2 Pre-Upgrade Checklist
You must complete all applicable tasks before you begin the upgrade process. Failure to do so may result in a failed upgrade.
The tasks described in this pre-upgrade checklist assume that you have read Planning an Upgrade to Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c and understand the requirements of this upgrade.
Note:
The pre-upgrade procedures you perform depend on the configuration of your existing system, the components you are upgrading, and the environment you want to create at the end of the upgrade and configuration process.
In addition to the common, pre-upgrade procedures described here, you may also have component-specific tasks to perform. Consult your component-specific upgrade documentation for other required procedures.
Table 2-1 Tasks to Perform Before You Upgrade to Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c
| Task | Description | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
|
Create a complete backup of your pre-upgrade environment. |
REQUIRED FOR ALL UPGRADES. Back up all system-critical files and database(s) that contain any schemas that are to be upgraded before you begin your upgrade. If the upgrade fails, you need to restore your pre-upgrade environment and begin the upgrade again. |
|
|
Verify that you are installing and upgrading your product on a supported hardware and software configuration. NOTE: Do not attempt an upgrade if you are unable to use the latest supported operating system. As with all supported configurations, failure to comply with these requirements may cause your upgrade to fail. |
As part of the upgrade planning process, you already verified that your hardware and software configurations (including operating systems) are supported by the latest certifications and requirements documents. Just before you start the upgrade, verify this information again, as the certification requirements may have changed. Make sure that you have applied the latest patches to your components before you upgrade. |
|
|
Remove any outdated or unused data before you upgrade. |
To optimize performance, consider purging data and objects that will not be used in the upgraded environment. |
|
|
Clone your production environment to use as an upgrade testing platform. |
In addition to creating a complete backup of your system files, you should also clone your production environment. This environment can be used to test the upgrade. |
Cloning Your Production Environment for Testing (Recommended) |
|
Verify that you are running a 64-bit operating system. Most Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c components require a 64-Bit operating system. |
Required only if you are currently running a 32-bit operating system. |
|
| Depending on your upgrade starting point, you may be required to create new 12c schemas before an upgrade. | Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c requires that you use the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) to create new schemas before you can upgrade your existing environment. | Creating the Required Schemas Before an Upgrade |
|
If you are using a file-based policy store, then you must reassociate it to a database-based policy store. |
This step is not required if you are upgrading from a previous 12c release. |
Reassociating File-based Policy Stores to Database-based Policy Stores (Required) |
|
Understand the schema requirements when using an OID-based security store. |
If you are using an OID-based security store, you need to create a 12c OPSS schema before you upgrade. |
Creating the 12c OPSS Schema for an OID-based Security Store |
|
Oracle recommends that you maintain the highest level of security for all Fusion Middleware security stores. |
Before the upgrade, back up your existing security stores and then upgrade them using the security store-specific procedures. |
|
|
Some of the security algorithms used in Fusion Middleware 12c require additional policy files for the JDK. |
Required only if you plan to use enhanced encryption (such as AES 256). Oracle recommends that you apply the required policy files to the JDK before you upgrade. |
|
| Create a new Non-SYSDBA user to avoid running the upgrade as SYS AS SYSDBA. | Oracle recommends that you create a non-SYSDBA user called fmw to run Upgrade Assistant with only those privileges required by the Upgrade Assistant. | Creating a Non-SYSDBA User |
|
Oracle Database Users: Before upgrading an Edition-Based Redefinition (EBR) enabled schema, you must connect to the database server and create an edition on the database server for 12c (12.2.1). |
This step is required only if you are using an Edition-Based Redefinition (EBR) database. |
Creating an Edition on the Server for Edition-Based Redefinition (Optional) |
|
Download and install the new 12c products in to a new Oracle home before you upgrade. |
Install the 12c (12.2.1) versions of the products you already have in your pre-upgrade environment. Note that some products have not yet been released for 12c (12.2.1), but will become available in a future release. |
Downloading and Installing the 12c Oracle Fusion Middleware Product Distributions |
