| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Sun Ethernet Fabric Operating System LA Administration Guide |
Configuring Port-Channel Interfaces
Configure Port-Channel Interfaces
Configure the LACP Port Priority
Configure the LACP System Priority
Configure Port Channel Load Balancing
Configure the LACP System Identifier
Configure the LACP Port Identifier
Set the MTU Value on one or More Ports
Set the MTU Value of the Port Channel
LA enables aggregation of point-to-point links operating at the same data rate. LA is supported only on point-to-point links with MAC clients operating in full-duplex mode.
A MAC client communicates with a set of ports through an aggregator, which presents a standard IEEE 802.3 service interface to the MAC client. The aggregator binds to one or more ports within a system.
LACP is used for automatic communication of aggregation capabilities and automatic configuration of link aggregation between systems. The list of ports that are aggregated to a particular aggregator, is transparent to the higher modules (such as spanning tree).
LA features include:
Load sharing
Increased availability
Increased bandwidth
Linear incremental bandwidth
Low risk of duplication or misordering
Upon link aggregation, individual point-to-point ports or interfaces are aggregated into a group that is regarded as a single port or interface by the higher layers, such as the spanning tree. The total capacity of such an aggregated group is the sum of the capacities of the individual links that compose the aggregate. Thus, LA provides higher bandwidth to the MAC client (such as spanning tree).
As shown in the following illustration, multiple links on the server side of the switch are aggregated together to form a single link.
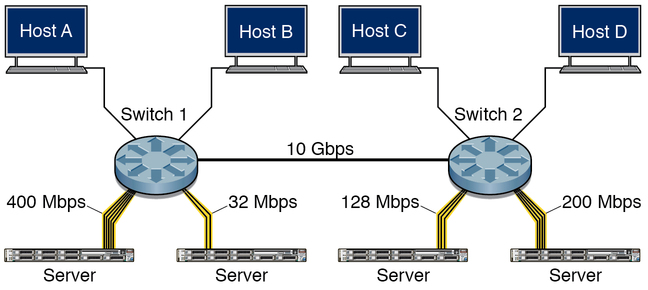
SEFOS LA takes frames from the aggregator and submits them for transmission on the appropriate port. The physical port for transmission is chosen based on the selection policy in the chip set. Similarly, SEFOS LA collects the frames that are received on various ports of the aggregator.
You can configure a specific distribution policy for the traffic flow based on the deployment scenario. This scenario allows the switches to take advantage of the increased bandwidth for the traffic between the hosts and the server. Also, if one of the links in the aggregation group is brought down for maintenance, the loss of the link will not affect the traffic between the hosts and the server.