Using Storage-Based Data Replication Within a Campus Cluster
Storage-based data replication uses software installed on the storage device to manage the replication within a cluster, called a campus cluster. Such software is specific to your particular storage device, and is not used for disaster recovery. Refer to the documentation that shipped with your storage device when configuring storage-based data replication.
Depending on the software you use, you can use either automatic or manual failover with storage-based data replication. Oracle Solaris Cluster supports both manual and automatic failover of the replicants with EMC SRDF software.
This section describes storage-based data replication as used in a campus cluster. Two-Room Configuration With Storage-Based Data Replication shows a sample two-room configuration where data is replicated between two storage arrays. In this configuration, the primary storage array is contained in the first room, where it provides data to the nodes in both rooms. The primary storage array also provides the secondary storage array with data to replicate.
Note - Two-Room Configuration With Storage-Based Data Replication illustrates that the quorum device is on an unreplicated volume. A replicated volume cannot be used as a quorum device.
Figure 1 Two-Room Configuration With Storage-Based Data Replication
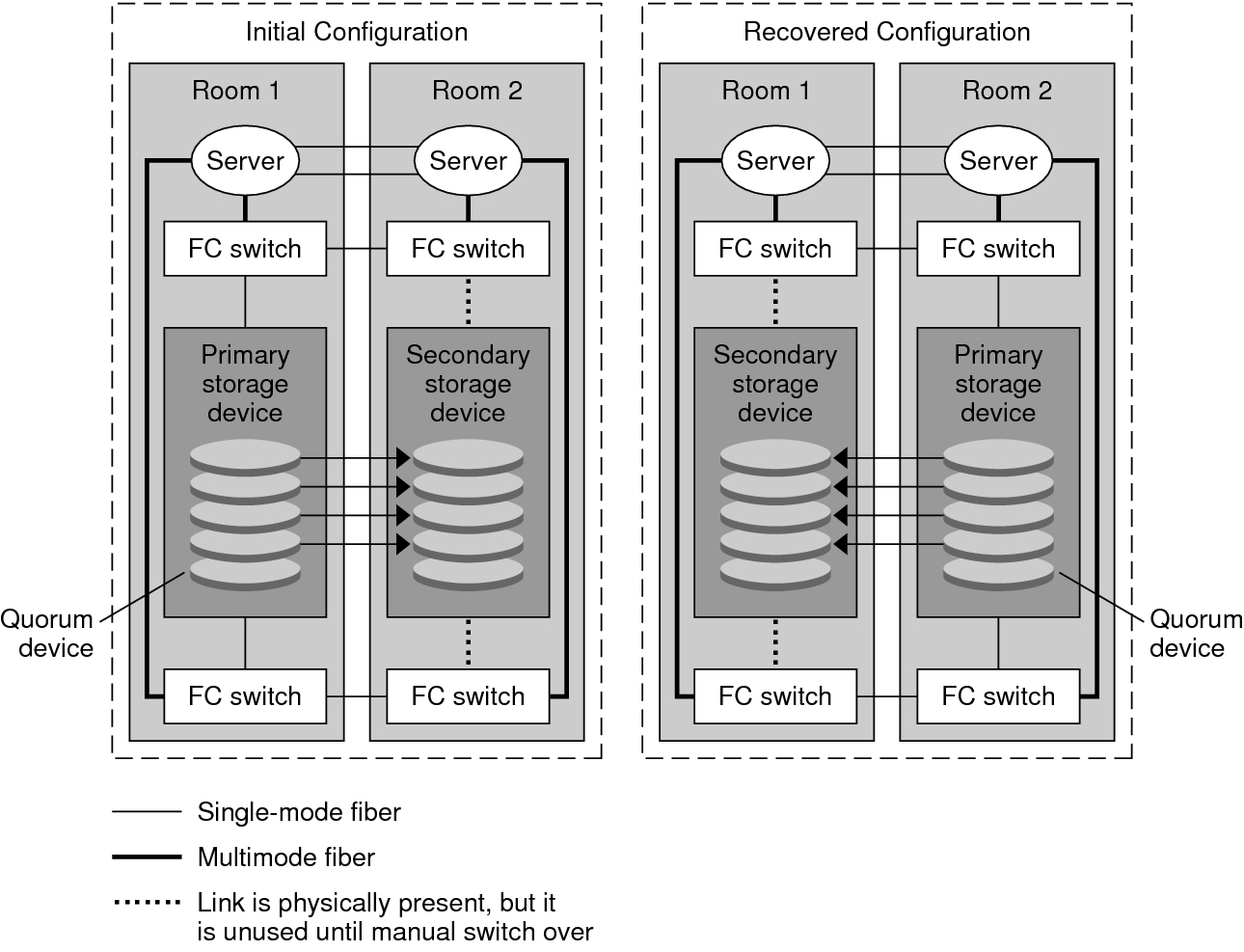
Storage-based synchronous replication with EMC SRDF is supported with Oracle Solaris Cluster. Asynchronous replication is not supported for EMC SRDF.
