADF Mobile application. For more information, see Section 5.6.2, "What You May Need to Know About Feature Reference IDs and Feature IDs."
As shown in Table 4-3, these resources include the configuration file for application features called adfmf-feature.xml.
Table 4-3 View Controller Artifacts
| Artifact(s) | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
For example:
|
A stub XML descriptor file that enables you to define application features. For more information, see Section 5.8, "About the Mobile Feature Application Configuration File." After you have configured the Mobile Preferences as described in Section 3.3.1, "How to Configure the Development Environment for Platforms and Form Factors," you can deploy this application using the default deployment profile settings. For more information, see Chapter 17, "Deploying ADF Mobile Applications." |
|
Application-Specific Content |
For example:
|
The application features defined in |
4.2.2.3 About Automatically Generated Deployment Profiles
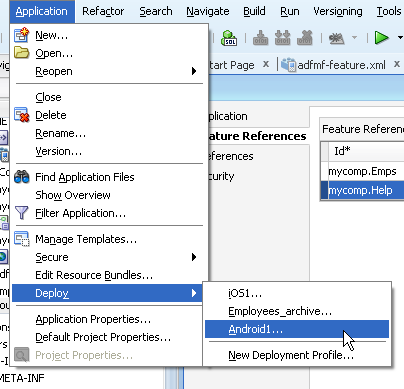
After you create an application, ADF Mobile generates deployment profiles that are seeded with default settings and image files. Provided that you have configured the environment correctly, you can use these profiles to deploy an ADF Mobile application immediately after creating it by choosing Applications and then Deploy, as shown in Figure 4-11.
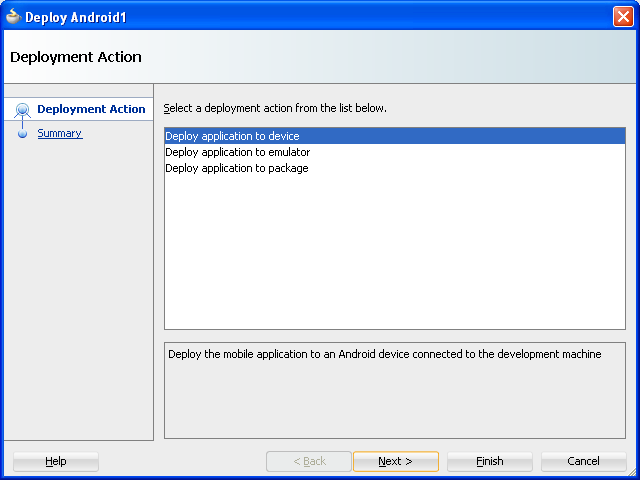
Using the Deployment Action page, shown in Figure 4-12, you then select the appropriate deployment target.
Note:
iOS and Android application deployments to simulators and devices have distinct environment set up and configuration requirements. For more information, refer to the "Before You Begin" sections throughout Section 17.3, "Deploying an Android Application," and Section 17.4, "Deploying an iOS Application."
As illustrated in Figure 4-11, ADF Mobile creates application-level profiles for both supported platforms (iOS and Android) and names them iOS1 and Android1.
Note:
ADF Mobile increments the name of each new deployment profile by 1. For example, iOS2, iOS3.
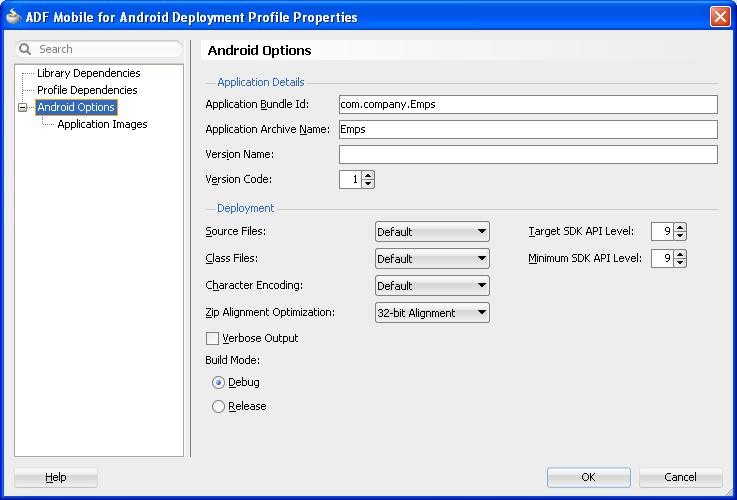
You can accept the default values used for these profiles, or edit them by selecting the profile from the Deployment page of the Application Properties dialog and then clicking Edit. Figure 4-13 illustrates the Options page for a default Android application profile. For information on the values configured for ADF Mobile application profiles, see Section 17.2.3, "How to Create an Android Deployment Profile" and Section 17.2.4, "How to Create an iOS Deployment Profile."
