Overview
Learn key concepts about the Oracle Database@Google Cloud service and resources in this section.
Oracle Exadata Database Machine is an integrated, preconfigured, and pretested full-stack platform for use in enterprise data centers. For Oracle Database@Google Cloud, Oracle and Google jointly identify Google Cloud Regions based on customer demand and install Oracle Exadata infrastructure in selected Google Cloud data centers. An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) managed network is configured between Google Cloud data centers and the nearest OCI region. When a Google Cloud region begins offering Oracle Database@Google Cloud, you can deploy Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure or Oracle Autonomous AI Database using the Google Cloud console.
To use the service, you configure it within your Google Cloud Project through a process referred to as onboarding. To begin onboard, contact your Oracle representative and request a Private Offer. After you agree on pricing, terms and conditions, you complete the purchase through Google Cloud Marketplace. After the purchase is complete, you link your Google Cloud Project with an OCI tenancy. This is called multicloud linking.
After you complete onboarding, you can begin provisioning the Oracle Database@Google Cloud system resources for Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure, Oracle Base Database Service, and Autonomous AI Database Serverless. Provisioning starts with creating an Oracle Database (ODB) network. Based on your workloads and requirements, you then create Exadata infrastructure and Exadata VM cluster for the Oracle Exadata Database Service, Oracle Base Database Service, or Autonomous AI Database Serverless.
When your database resources are available, you establish a connectivity between your application VPC and the Oracle Database created in an ODB network. This enables a direct, secure, and low latency connection between applications and Oracle Database@Google Cloud.
Architecture
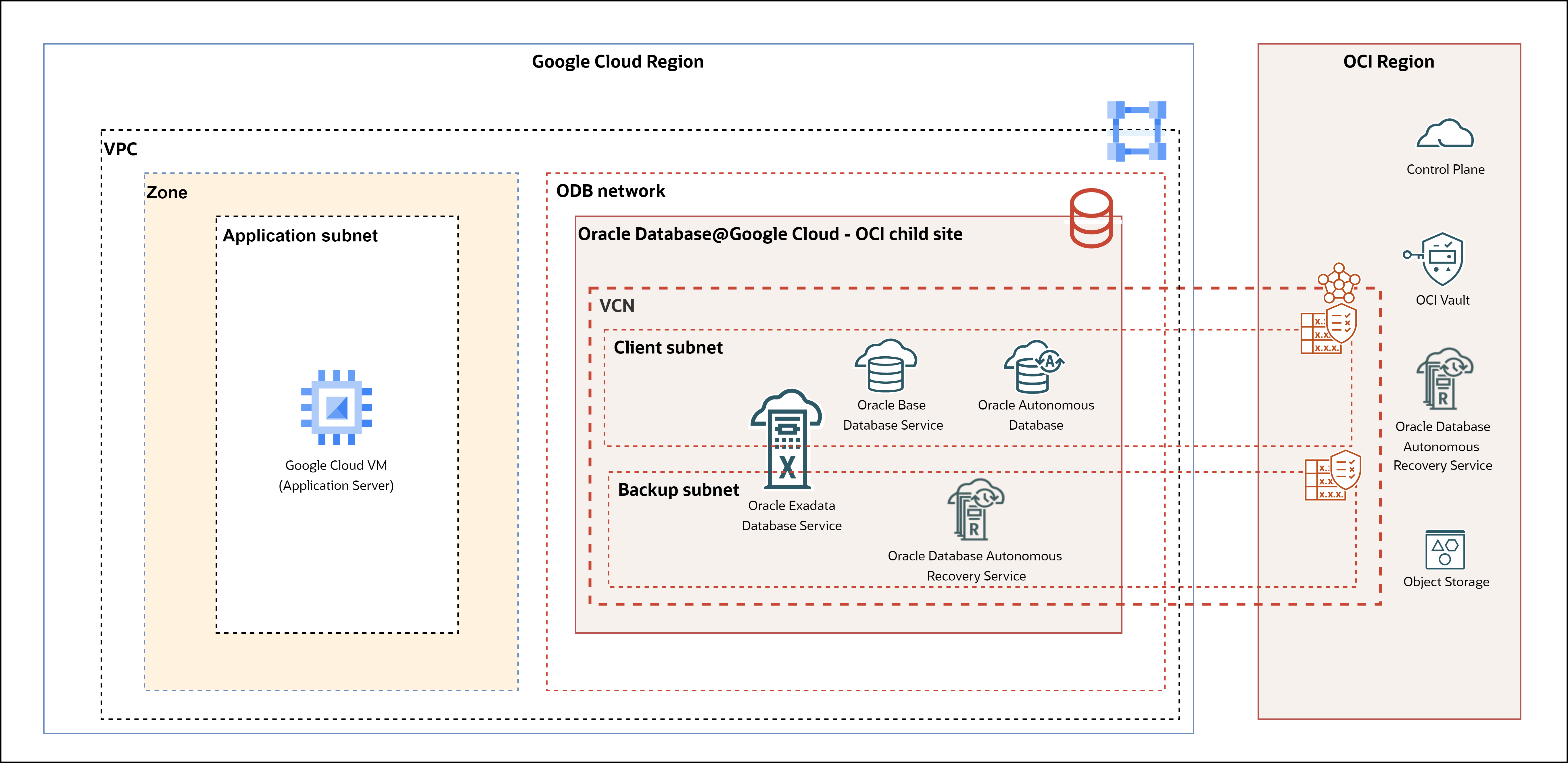
The following diagram shows the Oracle Database@Google Cloud architecture.
