1 Understanding Oracle Mobile Security Suite
This chapter provides conceptual information about Oracle Mobile Security Suite. It includes the following sections:
1.1 Understanding Oracle Mobile Security Suite
Oracle Mobile Security Suite is an Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) solution offering that is focused on simplifying and securing enterprise mobility by leveraging existing investments on Identity and Access Management platforms. It provides:
-
Interfaces to manage and secure devices and apps.
-
A Secure Workspace to secure enterprise apps and data. Productivity apps as part of OMSS include a browser, a file manager, and a corporate directory app. Available separately are a PIM app with e-mail, calendar, contacts, notes, and tasks functionality, and a doc viewer/editor app.
-
An app containerization tool that provides secure access to third-party apps added to the Secure Workspace.
-
An access server that brokers app authentication and establishes an app tunnel to allow access to corporate resources behind the firewall without the use of a device-level VPN.
The Secure Workspace isolates and protects corporate apps and data from other apps and data on the device, and policies control the movement of data into and out of the Workspace. Oracle Mobile Security Suite provides users with:
-
Seamless access to intranet resources and corporate data using enterprise-grade security.
-
Deep integration with Oracle Access Manager and directory server integration with Oracle Unified Directory server (OUD), Oracle Internet Directory (OID), Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition (ODSEE), and Microsoft Active Directory authentication for true single sign-on.
How IT departments deploy Oracle Mobile Security Suite typically depends on whether IT needs to manage the device, or just the corporate data on the device:
-
If IT does not need to manage the device, users download the Secure Workspace app, which provides access to enterprise-approved resources that are appropriate to the user's role. In this deployment, the user administers the device and can access company resources only from within the Secure Workspace app that IT manages. This type of deployment is called a Mobile Application Management (MAM) deployment. It is typically used for BYOD (bring-your-own-device) deployments in which the user is deploying the client on a personally owned device.
-
If IT needs to manage both the device and the data, the OMSS client provides device management capabilities such as the option to blacklist apps, disable device functions (such as the camera), or wipe compromised devices. The client provides the same comprehensive control over the Secure Workspace as found in the MAM deployment. This is a Mobile Device Management + Mobile Application Management (MDM+MAM) deployment. It is typically used for COPE (corporate-owned personally-enabled) deployments in which IT owns the device, but it can also be deployed to personally-owned devices if the user agrees to allow IT to manage their device.
MAM-only deployments can coexist with MDM solutions from other vendors. For customers who need to manage COPE devices, but do not have an MDM solution, Oracle Mobile Security Suite can address their device and application management requirements.
Oracle Mobile Security Suite is deployed as an Oracle Access Management component. Optionally, Oracle Mobile Security Suite, Oracle Access Management, and Oracle Identity Manager can be deployed together. For details, see Section 1.4, "Deployment Topologies."
1.2 Key Components
Oracle Mobile Security Suite consists of the following key components: the Secure Workspace app, the Mobile Security Access Server (MSAS) component, the Mobile Security Manager (MSM) component, the Policy Manager Server, the Mobile Security App Containerization Tool, and the Secure Mobile Mail Manager app for iOS/Android.
End-users install the Secure Workspace app on their iOS and Android devices. The Secure Workspace app acts as the security provider for all apps running within its realm. Any containerized app installed on the device makes use of the Secure Workspace app to take care of security functions such as authentication, single sign-on, data encryption, and a wide variety of access and data leakage prevention policy enforcement. The Secure Workspace app also comes with a set of embedded apps, like the Secure Browser for any corporate Web access, Secure File Manager for corporate data collaboration, and an option to view and install the list of apps that are allowed for that user. The Secure Workspace isolates and protects corporate apps and data from other apps and data on the device, and the movement of data into and out of the Workspace is controlled by policies.