| Run the Readiness Check on your production environment before you begin the upgrade. | The Upgrade Assistant can be run in -readiness mode to detect potential issues that could prevent a successful upgrade. |
Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check |
|
Use the component-specific upgrade documentation to complete your upgrade. |
The documentation covers component-specific tasks that are required for the upgrade. Some of the tasks are performed before the upgrade and some are performed after. Always consult your Oracle Fusion Middleware upgrade documentation to ensure you have a successful upgrade. |
- Creating a Complete Backup (Required)
Before you install any new 12c distributions and begin upgrading your Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g or 12c deployment, be sure you have backed up all system-critical files; including all of the databases that host your Oracle Fusion Middleware schemas. - Cloning Your Production Environment for Testing (Recommended)
Oracle strongly recommends that you create a copy of your actual production environment, upgrade the cloned environment, verify that the upgraded components work as expected, and then (and only then) upgrade your production environment. - Verifying Certification and System Requirements
The certification matrix and system requirements documents should be used in conjunction with each other to verify that your environment meets the necessary requirements for installation. - Migrating from a 32-Bit to a 64-Bit Operating System
Most Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c components require a 64-Bit operating system. If you are running a 32-bit environment, then you must migrate your 32-bit environment to a 64-bit software environment before you upgrade. - Purging Unused Data
Purging unused data before an upgrade can optimize the upgrade process. Automated purge scripts are available for some components and can run before an upgrade to purge unused and obsolete data. - Creating the Required Schemas Before Upgrade
Before you upgrade, you may be required to create new schemas for your 12c deployment. To determine which additional schemas need to be created for 12c, compare the component schemas you have in your existing environment to the schemas required for your upgrade. - Reassociating File-based Policy Stores to Database-based Policy Stores (Required)
Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c uses database-based policy stores. A database-based policy store is recommended for a production environment. If you are using a file-based or OID-based policy store, you must reassociate the store to a database-based store prior to upgrade. - Upgrading Security Stores to the Latest Version
Upgrading to the latest version of the OPSS security store enable you to use enhanced features and fixes. OPSS security store is a part of Oracle Fusion Middleware product installation and therefore, you can use the Upgrade Assistant directly to upgrade the OPSS schema. - Creating a Non-SYSDBA User
Oracle recommends that you create a non-SYSDBA user to run the Upgrade Assistant. The user created using this procedure has the privileges required to complete the upgrade. - Using Enhanced Encryption (AES 256)
The Java platform defines a set of APIs spanning major security areas, including cryptography, public key infrastructure, authentication, secure communication, and access control. These APIs allow developers to easily integrate security mechanisms into their application code If you plan to use enhanced encryption (such as AES 256), Oracle recommends that you apply these policy files to the JDK before you upgrade. - Creating an Edition on the Server for Edition-Based Redefinition (Optional)
Edition-based redefinition enables you to upgrade an Oracle Database component of an application, such as PL/SQL objects, views, and synonyms, while it is in use, thereby minimizing or eliminating down time. - Maintaining Custom Domain Environment Settings
Every domain includes dynamically generated domain and server startup scripts, such assetDomainEnv. Oracle recommends that you do not modify these startup scripts, as any changes made to them are overwritten during subsequent domain upgrade and reconfiguration operations. - Downloading and Installing the 12c Oracle Fusion Middleware Product Distributions
Oracle Fusion Middleware product distributions are available for download on Oracle Technology Network (OTN) and Oracle Software Delivery Cloud. - Using the Upgrade Assistant to Run a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
The Upgrade Assistant can be run in the -readiness mode to perform a read-only, pre-upgrade check on your domain. If issues are detected, you can correct them before starting the actual upgrade. - Locating the Component-Specific Upgrade Documentation
The component specific upgrade documentation provides upgrade procedure and information for every individual component including Oracle WebLogic Server, Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure, Oracle HTTP Server, Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management, Oracle Webcenter, User Messaging Service, and Oracle Data Integrator.