Do not use EMC SRDF's Domino mode or Adaptive Copy mode. Domino mode makes the local and target SRDF volumes unavailable to the host when the target is unavailable. Adaptive Copy mode is generally used for data migrations and data center moves and it not recommended for disaster recovery.
If contact with the remote storage device is lost, ensure that an application that is running on the primary cluster is not blocked by specifying a Fence_level of never or async. If you specify a Fence_level of data or status, the primary storage device refuses updates if the updates cannot be copied to the remote storage device.
Requirements and Restrictions When Using Storage-Based Data Replication Within a Campus Cluster
-
If configuring the cluster for automatic failover, use synchronous replication.
For instructions on configuring the cluster for automatic failover of replicated volumes, see Configuring and Administering Storage-Based Replicated Devices. For details on the requirements to design a campus cluster, see Shared Data Storage in Oracle Solaris Cluster Hardware Administration Manual.
-
Particular application-specific data might not be suitable for asynchronous data replication. Use your understanding of your application's behavior to determine how best to replicate application-specific data across the storage devices.
-
Node-to-node distance is limited by the Oracle Solaris Cluster Fibre Channel and interconnect infrastructure. Contact your Oracle service provider for more information about current limitations and supported technologies.
-
Do not configure a replicated volume as a quorum device. Locate any quorum devices on a shared, unreplicated volume or use the quorum server.
-
Ensure that only the primary copy of the data is visible to cluster nodes. Otherwise, the volume manager might try to simultaneously access both primary and secondary copies of the data. Refer to the documentation that was shipped with your storage array for information about controlling the visibility of your data copies.
-
EMC SRDF allows the user to define groups of replicated devices. Each replication device group requires an Oracle Solaris Cluster device group with the same name.
-
For a three-site, or three-data-center, configuration using EMC SRDF with concurrent or cascaded RDF devices, you must add the following entry in the Solutions Enabler SYMCLI options file on all participating cluster nodes:
SYMAPI_2SITE_CLUSTER_DG=device-group:rdf-group-number
This entry enables the cluster software to automate the movement of the application between the two SRDF synchronous sites. The rdf-group-number in the entry represents the RDF group that connects the host's local symmetrix to the second site's symmetrix.
For more information about three-data-center configurations, see Three-Data-Center (3DC) Topologies in Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.3 Geographic Edition Overview.
-
Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) is not supported with SRDF when replicating within a cluster. Nodes connected to replicas that are not currently the primary replica will not have write access. Any scalable application that requires direct write access from all nodes of the cluster cannot be supported with replicated devices.
-
Solaris Volume Manager for Sun Cluster multi-owner disksets are not supported.
-
Do not use the Domino mode or Adaptive Copy mode in EMC SRDF. See Using Storage-Based Data Replication Within a Campus Cluster for more information.
To ensure data integrity, use multipathing and the proper RAID package. The following list includes considerations for implementing a cluster configuration that uses storage-based data replication.
Manual Recovery Concerns When Using Storage-Based Data Replication Within a Campus Cluster
As with all campus clusters, those clusters that use storage-based data replication generally do not need intervention when they experience a single failure. However, if you are using manual failover and you lose the room that holds your primary storage device (as shown in Two-Room Configuration With Storage-Based Data Replication), problems arise in a two–node cluster. The remaining node cannot reserve the quorum device and cannot boot as a cluster member. In this situation, your cluster requires the following manual intervention:
-
Your Oracle service provider must reconfigure the remaining node to boot as a cluster member.
-
You or your Oracle service provider must configure an unreplicated volume of your secondary storage device as a quorum device.
-
You or your Oracle service provider must configure the remaining node to use the secondary storage device as primary storage. This reconfiguration might involve rebuilding volume manager volumes, restoring data, or changing application associations with storage volumes.
Best Practices When Using Storage-Based Data Replication
When using EMC SRDF software for storage-based data replication, use dynamic devices instead of static devices. Static devices require several minutes to change the replication primary and can impact failover time.