Mobile Security Access Server is a gateway component that typically sits in a DMZ to provide an AppTunnel connection from containerized apps. Some of the functions that the Mobile Security Access Server provides include the following:
-
Acts as a mutually authenticated SSL tunnel from each Workspace app to provide secure access to any containerized apps.
-
Serves as the authentication broker between devices and authentication servers such as Oracle Access Manager and Active Directory.
The Mobile Security Access Server can sit in front of other Oracle gateway servers (OAG) if needed and brokers authentication and proxy requests to their destinations. Multiple Mobile Security Access Server instances can be installed and active simultaneously. You can control these instances from a single browser-based administrative console. The Mobile Security Access Server is a Java SE server that runs the Grizzly NIO framework (https://grizzly.java.net/).
Mobile Security Manager is installed with Oracle Access Management on a WebLogic application server in the green zone. Some of the functions that the Mobile Security Manager provides include the following:
-
Enrolls devices and Secure Workspaces
-
Allows administrators and end-users to manage their devices/Workspaces remotely (for example, by locking or wiping a lost or stolen device)
-
Allows administrators to define and enforce device and application level policies in conjunction with the Secure Workspace (for example, device/Workspace lifecycle management, mobile application management, mobile security policy administration, and so on)
-
Allows administrators to manage the Mobile Application Catalog
-
Hosts the file manager service
Unified Administrative Console
System Administrators manage the Mobile Security Manager and Mobile Security Access Server components using the Oracle Access Management console, which is hosted on the Policy Manager Server. Administrators open the console in a desktop web browser. The OAM console contains multiple LaunchPad pages, each of which contains a grid of boxes or tiles that can open additional console pages if selected. The Mobile Security Manager console and the Mobile Security Access Server console are two such consoles for System Administrators. The Policy Manager Server also hosts the Help Desk console for Help Desk administrators, and the Self-Service console for end-users in environments without Oracle Identity Manager. If Oracle Identity Manager is available, end-users instead use the OIM self-service console to make Mobile Security Manager requests, while System Administrators can use both the OIM console and the OAM console to manage Mobile Security Manager. (System Administrators can only use the OAM console to manage the Mobile Security Access Server.)
Mobile Security App Containerization Tool
The Mobile Security App Containerization Tool "containerizes" mobile iOS and Android apps by:
-
Injecting the apps with Oracle app security services
-
Signing the apps with the customer's enterprise distribution certificate, and
-
Adding the apps to the Secure Workspace
The Containerization Tool is a MacOS application that features a command-line interface.
The Secure Mobile Mail Manager is an iOS and Android mobile personal information manager (PIM) app for secure mail, calendar, contacts, task, and notes apps. It syncs with corporate mail servers using ActiveSync. Note that this app is licensed separately and may not be included in your environment.
The Secure White Pages App is an iOS and Android mobile corporate directory app that interfaces with existing LDAP directories and can be containerized and deployed as part of the Secure Workspace. The White Pages app only supports OAM-based authentication and is only applicable for OAM deployments.
1.3 Key Concepts
This section introduces Oracle Mobile Security Suite concepts.
Oracle Mobile Security Suite supports devices that run the iOS or Android mobile operating system. Forked Android devices like Kindle Fire are supported. Refer to the Oracle Mobile Security Suite certification matrix for updated information about supported devices.
The Secure Workspace is the security container deployed to the mobile device that provides secure access to your employer's IT network. (The Secure Workspace is an app that runs on the device.) The Secure Workspace provides superior app-level encryption and a superior app-level VPN to protect enterprise data and networks. It also includes a set of trusted containerized apps that are isolated from the user's personal apps on the mobile device.
In Oracle Mobile Security Suite, users enroll each mobile device as either a MAM-only device or a MDM+MAM device.
-
A user with a MAM-only (Mobile Application Management) device retains control over the device and has total freedom with their personal apps and data. For this reason MAM-only devices are called unmanaged devices.
