Oracle®
Agile Product Lifecycle Management for Process
Extended Attribute Calculation Guide
Extensibility
Pack 3.7
E51191-01
January 2014
![]()
Copyrights
and Trademarks
Agile Product Lifecycle Management for Process
Copyright © 1995, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications which may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure the safe use of this software. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software and documentation may provide access to or information on content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.
Contents
Available PLM for Process Functions and Properties
Calculation Warnings and Errors
Processing Results Returned by an Enumerator
Custom Calculation Classes (aka Dynamic Script Methods)
Determining Calculation Location
Available Properties and Functions
Variables of Current Business Object
Distinct Extended Attribute Value Functions
Distinct Extended Attribute Boolean Functions
Custom Section Cell Properties
Custom Section Cell Retrieval Functions
Preface
Audience
This guide is intended for client programmers involved with integrating Oracle Agile Product Lifecycle Management for Process. Information about using Oracle Agile PLM for Process resides in application-specific user guides. Information about administering Oracle Agile PLM for Process resides in the Oracle Agile Product Lifecycle Management for Process Administrator User Guide.
Variability of Installations
Descriptions and illustrations of the Agile PLM for Process user interface included in this manual may not match your installation. The user interface of Agile PLM for Process applications and the features included can vary greatly depending on such variables as:
§ Which applications your organization has purchased and installed
§ Configuration settings that may turn features off or on
§ Customization specific to your organization
§ Security settings as they apply to the system and your user account
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Access to Oracle Support
Oracle customers have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.
Software Availability
Oracle Software Delivery Cloud (OSDC) provides the latest copy of the core software. Note the core software does not include all patches and hot fixes. Access OSDC at:
http://edelivery.oracle.com
Overview
Calculated Extended Attributes allow you to create a read-only extended attribute (EA) that displays results of a calculation to the user. The calculation, specified in the Data Admin user interface for Extended Attributes, must be written in JScript, an interpreted, object-based scripting language that is the Microsoft implementation of the ECMA 262 language specification (ECMAScript Edition 3).
The calculation script can access data from other extended attributes, custom sections, nutrients, and other data from the business object (e.g., specifications) the EA is attached to. Additionally, the script can execute a call to a custom class to return additional data to the script.
This document details the process of creating JScript calculation scripts, accessing data from various available sources, and leveraging custom classes for the calculation.
Reference implementation code is also available in the Extensibility Pack release that provides guidelines and example implementations of creating a custom calculation class extension point.
Calculation
Scripting
All Calculated EAs (Calculated Numeric, Calculated Text, and Calculated Boolean) must implement a calculation using JScript. However, most calculations require data available on the business object (specification, sourcing approval, etc.). Therefore, PLM for Process allows for ways to extend the JScript feature set by exposing many predefined PLM for Process functions and properties that give access to specific data. Additionally, JScript can be used to execute custom classes and get a return value to aid in the calculation.
The basic calculation script requirement is to return a value that can be converted to the relevant .NET type.
- Calculated Boolean –
must return a Boolean, or NULL
- Calculated Numeric –
must return an integer, double, or float
- Calculated Text – must
return a string.
For example:
var x @ GetNutrientPer100g('PROCNT');
return x/2;
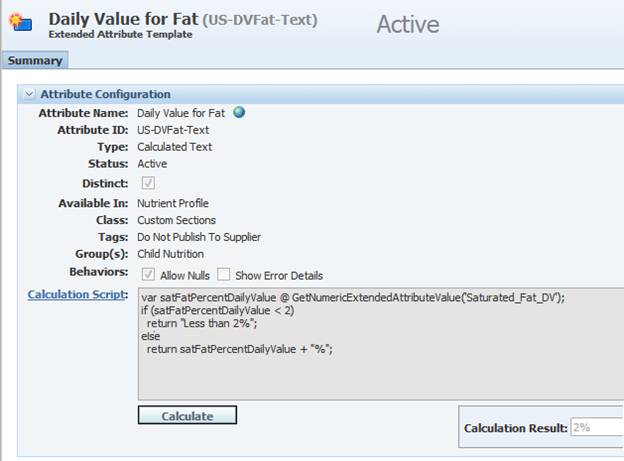
The following screenshot demonstrates a Calculated Text extended attribute that uses JScript to determine if the daily value for fat is less than 2%. If it is it returns “Less than 2%”, otherwise it returns the daily value for fat, followed by a % symbol.
