2 Planning Your Mobile Synchronization Gateway Installation
This chapter provides information about planning your Oracle Communications Mobile Synchronization Gateway installation.
About Mobile Synchronization Gateway
Mobile Synchronization Gateway extends Oracle Communications Messaging Server, Oracle Communications Calendar Server, and Oracle Communications Contacts Server to mobile devices. Mobile Synchronization Gateway enables users to synchronize their email, calendar, and contacts with mobile devices. Mobile Synchronization Gateway uses the Microsoft® Exchange ActiveSync protocol. Using Microsoft® Exchange ActiveSync, users can access their email, calendar, and contacts even while offline. In addition, Mobile Synchronization Gateway uses real-time push synchronization. Mobile Synchronization Gateway enables native applications on iOS, basic Android, and Samsung Android devices to synchronize with Unified Communications Suite servers.
Note:
You can configure Mobile Synchronization Gateway to support both the legacy Convergence Personal Address Book (PAB) (Web Address Book protocol) and the Contacts Server address book (CardDAV protocol). For more information, see Mobile Synchronization Gateway System Administrator's Guide.Mobile Synchronization Gateway Front-End and Back-End Components
Mobile Synchronization Gateway consists of a gateway server and an engine component, both deployed in a GlassFish Server web container. The gateway is the web front end that performs HTTP and HTTPS authentication and authorization, forwards client requests to the engine component, and keeps track of long-lived HTTP connections for the ping command. The engine responds to HTTP and HTTPS requests from the gateway, and implements the synchronization logic for email, calendar, and contacts.
You deploy Mobile Synchronization Gateway as a front end that communicates to back-end Unified Communications Suite hosts. You can locate the Mobile Synchronization Gateway components on a separate host or on a Unified Communications Suite host.
Figure 2-1 shows a Mobile Synchronization Gateway configuration that uses four hosts. It assumes that you have deployed Messaging Server, Calendar Server, and Contacts Server.
Figure 2-1 Mobile Synchronization Gateway Front-End and Back-End Configuration
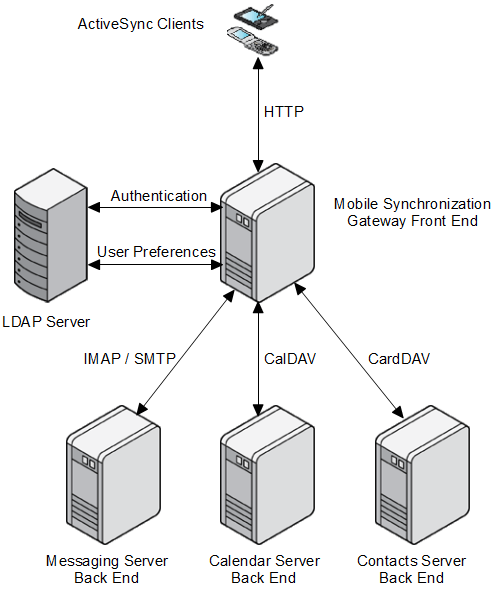
Description of ''Figure 2-1 Mobile Synchronization Gateway Front-End and Back-End Configuration''
This figure represents a simplified Mobile Synchronization Gateway front-end and back-end configuration that uses four hosts. In this figure, the ActiveSync clients are connected to the Mobile Synchronization Gateway host through HTTP. This host accesses an LDAP database for user preference and authentication information. The Mobile Synchronization Gateway host also accesses the email, calendar, and contact information, which is located on separate hosts.
Multiple Mobile Synchronization Gateway front-end hosts can be grouped together by using a simple load balancer.
Note:
For the Contacts Server back-end host, you can use the Convergence Personal Address Book (PAB), for existing deployments that have not yet migrated to Contacts Server. When using the Convergence PAB, you use the Web Address Book protocol (WABP) to communicate to the Mobile Synchronization Gateway host.Planning Your Mobile Synchronization Gateway Installation
This section contains the following planning topics you must consider before installing Mobile Synchronization Gateway:
Deploying Mobile Synchronization Gateway to GlassFish Server
Mobile Synchronization Gateway requires that you use Oracle GlassFish Server as its web container. For production deployments, deploy Mobile Synchronization Gateway to the root context (/) to simplify configuring mobile clients. The resulting URI syntax from using the root context is:
https://host-name:port/Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync
Note:
You cannot deploy Mobile Synchronization Gateway and any other Unified Communications Suite server in the same GlassFish Server domain, even if you use different contexts. You must deploy Mobile Synchronization Gateway and Unified Communications Suite servers in different GlassFish Server domains.Planning for Multiple Mobile Synchronization Gateway Hosts
Using multiple Mobile Synchronization Gateway hosts can help you:
-
Avoid network latency and unnecessary bandwidth consumption in a geographically distributed environment by positioning the server closer to the client.
-
Scale your deployment by distributing end users onto different machines, thus avoiding possible bottlenecks in terms of I/O, memory, CPU, and backup time. A very large deployment can also be geographically distributed.
Planning for Address Books
Mobile Synchronization Gateway enables you to synchronize contacts with Contacts Server or Convergence Personal Address Book (PAB). A scenario that includes both Contacts Server and PAB is useful if you are migrating data from PAB to Contacts Server.
System Deployment Planning
This section contains the following system-level planning topics you must consider before installing Mobile Synchronization Gateway:
Planning for High Availability
You can configure Mobile Synchronization Gateway to be highly available by installing multiple Mobile Synchronization Gateway hosts or by using GlassFish Server high availability features. Refer to the GlassFish Server documentation for more information.
Using Load Balancing
When you deploy multiple Mobile Synchronization Gateway front-end hosts, a load balancer is necessary to distribute the load across the front-end hosts. You can base client-to-server affinity either on the Microsoft® Exchange ActiveSync clientid HTTP parameter or on the Authorization HTTP request header. The latter is considered the best practice for Microsoft® Exchange ActiveSync.
Multiple Mobile Synchronization Gateway front-end hosts can be grouped together, either by using a simple load balancer or by using the GlassFish Server cluster functionality.
About Installing a Secure System
You can configure Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) between:
-
The Mobile Synchronization Gateway GlassFish Server front-end hosts and Unified Communications Suite back-end hosts
-
The Mobile Synchronization Gateway GlassFish Server front-end hosts and the Directory Server host
For information about secure installation and configuration of Mobile Synchronization Gateway, see Mobile Synchronization Gateway Security Guide.