-
A user with a MDM+MAM (Mobile Device Management+Mobile Application Management) device does not administer the device. For example, an MDM+MAM device can be remotely wiped by an administrator, and policies can enforce device restrictions, such as preventing the camera from being used. For this reason MDM+MAM devices are called managed devices.
On both managed and unmanaged devices, users access company resources from within the Secure Workspace.
Users and roles are not managed by Oracle Mobile Security Suite but are managed using your existing directory or identity management tools. Users are assigned to one or more roles/groups on the directory server. User and role definitions are then referenced in real-time (without any sync from LDAP to the OMSS database). Administrators can use roles to send groups of users notifications to enroll a mobile device in Oracle Mobile Security Suite. System administrators can also use role assignments to manage devices and workspaces. For example, System Administrators can lock, unlock, and wipe devices and workspaces by role assignment.
System Administrators use security policies to provision apps and network access to mobile users, and to limit mobile users' actions and access to maintain security. Using the Mobile Security Manager console, administrators assign one or more policies to a role. If conflicting policies apply to a role, Mobile Security Manager enforces whichever policy rules are the most restrictive. All policies are managed on the server, but enforced on the client. Therefore policies are enforced even when the client is offline. Policies are defined using the Mobile Security Policies page, which consists of six configuration tabs: a tab for defining general policy info, a tab for assigning the policy to roles, a tab for configuring device policy settings, and three tabs for configuring Workspace policy settings.
A policy that either restricts device features or specifies device authentication details is a device policy. Device policies are only enforced on managed devices. When defining a policy, all MDM and device-specific settings are located together on the Device tab, so a device policy is any policy that has the Device tab configured. A device policy can disable almost two dozen iOS features, such as access to the Safari browser, or device access to the Apple app store. Android's device management capabilities are limited to disabling the camera. For a list of device restrictions, see "Restrictions" in the Help Reference for Oracle Mobile Security Suite Consoles.
Workspace policies affect the operations of the Secure Workspace and are enforced on both managed and unmanaged devices. System Administrators use Workspace policies to specify Workspace authentication details, allow (or restrict) Workspace privileges, enable and configure application settings, and set Time Access and Geo Access settings. Policies that specify enrollment requirements, compliance rules, and app assignments are also Workspace policies. In terms of the Mobile Security Policies page, a workspace policy is a policy that has any tab other than the Device tab configured.
Following enrollment, compliance policies verify that a device is policy compliant. Compliance policies can look for blacklisted apps, check for extended periods of inactivity, detect if a device is jailbroken, and enforce passcode compliance. Compliance policies also continue to check that enrollment requirements are being met. If a device is flagged as non-compliant, the policy can lock the Workspace, wipe the device/Workspace, or take no action, depending on configuration. Compliance polices are enforced on both managed and unmanaged devices. On unmanaged devices, the compliance policy can wipe the Workspace, but it cannot wipe the device.
The Secure Workspace includes a corporate app catalog that is managed by system administrators. The App Catalog can include native iOS or Android apps and virtual apps. Native apps are installed to the device at the OS level and can be containerized or uncontainerized. On an unmanaged device, a user can only install an app from the Mobile Application Catalog if the policies assigned to the user's role allow for access to the app. On a managed device, administrators can additionally blacklist specific apps. This feature checks for device compliance and, depending on how the policy is enforced, the system locks or wipes the device if blacklisted apps are found.
Policies can define which apps and device configuration settings are available for users belonging to a specific role or group. Note: Device configuration settings (Wi-Fi, VPN, e-mail, calendar) are available for iOS devices only.
De-Register or Wipe the Device
To protect the device, administrators can de-register or wipe the device. De-registering the device removes the provisioning profiles installed on the device along with the Secure Workspace app while retaining the remaining personal data. Wiping the device restores the device to the factory-installed state, wiping the entire device, its contents, and any custom configuration settings.