JScript
Syntax Changes
When creating a JScript calculation script, there are several special syntactical modifications required for PLM for Process that differ from JScript.
Variable
Assignment
You must use the ‘@’ sign for assignment, which will get converted to an equals (=) sign when the script is being interpreted. For example:
var x @ 3.75; //declare variable x to be 3.75
Comparison
Operators
When comparing values, use a single equals (=) sign, which will get converted to a double equals (==) sign when the script is being interpreted. For example:
if (x = y) //checks to see if x is equal to y
{ \\ do something . . . }
Likewise, use the <@ and @> signs for less than or equal to and greater than or equal to, respectively.
To test inequality, use !@ for not equals (!=).
|
Operation |
Use this |
Instead of this |
|
Variable assignment |
@ |
= |
|
Equals |
= |
== |
|
Not equals |
!@ |
!= |
|
Less than or equal to |
<@ |
<= |
|
Greater than or equal to |
>@ |
>= |
This sample JScript calculation shows how to do use conditional logic, variable assignment, and comparison with the required syntax changes for PLM for Process scripts.
var x @ 3; //declare variable x to be 3
var y @ 7; //declare variable y to be 7
var z @ 6; //declare variable z to be 6
var result; //declares a variable called result
result @ GetNutrientPer100g('PROCNT'); //assigned the Protein amount per 100g to result variable
if ( x = y ) //checks to see if x is equal to y
{
if (z<y && y>x) //checks to see if z is less than y and y is greater than x
result@result+1; //adds one to the result
else
result@result+2; //adds two to the result
}
else if ( x <@ y ) //checks to see if x is less than or equal to y
{
if (z<y || y>x) //checks to see if z is less than y or y is greater than x
result@result+10; //adds ten to the result
else
result@result+12; //adds twelve to the result
}
else // x is greater than y
{
result @ 100; //set the result to 100
}
return result;
Available
PLM for Process Functions and Properties
One of the major features available to EA calculation scripts is the ability to access many out of the box PLM for Process functions and properties. These functions and properties provide access to various data elements of the business object that the EA is added to, such as nutrition information, compliance values, custom section and extended attribute values, and more.
Referencing the name of the function or property in the script will allow it to be called.
For example, the following script would return the value of the numeric extended attribute with a unique attributeID of “HeatIndex.” This is an example of how to set up a calculated attribute that references another extended attribute.
var heat @ GetNumericExtendedAttributeValue('HeatIndex');
return heat;
In the following example, a property called BeginningBatchSize, which returns the beginning batch size of a formulation specification, is used to evaluate the Protein per Batch calculation. The GetNutrientPer100g function is passed “PROCNT”, a nutrient id (see InFoods IDs in the Appendix) representing Protein. This script simply returns the result of dividing the protein amount per 100g by beginning batch size.
return BeginningBatchSize/GetNutrientPer100g('PROCNT');
A detailed listing of all available functions and properties is available in Available Properties and Functions.
Calculation
Warnings and Errors
When calling some of the predefined functions, warning messages may get generated under certain conditions. For instance, when trying to retrieve a specific EA that is not on the business object, a warning is created and would be viewable to the user. Turning calculation warnings off prior to the EA retrieval would prevent that warning message from being displayed.
You can control calculation warnings and errors using the following techniques:
§ TurnWarningsOff() — Turns warnings off in the following lines of code until it is turned back on or the script ends
§ TurnWarningsOn() — Turns warnings on in the following lines of code until it is turned off explicitly. Warnings are on by default
§
AddErrorMessage(<string>)
— Displays an error message within quotes
ex: AddErrorMessage('Error in running this script')
For example:
TurnWarningsOff();
var override @ GetNumericExtendedAttributeValue('FPCalciumOverride','ME', -1, -1);
TurnWarningsOn();
var roundedCalciumPerServing @ GetNumericExtendedAttributeValue('FPCalciumRounded', -1234567890, -1234567890);
if (roundedCalciumPerServing = -1234567890)
{
AddErrorMessage('Please correct this problem by adding Calcium to the Nutrition Panel.');
}
else
{
if(override > -1)
{
return override;
}
}
return roundedCalciumPerServing;
In this example, if the FPCalciumOverride extended attribute is not found it will not display a warning icon, however if it cannot find FPCalciumRounded it will display the warning. In addition, if FPCalciumRounded is null (-1234567890) then it will also display the additional error message. You could also turn warnings off here and just display your added error message.