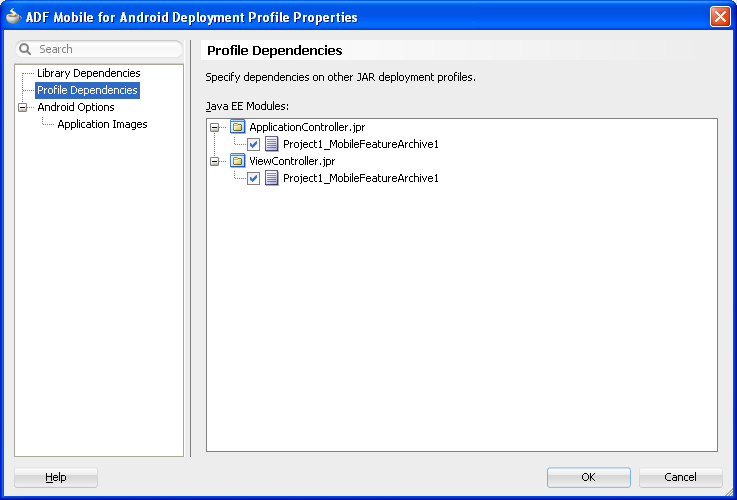
ADF Mobile packages the application and view controller projects as separate Feature Archive (FAR) files. These JAR files of ADF Mobile files are used as resources for other applications and are described in Section 17.5, "Deploying Feature Archive Files (FARs)." Because ADF Mobile creates these FAR files as dependencies to the ADF Mobile application profile, you can include or exclude them using the Profile Dependencies page of the Application Properties dialog, as illustrated in Figure 4-14.
Note:
The application controller project must contain a single FAR profile dependency; otherwise, the deployment will fail.
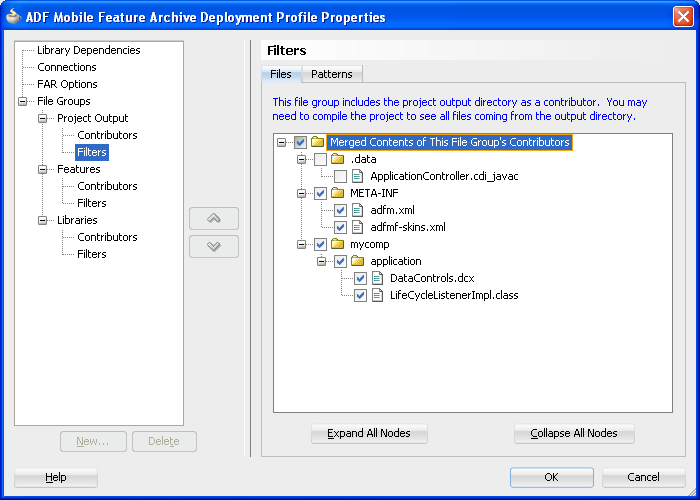
Using the File Groups-related pages of the Project Properties dialog, you can customize the contents of the view controller FAR file, as shown in Figure 4-15. For more information on the Project Properties dialog, see the Oracle JDeveloper online help and also the "Configuring Deployment Profiles" in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle JDeveloper.
In addition to the platform-specific deployment profiles, ADF Mobile also creates a deployment profile that enables you to package the ADF Mobile application as a Mobile Application Archive (.maa) file. Using this file, you can create a new ADF Mobile application using a pre-existing application that has been packaged as an .maa file. For more information, see Section 17.6, "Creating a Mobile Application Archive File" and Section 17.7, "Creating Unsigned Deployment Packages."