The key components of this architecture are the following:
- Google Cloud Region: A Google Cloud Region is a geographical area that has a cluster of data centers known as Zones. Each region is isolated from other regions to ensure data sovereignty, fault tolerance, and low-latency performance for workloads deployed in that geographical area.
- Google Cloud Zone: A Google Cloud Zone is a distinct, isolated location within a Google Cloud Region, consisting of one or more data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity. Zones provide a highly available and fault-tolerant environment for your applications and services.
-
Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud and Subnet: A Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a virtual network that provides a secure and flexible environment to run your Google Cloud resources. VPCs allow you to define private IP spaces, subnets, and routing rules, offering isolation and control over your cloud infrastructure. Subnets within a VPC segment the network into smaller, manageable ranges of IP addresses, which are assigned to resources in specific Google Cloud regions. Each subnet can be configured with custom IP ranges, security policies, and routing, enabling you to organize and secure your workloads efficiently.
-
OCI Region (Parent Site): An OCI region is a geographic area that has one or more data centers known as availability domains. In the Oracle multicloud model, an OCI region connected to a paired Google Cloud region is called a Parent Site. While OCI has regions worldwide, Oracle Database@Google Cloud is available only in the regions discussed in Regional Availability.
Each OCI region operates independently of other regions, providing fault tolerance and disaster recovery capabilities. Each region consists of one or more availability domains. An OCI Availability domain (AD) is one or more data centers within an OCI region. In regions that have multiple ADs, the ADs are physically isolated from each other. They don't share infrastructure, power, cooling, or internal networking, so a failure in one AD is unlikely to affect other ADs in the same region.
- OCI Child Site: An OCI child site is a data center that extends an OCI Availability domain (AD) to a Zone in a Google Cloud region. With the OCI child site model, the Exadata infrastructure used for Oracle Database@Google Cloud physically resides in a Google Cloud data center, but is logically mapped to an OCI region and its network components.
- ODB Network: The ODB network creates a metadata construct for the Google Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), facilitating database provisioning. It supports Standalone VPC and Shared VPC by centralizing network configurations such as subnets and routing, enabling independent management of connectivity. The ODB Network connects Oracle Database@Google Cloud resources in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) to the Google Cloud VPC, mapping OCI network resources back to Google Cloud. Upon creating an ODB Network, essential components such as the Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) and subnets are provisioned automatically, while other elements for private connection are created during deployment. Users can also create up to five ODB Subnets within an ODB Network for better network segmentation.
- Oracle Exadata Infrastructure: Oracle Exadata infrastructure is a high-performance, integrated hardware and software platform designed for running Oracle Databases. Exadata is a preconfigured and pretested full-stack platform, meaning all the necessary hardware and software components are integrated and optimized to work together seamlessly.
Exadata features a scale-out architecture with database servers and intelligent storage servers that can be independently scaled to meet changing workload demands. Exadata storage servers go beyond traditional storage by having their own CPUs and specialized software that enable them to perform database operations such as SQL query processing close to the data. Exadata uses a high-bandwidth, low-latency network fabric (such as RDMA over Converged Ethernet or RoCE) to connect database servers and storage servers, ensuring rapid data access and transfer rates. In Oracle multicloud architecture, Exadata infrastructure is the underlying hardware for both Oracle Exadata Database Service and Oracle Autonomous AI Database.
- Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure: Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure lets you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. The service delivers proven Oracle Database capabilities on purpose-built, optimized Oracle Exadata infrastructure in the public cloud. Built-in cloud automation, elastic resource scaling, security, and fast performance for all Oracle Database workloads helps you simplify management and reduce costs.
- Oracle Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure: Oracle Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure provides a fully managed, high-performance cloud database platform designed to scale effortlessly with business needs. Leveraging Oracle's powerful Exadata hardware and advanced software optimizations, this service delivers exceptional performance, availability, and security for mission-critical workloads. Customers benefit from automated management, elastic scaling, and seamless integration with Oracle Cloud, enabling them to run their databases efficiently and reliably while focusing on innovation rather than infrastructure maintenance.
- Oracle Base Database Service: Oracle Base Database Service is a fully managed cloud solution that enables organizations to quickly deploy, manage, and scale Oracle databases in the cloud. It provides automated provisioning, patching, backups, and monitoring, freeing users from administrative overhead and allowing them to focus on application development and innovation. The service is designed for high performance, security, and seamless integration with other Cloud services, making it an ideal choice for both transactional and analytical workloads.
- Oracle Autonomous AI Database: Oracle Autonomous AI Database is a fully managed cloud database service that automatically handles provisioning, tuning, backups, patching, and scaling without any user intervention. It elastically scales compute and storage up or down based on workload demand, so you can only pay for what you use. Because it's serverless, there's no need to manage underlying infrastructure - the service transparently optimizes performance, availability, and security.
- OCI Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) and Subnet: A Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) is a customizable, private network that you set up in an OCI tenancy within a specified Oracle Region. It provides a secure and scalable network environment where you can deploy and manage your OCI resources, such as compute instances, databases, and storage.
A VCN acts as a virtualized version of a traditional network, including key components such as subnets, route tables, and gateways. VCNs let you to isolate and segment your cloud resources within logically separated networks, enhancing security and manageability. VCNs are divided into subnets, which are smaller subdivisions that allow you to segment resources and control traffic at a finer level. Subnets can be either public (allowing public IP addresses and internet access) or private (restricting direct internet access). In Oracle multicloud architecture, when an Oracle database resource created with ODB network in a Google Cloud region, a corresponding OCI VCN with subnets is automatically created in your OCI tenancy in the paired OCI region.
- Network security group (NSG): In OCI, a Network Security Group (NSG) is a feature that acts as a virtual firewall for a set of cloud resources that share the same security posture. NSGs apply security rules to a specific group of Virtual Network Interface Cards (VNICs) within a Virtual Cloud Network (VCN), rather than applying rules to an entire subnet. In Oracle multicloud architecture, an NSG is used to control network traffic to Oracle Databases.
- OCI Vault: OCI Vault is a managed cloud service provided by OCI for securely storing and managing encryption keys and secrets. OCI Vault integrates with Oracle Database@Google Cloud in multicloud setup, enabling secure data-at-rest encryption. OCI Vault offers a rich set of REST APIs to manage vaults and keys. In Oracle multicloud architecture, OCI Vault is offered to securely store the Customer Managed Keys (CMK).
- Oracle Database Autonomous Recovery Service (ARS): Oracle Database Autonomous Recovery Service (ARS) at OCI & Google Cloud is a fully managed cloud backup solution designed to protect Oracle Databases. ARS is a key service within OCI for ensuring data protection and availability. The service aims to minimize data loss by providing real-time transaction protection, providing recovery to within less than a second of an outage or attack. This significantly reduces the recovery point objective (RPO) compared to traditional backup methods. In Oracle multicloud architecture, ARS at OCI & Google Cloud is offered as one of the automatic backup destinations for Oracle Exadata Database Service.
- OCI Object Storage: OCI Object Storage is a service offered by OCI for storing and managing large volumes of unstructured data. Object Storage is a scalable, durable, and cost-effective solution for various data types, including images, video, backups, and archives. OCI Object Storage offers virtually unlimited storage capacity, allowing you to scale as your data grows without worrying about capacity limitations. In Oracle multicloud architecture, OCI Object Storage is offered as one of the automatic backup destinations.