Calculation
Dependencies
If your custom calculation script is leveraging other calculated extended attributes, retrieving their value will force them to be calculated too, unless they have already been calculated. This occurs regardless of in which order the extended attributes are located in the UI.
Processing
Results Returned by an Enumerator
When results are returned as an enumerator by functions such as GetCells (see Available Properties and Functions), a loop structure is used to iterate through it in order to access a particular cell data.
Two methods are used to access each item in an enumerator:
Method 1
var item;
var cellsInRow @ GetCells(MyRow,,, 'LEFT');
while(cellsInRow.MoveNext())
{
item @ cellsInRow.Current;
// at this point your item variable is a cell object
}
Method 2
var cellsInRow @ GetCells(MyRow,,, 'LEFT');
for(;cellsInRow.MoveNext();)
{
item @ cellsInRow.Current;
// at this point your item variable is a cell object
}
Custom
Calculation Classes (aka Dynamic Script Methods)
Clients wishing to have more control over calculations, consolidate their calculation logic, or access other data not directly available through JScript (and the predefined functions), may call out to custom classes from their scripts. The custom classes get executed and return a result back to the script. They may optionally receive parameter data from the script.
Customers create a class, add the class to a configuration to make it accessible to the EA Calculation, and use a predefined PLM for Process function, called MethodInvoke, to call out the desired class. Most of the functions that are available in JScript are also available to the custom class, albeit with some slight differences in naming and parameters required. Additionally, the business object attached to the EA can be accessed.
The MethodInvoke JScript call takes two parameters:
- The key that references
your custom class. This name is added to the CustomerSettings.config
file. See below for more details.
- An array of data to pass
into your custom class. See example below.
For example:
var params @ new Array(1);
params(0) @ GetNumericExtendedAttributeValue('BOX_LENGTH');
var emptyVol @ MethodInvoke('MySampleEmptyVolumeCalculator', params);
Class
Structure
A custom calculation class must implement the interface Xeno.Prodika.ExtendedAttributes.Calculation.IDynamicScriptMethod, referencing the ProdikaLib.dll assembly.
Figure 1. IDynamicScriptMethod interface

Your custom business logic is coded in this Invoke method, and must return an object, which can be used as needed by the script that receives the result. JScript can then convert the returned object to the required data type.
The Invoke method takes the following arguments:
1. Parameters: an object array that is passed in from the JScript, which clients can use to pass relevant information to the custom calculation class.
2. Context: an IDynamicScriptMethodContext object. See below.
Figure 2. iDynamicScriptMethodContext object

The IDynamicScriptMethodContext object provides:
· Errors: Access to the Errors collection.
· WarningsOff: A property to allow for turning Warnings on/off.
· AddErrorMessage(): method that only adds an error if Warnings are set to Off
· DynamicScriptVariableResolver: returns a utility class (IDynamicScriptExtendedAttributeVariableResolver) that provides many of the same method calls and variables that are available in the JScript functions.
o The Entity property gives access to the in-memory business object that holds the EA (e.g., a trade specification).
o Note: If your custom calculation class is leveraging other calculated extended attributes, use the DynamicScriptVariableResolver to retrieve their values, which will ensure they get calculated. Do not retrieve them from the Entity directly, as they may not be calculated yet.
· VariableResolver – obsolete – do not use
Example
The following example demonstrates a simple custom calculation class that calculates the empty volume in a product package. For illustration purposes, it receives two values directly from the JScript, length and width, as input parameters. It then retrieves (with Warnings off) extended attribute values for two EAs, calculates and returns the volume, and adds a warning message if the calculated result is less than 0.