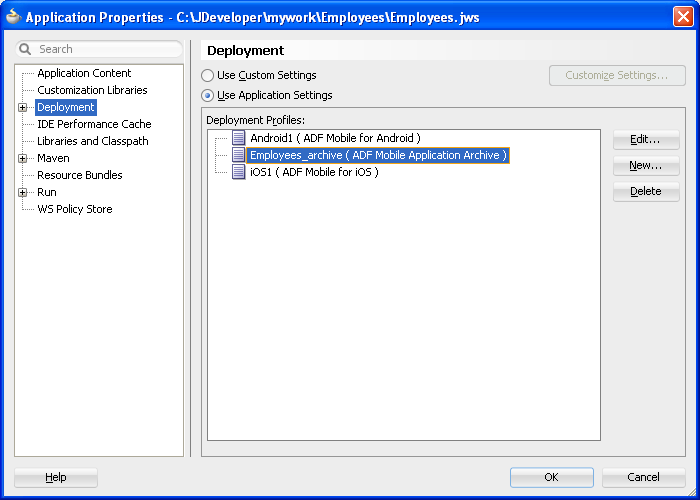
By default, this deployment file bears the name of the ADF Mobile application followed by _archive. As illustrated in Figure 4-11, this profile is called Employees_archive and, if needed, can be edited using the Application Properties dialog.
For more information on editing deployment profiles using the Application Properties dialog pages, see the "Viewing and Changing Deployment Profile Properties" section in described in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle JDeveloper and the Oracle JDeveloper online help for the Application Properties and Project Properties dialogs.
4.2.3 What You May Need to Know About Editing ADF Mobile Applications and Application Features
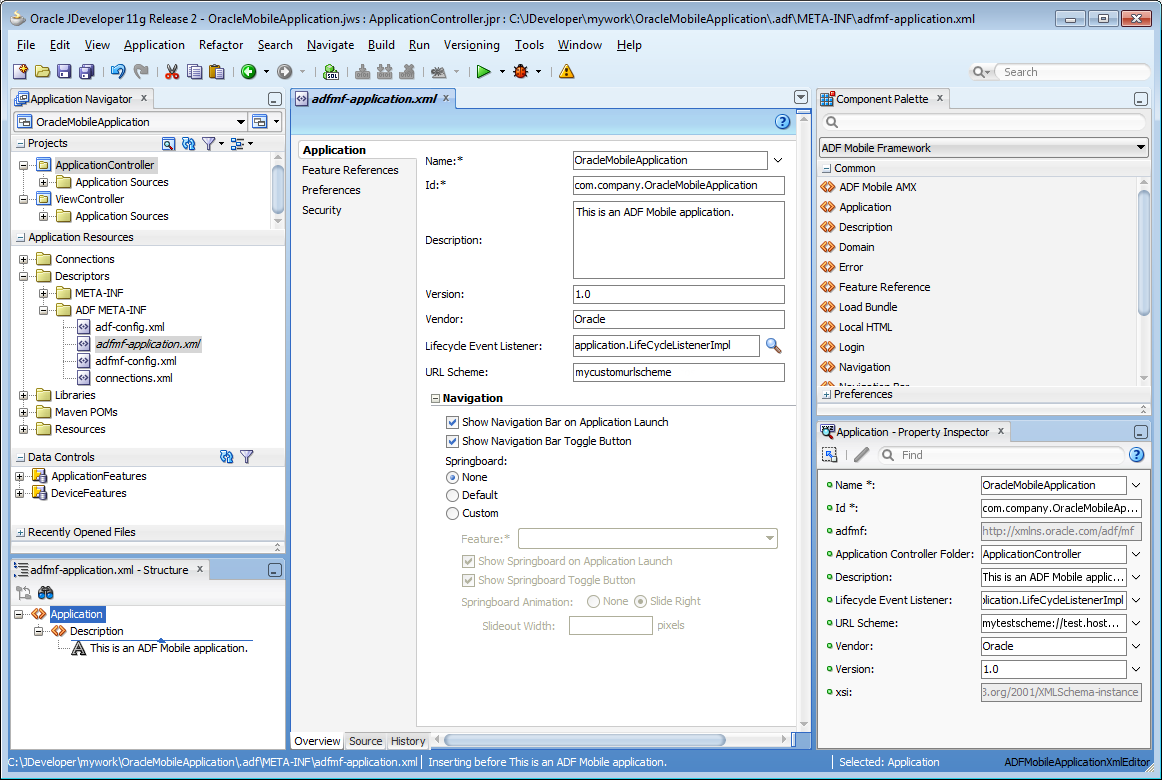
Creating an application results in the generation of the adfmf-application.xml file, which enables you to configure the mobile application and also the adfmf-features.xml file, which you use to add, remove, or edit the application features embedded within the mobile application. The ADF Mobile extension provides you with overview editors for both of these files, enabling you to declaratively change them. Figure 4-17 shows an example of the overview editor of the adfmf-application.xml file.