To protect data in the Secure Workspace, administrators can lock or wipe the Workspace. Locking the Workspace logs the user out of any existing sessions and does not allow re-authentication or access to Workspace apps, but all data remains and the Workspace can be unlocked and accessed again. Wiping the Workspace removes all data and configuration settings for Workspace apps and returns them to their original (pre-Workspace) system state without touching any personal data located outside of the Workspace.
Data in transit and data stored locally inside containerized apps on the mobile device is encrypted. Encrypted data storage includes cache, file store, user preference, and database data. OMSS encryption is certified FIPS140-2 Level 1 encryption.
OMSS employs a sophisticated key hierarchy to protect data. All keys are derived from user credentials that are never stored. The key hierarchy involves multiple keys to support different sensitivity of data. As an example, a unique key is used for the user's authentication certificate, which is allowed to be open for a very short period of time. A different key is used for the browser cache, which must remain decrypted for an entire session. The main Oracle Secure Container distributes and manages keys for the complete set of apps in the user's Secure Workspace.
The App Containerization Tool injects code around third-party native apps that provide enhanced security services for authentication and networking, secure storage, and policy enforcement. Containerization does not require any code changes. Instead, the tool injects code into standard framework calls. To be eligible for containerization, apps must use the HTTP/HTTPS protocol. Apps that use lower-level networking are not supported. The same enterprise certificate must be used to sign the Oracle Secure Container and all containerized apps.
Data Sharing and Data Leakage Protection (DLP)
Oracle Mobile Security Suite provides eleven data leakage protection settings for Workspace apps, including Restrict Copy/Paste, Allow/Deny E-mail, Allow/Deny Instant Messaging, Restrict File Sharing, and others. Administrators can define policies that restrict sharing to Workspace apps only, or allow data to leak out to non-Workspace apps.
Part of the trust model for the Secure Workspace is having all Workspace apps signed by the same enterprise certificate. You must use the same certificate to sign the Oracle Secure Container and all containerized apps. Signing the apps makes them available for enterprise distribution in the enterprise app store. Public app stores do not allow containerized apps that perform OS-level introspection (for example, encryption and network introspection).
When the enterprise certificate expires, the Secure Workspace app will no longer launch. Distribution certificates are valid for three years from the date of issue, or until the Enterprise Developer Program expires, whichever comes first. You can have two distribution certificates active at the same time, each independent from the other. The second certificate provides an overlapping period during which you can update your apps before the first certificate expires. Users will need to upgrade or reinstall the app (without uninstalling the old app) before the certificate expires. System Administrators can use the console to upload a new version of the app and alert users to upgrade.
The Workspace apps that are bundled with OMSS include a secure browser, a file manager for iOS (an Android file manager is available from a third-party vendor), a corporate white pages app, and an App Catalog. These apps can be enabled or disabled by policy as needed. An e-mail (PIM) app is also available as an add-on.
The Mobile File Manager app uses WebDAV to communicate directly to any WebDAV compliant file share. The Mobile File Manager Server converts WebDAV to CIFS to communicate with CIFS shares like Microsoft file shares.
The Oracle White Pages app is a corporate directory app that connects with an existing LDAP store. It is only compatible with OAM SSO.
Finally, you can add your own apps to the Workspace. This includes custom and third-party device-native apps, and "virtual apps"—either a web app that displays in a web browser, or a shared folder app that connects to a network file share.
A PIM (personal information manager) client named Oracle Secure Mobile Mail Manager is available as an add-on to the suite. The app is an OEM product from Nitrodesk/Symantec that uses the Microsoft ActiveSync mechanism to sync e-mail. Any ActiveSync mail server is supported, including Microsoft Exchange, IBM Lotus Domino, and Zimbra. In addition to mail, the app provides calendar, contacts, task, and notes apps.