using Xeno.Prodika.ExtendedAttributes.Calculation;
namespace CalculationExtensions.ExtendedAttributes
{public class SampleEmptyVolumeCalculator : IDynamicScriptMethod
{public object Invoke(object[] parameters, IDynamicScriptMethodContext context)
{double volume = 0.0;
double length = double.Parse(parameters[0].ToString());
double width = double.Parse(parameters[1].ToString());
context.WarningsOff = true;
double height = GetExtendedAttribute(context,"BOX_HEIGHT", "IN"); // inches
double fill = GetExtendedAttribute(context, "FILL", "CI"); //cubic inches context.WarningsOff = false;
volume = (length * width * height) - fill;if (volume < 0)
{// this adds errors to the UI when calculation is triggered, if the calculated value is negative.
context.AddErrorMessage("Empty Volume has returned a negative number");
}return volume;
} private double GetExtendedAttribute(IDynamicScriptMethodContext context
, string attributeID, string UOM)
{return context.DynamicScriptVariableResolver.GetExtendedAttributeValue(attributeID,
UOM, -1, -1); } }}
The JScript for the EA would look like the following:
var result;
var params @ new Array(2);
params(0) @ GetNumericExtendedAttributeValue('BOX_LENGTH');
params(1) @ GetNumericExtendedAttributeValue('BOX_WIDTH');
result @ MethodInvoke('MySampleEmptyVolumeCalculator', params);
return result;
Configuration
To enable your custom class for EA calculations, you must add it to the CustomerSettings.config file:
Find the <Extended Attributes><DynamicScriptMethods> section and add a new entry for your custom class:
<add key="YourCustomFunctionName"
value="Class:<Fully qualified namespace.classname>,<DLLName>"
/>
Example:
<add key="MySampleEmptyVolumeCalculator" value="Class:CalculationExtensions.ExtendedAttributes.SampleEmptyVolumeCalculator,CalculationExtensions" />
Deployment
Build your class library and copy the DLL to the bin folders of each module that will need to access it.
§ {PRODIKA_HOME}\Web\gsm\bin (For GSM)
§ {PRODIKA_HOME}\Web\scrm\bin (For SCRM)
§ {PRODIKA_HOME}\Web\pqm\bin (For PQM)
§ {PRODIKA_HOME}\Web\reg\bin (For ADMIN)
Reset IIS for configuration changes to take effect.
Determining
Calculation Location
Calculation scripts must be tested in Data Admin as well as when on an actual business object. However, when running the script in Data Admin, you will not have access to other EAs that may be required in when on the business object. This may lead your script to return an invalid result in Data Admin, but a valid result on a specification. Therefore, you can determine in your script whether or not you are executing the script on a real business object or not, and modify the script, if needed. For instance, you could turn warnings off when the script is running in Data Admin.
The following code will return true if you are running this for an actual business object, or false if running this in Data Admin:
if (context.DynamicScriptVariableResolver.Entity is IXUniqueObject) {…}
Performance
Considerations
Be aware that having a large number of calculated EAs on a business object may have a negative effect on performance. If utilizing many custom classes to perform calculations, try to limit their impact as much as possible by minimizing the scope of their work, using caching (if applicable), and consolidating classes if possible.
Other
JScript Syntax
All other syntax rules can be found in the Microsoft JScript documentation available online:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/z688wt03(VS.80).aspx
Available
Properties and Functions
Variables
of Current Business Object
Any variables that are not defined on a business object will return a zero (0).
|
Variable Name |
Return value |
|
BeginningPercentTS |
The beginning % total solids value from the specification |
|
FinalPercentTS |
The final % total solids value from the specification |
|
TotalSolids |
The total solids value from the specification |
|
FinalPercentTSOverride |
The final % total solid override value from the specification |
|
Density |
The density value from the specification |
|
FinalDensity |
The final density value from the specification |
|
FinalDensityOverride |
The final density override value from the specification |
|
AmountPerServing |
The amount per service value from the specification |
|
ReferenceAmount |
The reference amount value from the specification |
|
BeginningBatchSize |
The beginning batch size value from the specification |
|
ApproximateYield |
The approximate yield value from the specification |
Note: All values in the database are stored as % solid values even if your system is configured to display % moisture.