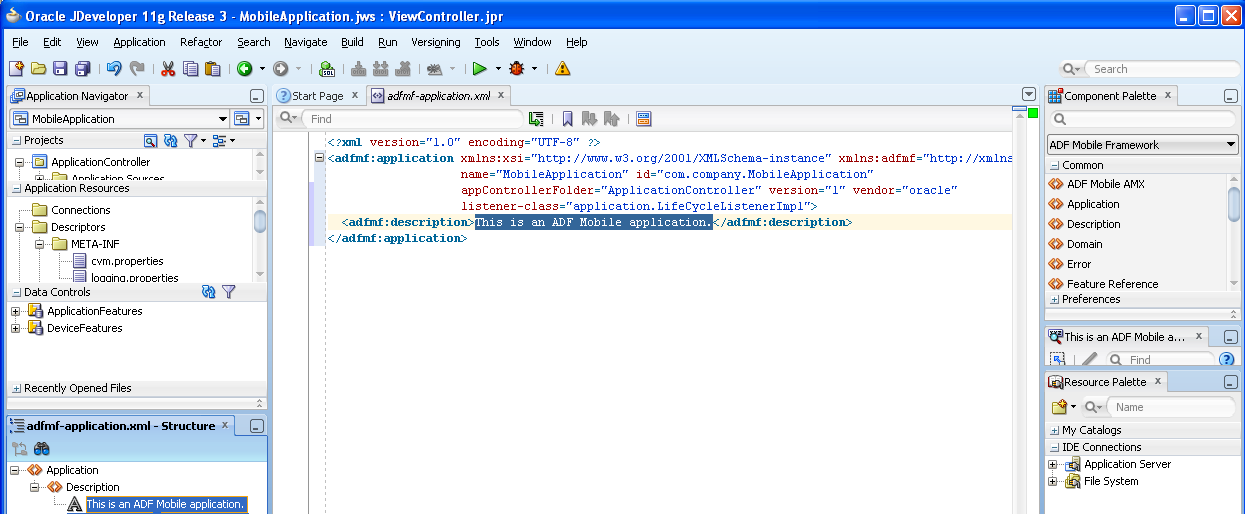
As shown in Figure 4-17, the adfmf-application.xml file is located in the Application Navigator in the Application Resources panel, under the Descriptors and ADF META-INF nodes. You can open this file by double-clicking it from this location. When you access this file, JDeveloper not only opens the associated overview editor, but also displays the pertinent page components in the component palette, which you can drag and drop into either the Source page of the editor or the Structure window, as shown in Figure 4-18. Section 5.2, "About the Mobile Application Configuration File" describes the components of the adfmf-application.xml page.
Figure 4-18 Using the Source Editor, Structure Window, and Properties Editor for the ADF Mobile Application
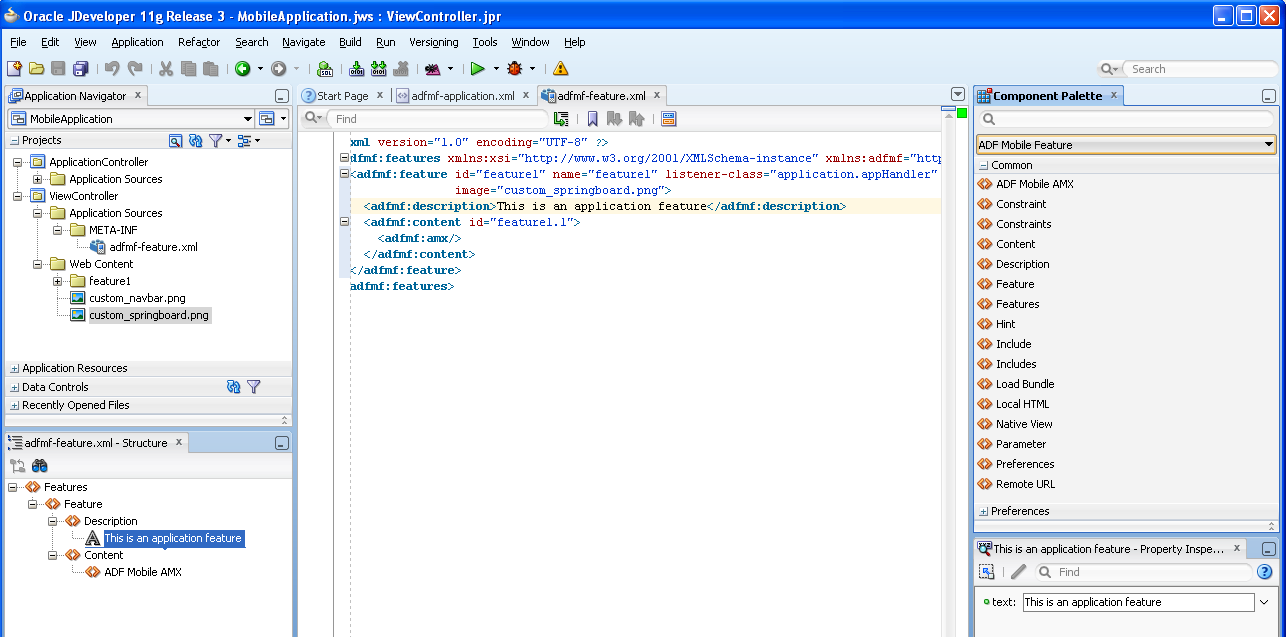
As illustrated in Figure 4-19, the adfmf-feature.xml configuration file is located in the Application Navigator in the Project panel under the view controller and META-INF nodes. You use this file to compose the content for the ADF Mobile application.