Allows access to corporate resources behind the firewall without the use of a device-level VPN. AppTunnel provides seamless integration with Active Directory and Oracle Access Manager for authentication, zero code-wrapping technology, extensive policies, and a complex key hierarchy that eliminates the need to cache the user password in the device. The AppTunnel is a mutually authenticated SSL tunnel from each Workspace app that provides secure access to any containerized app. The AppTunnel encrypts all data in transit and provides protection from rogue apps on a user's mobile device that device-level mobile VPNs are subject to. Data in transit in the AppTunnel in encrypted with OpenSSL FIPS.
Authentication and Single Sign-on Support
Oracle Access Manager and Microsoft Active Directory are supported for authentication. For single sign-on, OMSS supports Kerberos and NTLM in Microsoft environments, and OAM basic, OAuth, and SAML in Oracle Access Management environments. If using OAM, OAM can be configured to understand Kerberos token, effectively providing seamless SSO between the two authentication protocols. For more information on this configuration, refer to "Configuring Access Manager for Windows Native Authentication" in the Administrator's Guide for Oracle Access Management.
1.4 Deployment Topologies
There are two OMSS deployment topologies: OMSS + OAM Server, and OMSS + OAM Server + OIM.
Oracle Access Management 11.1.2.3 server is required to run Oracle Mobile Security Suite because OMSS utilizes the OAM server console. If you use Active Directory for authentication and single sign-on, you do not need to enable OAM authentication and single sign-on. Otherwise, OAM authentication is required if using any of the other supported directory servers.
If Oracle Access Management 11.1.2.2 is already deployed in your environment, Oracle Mobile Security Suite can use that version for authentication and SSO, provided that OMSS is deployed on Oracle Access Management 11.1.2.3 on a separate WLS domain. Note that if you use Oracle Internet Directory, this topology requires at least Oracle Internet Directory 11.1.1.7. Older versions of Oracle Internet Directory will need to updated to work with Oracle Mobile Security Suite.
Oracle Mobile Security Suite (including the OAM server) can also be integrated with Oracle Identity Manager 11.1.2.3. Customers can use the OIM Admin Console to manage mobile devices, policies and apps. Self-service users can use the OIM self-service console to manage mobile devices and Workspaces, in addition to managing their user profiles and accounts.
1.5 Understanding the Oracle Mobile Security Suite Process Flows
This section briefly covers Oracle Mobile Security Suite system architecture and how data flows between system components and the user's mobile device.
One or more Mobile Security Access Servers are located on the far side of a firewall in a DMZ (Figure 1-1). On the other side of the firewall, Mobile Security Manager and Oracle Access Management are deployed together in a WebLogic domain in the Green Zone. OAM and OMSS use the same LDAP store for users and groups. For system data, OAM and OMSS maintain separate data stores on a database server.
The Mobile Application Management (MAM) Data Flow
This diagram illustrates the data flow if Oracle Access Management provides authentication. Data flows between components as follows:
-
Users log in to the Secure Workspace app installed on the mobile device. The Secure Workspace first connects to the Mobile Security Access Server gateway component, which forwards the connection past the firewall to Access Manager for single sign-on authentication and authorization. SSO support is provided across Access Manager 11g and 10g WebGate-protected resources. Mobile Security Manager polices enforce each users' mobile access privileges.
-
The Oracle Access Management console, which includes the Mobile Security Manager console, the Help Desk console, and the Self-Service console, is hosted on the Policy Manager Server.
-
Oracle Access Management and Mobile Security Manager utilize the same identity store.
-
In the case of an MDM-enrolled device, Mobile Security Manager sends notifications, such as "device-policy update notifications," to the mobile device using either Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) for iOS devices, or Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) for Android devices. When the device receives its notification, it downloads the updated policy from the server.