Nutrient Functions
|
Function |
Definition |
Common Parameters and Definitions |
|
GetNutrientItemRoundedValue |
Returns the rounded value of the Nutrient declared. |
· <infoodsID>—String value representing the ID of the nutrient to obtain · <returnValIfNotDeclared>—Optional, numeric value to be returned if the nutrient is not declared · <returnValIfNotDefined>—Optional, numeric value to be returned if the nutrient is not defined |
|
GetNutrientPer100g |
Returns the declared value of the Nutrient declared Per 100 grams. |
|
|
GetNutrientPer100mL |
Returns the declared value of the Nutrient declared Per 100 ml. |
|
|
GetNutrientValuePerServing |
Returns the per-serving value of the Nutrient declared. |
Tare
Weight Functions
|
Function |
Definition |
Common Parameters and Definitions |
|
GetTareWeight |
Returns the Tare Weight information from the specification. |
· <uomISOCode>—Optional, string value representing the ISO code of the UOM the extended attribute is expressed · <returnValIfNotDefined>—Optional, numeric value to be returned if the tare weight additive is not defined |
|
GetTareWeightReferenceWeight |
Returns the Reference Weight information from the specification. |
Tare
Weight Properties
|
Function |
Definition |
Common Parameters and Definitions |
|
TareWeightPer |
Returns the value from the Tare Weight Per field as described on the specification. |
|
Compliance Functions
|
Function |
Definition |
Common Parameters and Definitions |
|
GetAdditiveKTCMax100g |
Returns the declared value of the Known To Contain Additive. |
· <ComplianceID>—String value representing the ID of the compliance item to obtain · <uomISOCode>—Optional, string value representing the ISO code of the UOM the extended attribute is expressed · <returnValIfNotDeclared>—Optional, numeric value to be returned if the compliance item is not declared · <returnValIfNotDefined>—Optional, numeric value to be returned if the compliance item is not defined |
|
GetAdditiveMCMax100g |
Returns the declared value of the May Contain Additive. |
|
|
GetAllergenKTCMax100g |
Returns the declared value of the Known To Contain Allergen. |
|
|
GetAllergenMCMax100g |
Returns the declared value of the May Contain Allergen. |
|
|
GetSensitivityKTCMax100g |
Returns the declared value of the Known To Contain Intolerances/Sensitivity. |
|
|
GetSensitivityMCMax100g |
Returns the declared value of the May Contain Intolerances/Sensitivity. |
Extended
Attribute Functions
Distinct
Extended Attribute Value Functions
Note that when retrieving EAs by the attribute ID, the EA must be configured as Distinct in Data Admin.
|
Function |
Definition |
Common Parameters and Definitions |
|
GetMaxRangeExtendedAttributeValue |
Returns the declared value of the extended attribute |
§ <extAttrID>—String value representing the Attribute ID of the extended attribute to obtain for use in the calculation § <uomISOCode>—Optional, string value representing the ISO code of the UOM in which the extended attribute is expressed § <returnValIfNotDeclared>—Optional, numeric value to be returned if the extended attribute is not declared § <returnValIfNotDefined>—Optional, numeric value to be returned if the extended attribute is not defined, or if the extended attribute has been defined but is not of type Numeric |
|
GetMinRangeExtendedAttributeValue |
||
|
GetNumericExtendedAttributeValue |
||
|
GetTargetRangeExtendedAttributeValue
|
Distinct
Extended Attribute Boolean Functions
|
Function |
Definition |
Common Parameters and Definitions |
|
IsBooleanExtendedAttributeSet |
Each of these functions returns true if the <extAttrID> exists and a value is set; otherwise false. |
<extAttrID>—String value representing the Attribute ID of the extended attribute to obtain for use in the calculation |
|
IsExtendedAttributeMinValueSet |
||
|
IsExtendedAttributeMaxValueSet |
||
|
IsExtendedAttributeTargetValueSet |
||
|
IsNumericExtendedAttributeSet |