Like the overview editor for the adfmf-application.xml file, JDeveloper presents the ADF Mobile components used for building the elements of the adfmf-features.xml configuration file, which are described in Section 5.8, "About the Mobile Feature Application Configuration File." You can use the Overview page or you can drag and drop components from the Component Palette into the Structure window or into the Source editor itself. When you select the adfmf-feature.xml file, JDeveloper populates the Component palette with ADF Mobile Feature components.
4.2.4 Creating an Application Workspace for an ADF Mobile AMX Application
As described in Chapter 6, "Creating ADF Mobile AMX Pages," the ADF Mobile AMX components enable you to build pages that run identically to those authored in a platform-specific language. These pages may be created by the application assembler, who creates the ADF Mobile application and embeds application features within it, or they can be developed by another developer and then incorporated into the ADF Mobile application either as an application feature or as a resource to an ADF Mobile application.
The project in which you create the ADF Mobile AMX page determines if the page is used to deliver the content for a single application feature or be used as a resource to the entire ADF Mobile application. For example, a page created within the application controller project, as shown in Figure 4-23, would be used as an application-wide resource. An ADF Mobile AMX page created within a view controller project, on the other hand, would be used only to deliver content to an application feature.
An ADF Mobile task flow can likewise be used to deliver the content to an application feature. As shown in Figure 4-21, ADF Mobile provides wizards for adding ADF Mobile AMX pages, task flows, and application features.
To access these wizards, you first select a project within the Application Navigator and then choose File and then New. You select one of the wizards after selecting ADF Mobile within the Client Tier.
4.2.4.1 How to Create an ADF Mobile AMX Page
You can use the ADF Mobile AMX Page wizard to create AMX pages used as application feature content and separately as a resource to the ADF Mobile application. For more information on application feature content, see Section 5.10.1, "How to Define the Application Content."
To create an ADF Mobile AMX page as content for an application feature:
-
In the Application Navigator, right-click the view controller project.
-
Choose File and then New.
-
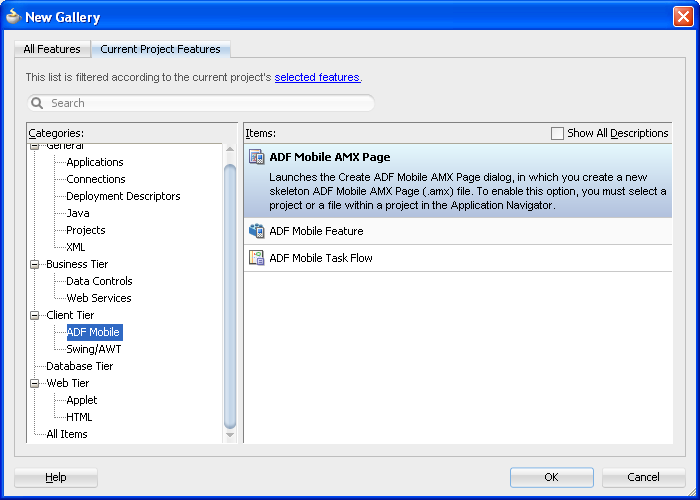
From the Client Tier node in the New Gallery, choose ADF Mobile AMX Page and then click OK.