Note:
For details about APNS and GCM, refer to the following Web pages:
Figure 1-1 Logical diagram showing Oracle Mobile Security Suite required components
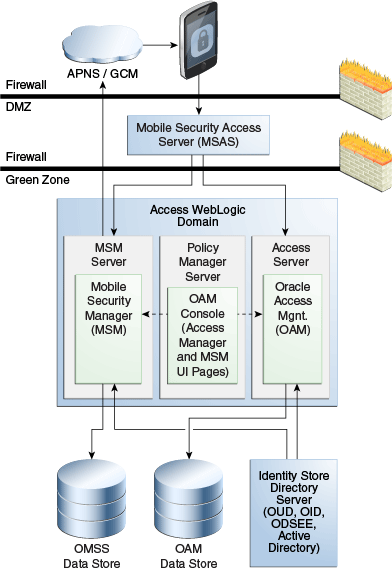
Description of ''Figure 1-1 Logical diagram showing Oracle Mobile Security Suite required components''
Note:
If Oracle Access Management 11.1.2.2 is used for SSO and authentication, install Oracle Access Management 11.1.2.3 with Oracle Mobile Security Suite in a separate domain.If Active Directory is the authentication provider, the Mobile Security Access Server (MSAS) interacts directly with Active Directory. The KINIT/PKINIT registration uses this flow for Workspace (MAM) registration, and the Active Directory Authenticator uses this flow for managed device (MDM) registration.
Figure 1-2 Logical diagram showing data flow if Active Directory is the identity store
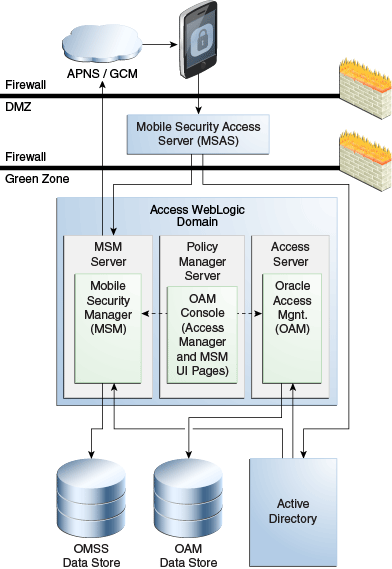
Description of ''Figure 1-2 Logical diagram showing data flow if Active Directory is the identity store''
If Deployed With Oracle Identity Manager
In this topology (Figure 1-3), the directory server provides LDAP updates to the Access Manager, Mobile Security Manager, and Oracle Identity Manager components. Users can manage their Oracle Mobile Security Suite accounts from Oracle Identity Manager. Oracle Identity Manager persists its system data in the OIM data store.
Note:
For details about integrating Oracle Identity Manager and Oracle Mobile Security Suite, see "Integrating Oracle Mobile Security Suite and Oracle Identity Manager."If Oracle Identity Manager is integrated with Oracle Mobile Security Suite, install Oracle Identity Manager in a WebLogic domain separate from the Oracle Access Management WebLogic domain.
Figure 1-3 Logical diagram showing Oracle Identity Manager integrated with Oracle Mobile Security Suite
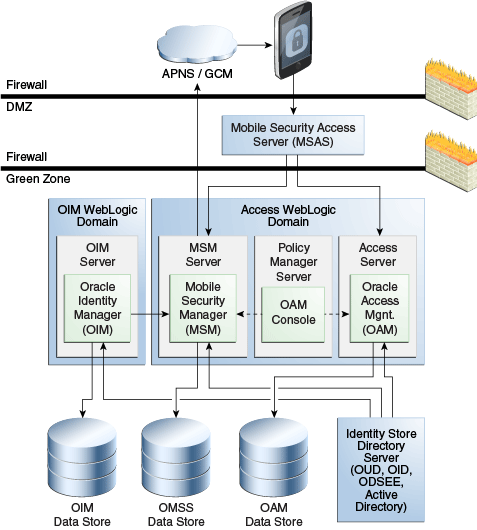
Description of ''Figure 1-3 Logical diagram showing Oracle Identity Manager integrated with Oracle Mobile Security Suite''