||
|
IsQualitativeExtendedAttributeValueSet |
||
|
IsQualitativeLookupExtendedAttributeSet |
Custom
Section Functions
Custom
Section Cell Properties
|
Property |
Definition |
Return Value |
Example |
|
MyCell |
A property that identifies a cell of a current extended attribute. |
A cell object value |
var selfCell @ MyCell; |
|
MyColumn |
A property that identifies an Agile handle of a column that extended attribute is located on. |
String value that represents column Agile handle |
var currentCollumn @ MyColumn; |
|
MyRow |
A property that identifies an Agile handle of a row that extended attribute is located on. |
String value that represents row Agile handle |
var currentRow @ MyRow; |
Custom
Section Cell Retrieval Functions
|
Function |
Definition |
Return value |
Common Parameters and Definitions |
|
GetCell |
A function that identifies a cell specified by a row and a column. |
A cell object |
<rowHandle>—An Agile handle of a row <columnHandle>—An Agile handle of a column |
|
GetCells typeFilter[0] @ 'Boolean'; typeFilter[1] @ 'Numeric'; var allCellsInTestColumn @ GetCells( ,'Test',,); var allFilteredCellsInLeftToMyCell @ GetCells(MyRow,,typeFilter,'LEFT'); |
A function that identifies list of cells specified by a combination of row, column, EA type, and direction. It may include current cell as a part of the result. If both <rowID> and <columnID> are null parameters, returns an empty enumeration. |
A list of cell objects |
<rowID>—User-defined row ID or an Agile handle of a row. If a null parameter, it acts as all rows. <columnID>—User-defined column ID or an Agile handle of a column. If a null parameter, it acts as all columns <typeFilter>—An array of string values that represent extended attribute types that needs to be filtered. If a null parameter, it ignores this filtering. Valid values are: - Boolean - Calculated Boolean - Calculated Numeric - Calculated Text - Date - Free Text - Numeric - Qualitative Lookup - Qualitative - Quantitative Range - Quantitative Tolerance - Referenced Item Collection
<directionFilter>—A string that represents a location of cells relative to the current extended attribute. If a null parameter, it ignores this filtering. Valid values are: - UP - DOWN - LEFT - RIGHT |
|
|
|||
|
GetCellInMyColumnByRowID
Example: var x @ GetCellInMyColumnByRowID ('XY'); |
A function that identifies a cell in a current extended attribute column specified by a row. If more than one cell matches, returns the first cell in the result. |
A cell object |
<rowID>—User-defined row ID or an Agile handle of a row |
|
GetCellInMyRowByColumnID
Example: var x @ GetCellInMyRowByColumnID('B'); |
A function that identifies a cell in a current extended attribute row specified by a column. |
A cell object |
<columnID>—User-defined column ID or an Agile handle of a column |
|
GetCellsByRow
Example: var x @ GetCellsByRow(MyRow) |
A function that identifies an enumeration of cells in a specified row. Can return cells from multiple rows if they are bounded by the same ID. It may include current cell as a part of the result. |
A list of cell objects |
<rowID>—User-defined row ID or an Agile handle of a row |
|
GetCellsByColumn
Example: var x @ GetCellsByColumn('Test') |
A function that identifies an enumeration of cells in a specified column. It may include current cell as a part of the result. |
A list of cell objects |
<columnID>—User-defined column ID or an Agile handle of a column |
Cell
Object Properties
|
Property |
Return value |
|
ColumnHandle |
String value representing a column’s Agile handle |
|
ColumnId |
String value representing the user-defined column ID |
|
ColumnSequence |
Integer representing a cell column sequence |
|
RowHandle |
String value representing a row’s Agile handle |
|
RowId |
String value representing the user-defined row ID |
|
RowSequence |
Integer representing a cell row sequence |
|
Type |
Extended attribute type.