-
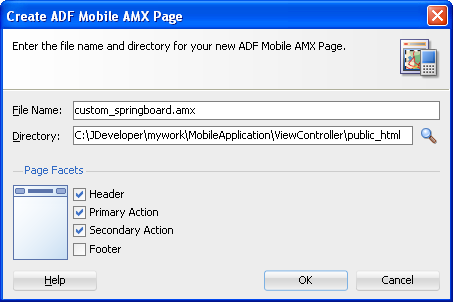
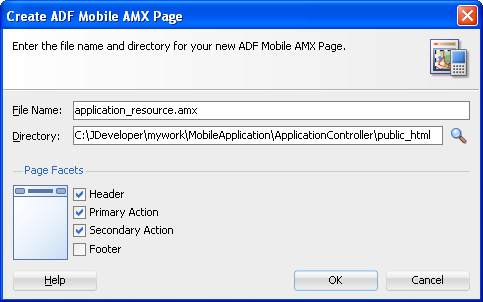
Complete the Create ADF Mobile AMX Page dialog, shown in Figure 4-22, by entering a name in the File Name field. In the Directory field, enter the file location, which must be within the
public_htmlfolder of the view controller project. -
Select (or deselect) the Facets within the Panel Page that are used to create a header and footer. Click OK.
For more information, see Section 7.2.2, "How to Use a Panel Page Component."
-
Build the ADF Mobile AMX page. For more information using the ADF Mobile AMX components, see Section 6.3.1.2, "Creating ADF Mobile AMX Pages." See also Section 5.10.1, "How to Define the Application Content."
To create an ADF Mobile AMX page as a resource to an ADF Mobile application:
-
In the Application Navigator, select the application controller project.
-
Choose File and then New.
-
From the Client Tier node in the New Gallery, select ADF Mobile AMX Page, and then click OK.
-
Complete the Create ADF Mobile AMX Page dialog, shown in Figure 4-23, by entering a name in the File Name field. In the Directory field, enter the file location, which must be within the
public_htmlfolder of the application controller project. Click OK. -
Build the ADF Mobile AMX page. For more information, see Section 6.3.1.2, "Creating ADF Mobile AMX Pages."
4.2.4.2 How to Create ADF Mobile Task Flows
You can deliver the content for an application feature as an ADF Mobile task flow.
To create an ADF Mobile Task Flow as content for an application feature:
-
In the Application Navigator, select the view controller project.
-
Choose File and then New.
-
From the Client Tier node in the New Gallery select ADF Mobile Task Flow and then click OK.
-
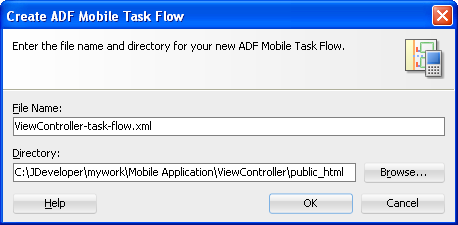
Complete the Create ADF Mobile AMX Page dialog, shown in Figure 4-24, by entering a name in the File Name field. In the Directory field, enter the file location, which must be within the
public_htmlfolder of the view controller project. Click OK. -
Build the task flow. See also Section 6.2, "Creating Task Flows."
4.2.4.3 What Happens When You Create ADF Mobile AMX Pages and Task Flows
JDeveloper places the ADF Mobile AMX pages and task flows in the Web Content node of the view controller project, as shown by custom_springboard.amx and ViewController-task-flow.xml (the default name for a task flow created within this project) in Figure 4-25. These artifacts are referenced in the adfmf-feature.xml file as described in Section 5.6, "Configuring the Application Features within a Mobile Application." Figure 4-25 also illustrates that other resources, such as customized application splash screen (or launch) images and navigation bar images, are also housed in the Web Content node. For more information, refer to Table 4-3.
Figure 4-25 ADF Mobile AMX Pages and Task Flows within Application Controller and View Controller Projects
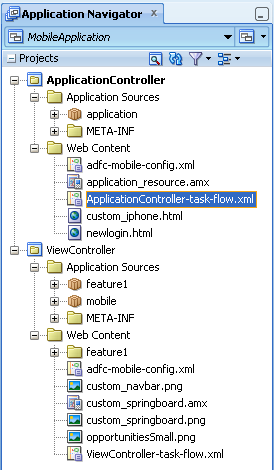
JDeveloper places the ADF Mobile AMX page and task flow as application resources to the ADF Mobile application in the Web Content node of the application controller project. As illustrated in Figure 4-25, the file for the ADF Mobile AMX page is called application_resource.amx and the task flow file is called ApplicationController-task-flow.xml (the default name).