Possible types are: 'Calculated Boolean' 'Calculated Numeric' 'Calculated Text' 'Date' 'Free Text', 'Numeric' 'Qualitative Lookup' 'Qualitative' 'Quantitative Range' 'Quantitative Tolerance' 'Referenced Item Collection' |
|
Value |
A property
that lets you retrieve the extended attribute value of a cell object. |
Cell
Object Value Functions
|
Function |
Definition |
Return value |
Parameters and Definitions |
|
GetBooleanValue umnID('Test').Value.GetBooleanValue() |
Retrieves boolean value of an extended attribute. |
integer 1 is true, -1 if not set |
none |
|
GetDateValue umnID('Test').Value.GetDateValue() |
Retrieves datetime value of an extended attribute. |
dateTime |
none |
|
GetFreeTextExtendedAttributeValue umnID('Test').Value.GetFreeTextExten dedAttributeValue() |
Retrieves string value of a free-text extended attribute. |
String |
none |
|
GetMultipleValues umnID('Test').Value.GetMultipleValues() |
Retrieves selected qualitative values that are on an extended attribute. |
Array of strings |
none |
|
GetNumericValue umnID('Test').Value.GetNumericValue
var x @ GetCellInMyRowByCol umnID('Test').Value.GetNumericValue |
Retrieves numeric value of an extended attribute. Reports an error if it is unable to convert to the specified UOM, returns -123456789. |
numeric |
<ISOCode>—An optional parameter, specifying a UOM. If specified, the extended attribute’s value is firstly converted from the extended attribute’s default UOM to this UOM, then that value is returned. |
|
GetQualitativeExtendedAttributeValue umnID('Test').Value.GetQualitativeExten dedAttributeValue() |
Retrieves string value of a qualitative extended attribute. |
A comma-delimited string that represents the selected extended attribute value(s) |
none |
|
GetQualitativeLookupExtended umnID('Test').Value. |
Retrieves string value of a qualitative-lookup extended attribute. |
A comma-delimited string that represents the selected extended attribute value(s) |
none |
|
GetRangeValue umnID('Test').Value. .GetRangeValue( 'max')
var x @ GetCellInMyRowByCol umnID('Test').Value.GetRangeValue( 'min','KG') |
Retrieves numeric value of an extended attribute based on a property type provided. Reports an error if it is unable to convert to specified UOM, returns -123456789. |
numeric |
<rangeType>—A string value that specifies type of property to retrieve; case insensitive. Valid values are ‘min’, ‘max’, ‘target’.
<ISOCode>—An optional parameter, specifying a UOM. If specified, the extended attribute’s value is firstly converted from the extended attribute’s default UOM to this UOM, then that value is returned. |
|
GetStringValue umnID('Test').Value.GetStringValue() |
Retrieves the string value of an extended attribute. |
String |
none |
Appendix
InFoods
IDs
Run the following SQL query to retrieve the list of InFoods IDs:
select ml.Name, p.InFoodsID, p.UNID, p.SequenceNumber
from
comStandardNutrientProperties p
inner join comStdNutrientPropertiesML ml
on ml.fkStandardNutrientProperties = p.pkid
and langID = 0 and Status = 1
order by ml.name
Some common InFoods IDs:
|
Name |
InFoods ID |
UNID |
Sequence |
|
Calcium |
CA |
CA |
350 |
|
Calories |
ENERC_KCAL |
ENERC_KCAL |
10 |
|
Carbohydrate (Available) |
CHOAVL |
CHOAVL |
45 |
|
Carbohydrates |
CHOCDF |
CHOCDF |
40 |
|
Cholesterol |
CHOLE |
CHOLE |
190 |
|
Dietary Fiber |
FIBTS |
FIBTS |
50 |
|
Energy kJ |
ENERC_KJ |
ENERC_KJ |
20 |
|
Iron |
FE |
FE |
370 |
|
Polyunsaturated Fat |
FAPU |
FAPU |
150 |
|
Potassium |
K |
K |
400 |
|
Protein |
PROCNT |
PROCNT |
30 |
|
Protein (Nx6.25) |
PROCNT_NX625 |
PROCNTx625 |
32 |
|
Saturated Fat |
FASAT |
FASAT |
130 |
|
Sodium |
NA |
NA |
410 |
|
Total Fat |
FAT |
FAT |
120 |
|
Total solids |
TTLSOLID |
TTLSOLID |
205 |
|
Total Sugar |
SUGAR |
SUGAR |
70 |
|
Trans Fatty Acid |
FATRN |
FATRN |
180 |
|
Vitamin A - IU |
VITA_IU |
VITA_IU |
223 |
|
Vitamin A - Total |
VITA- |
VITA- |
220 |
|
Vitamin C |
VITC |
VITC |
290 |
|
Vitamin D |
VITD- |
VITD- |
300 |
|
Vitamin E |
VITE |
VITE |
310 |
|
Vitamin K |
VITK |
VITK |
330 |
|
Zinc |
ZN |
ZN |
420 |
Unit
of Measure ISO Codes
Run the following SQL query to retrieve the list of UOMs:
SELECT Name, Abbreviation, id, ISOCode, Status
FROM UOM a INNER JOIN UOMML ml
ON ml.fkUOM = a.pkid AND ml.langID = 0
ORDER BY name