2.1 Creating a Complete Backup (Required)
Before you install any new 12c distributions and begin upgrading your Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g or 12c deployment, be sure you have backed up all system-critical files; including all of the databases that host your Oracle Fusion Middleware schemas.
For more information, see Backing Up Your Oracle Fusion Middleware Environment and Upgrading and Preparing Your Oracle Databases for 12c.
2.2 Cloning Your Production Environment for Testing (Recommended)
Oracle strongly recommends that you create a copy of your actual production environment, upgrade the cloned environment, verify that the upgraded components work as expected, and then (and only then) upgrade your production environment.
Note:
Cloning procedures are component-specific. At a high level, you will install the pre-upgrade version of your component domain on a test machine, create the required schemas using the Repository Creation Utility (RCU), and perform the upgrade. Depending on what you are upgrading, you may be required to perform additional cloning tasks to replicate your production environment. Your component-specific upgrade documentation provides the complete upgrade procedure.-
Uncover and correct any upgrade issues.
-
Practice completing an end-to-end upgrade.
-
Understand the upgrade performance and how purge scripts can help.
-
Understand the time required to complete the upgrade.
-
Understand the database resource usage (such as temporary tablespace; PGA, etc).
Note:
You can run the pre-upgrade Readiness Check on the cloned production environment to help identify potential upgrade issues with your data, but you must perform a complete test upgrade on a cloned environment to ensure a successful upgrade.2.3 Verifying Certification and System Requirements
The certification matrix and system requirements documents should be used in conjunction with each other to verify that your environment meets the necessary requirements for installation.
Note:
When checking the certification, system requirements, and interoperability information, be sure to check specifically for any 32-bit or 64-bit system requirements. It is important for you to download software specifically designed for the 32-bit or 64-bit environment, explicitly.WARNING:
Make sure that your current environment has been patched to the latest patch set BEFORE you begin the upgrade. Certifications are based on fully patched environments unless stated otherwise.- Verify Your Environment Meets Certification Requirements
Oracle has tested and verified the performance of your product on all certified systems and environments. Make sure that you are installing your product on a supported hardware or software configuration - Verify System Requirements and Specifications
It is important to verify that the system requirements such as disk space, available memory, specific platform packages and patches, and other operating system-specific items are met. - Verify that the database hosting Oracle Fusion Middleware is supported
You must have a supported Oracle database configured with the required schemas before you run Fusion Middleware 12c. - Verify that the JDK is certified for this release of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Before you can install any Oracle Fusion Middleware product using a generic installer, you must download and install a supported JDK on your system.
2.3.1 Verify Your Environment Meets Certification Requirements
Oracle has tested and verified the performance of your product on all certified systems and environments. Make sure that you are installing your product on a supported hardware or software configuration
Whenever new certifications occur, they are added to the proper certification document right away. New certifications can occur at any time, and for this reason the certification documents are kept outside of the documentation libraries and are available on Oracle Technology Network. For more information, see Certification Matrix for 12c (12.2.1).
2.3.2 Verify System Requirements and Specifications
It is important to verify that the system requirements such as disk space, available memory, specific platform packages and patches, and other operating system-specific items are met.
The Oracle Fusion Middleware System Requirements and Specifications document should be used to verify that the requirements of the certification are met. For example, if the certification document indicates that your product is certified for installation on 64-Bit Oracle Linux 7, this document should be used to verify that your Oracle Linux 7 system has met the required minimum specifications, like disk space, available memory, specific platform packages and patches, and other operating system-specific items. This document is updated as needed and resides outside of the documentation libraries. The latest version is available on Oracle Technology Network.
For a complete description of the system requirements for installing and upgrading to Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c, see Review System Requirements and Specifications.
Note:
When you install the Oracle Fusion Middleware Release 12c software in preparation for upgrade, you should use the same user account that you used to install and configure the Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g software. On UNIX operating systems, this will ensure that the proper owner and group is applied to new Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c files and directories2.3.3 Verify that the database hosting Oracle Fusion Middleware is supported
You must have a supported Oracle database configured with the required schemas before you run Fusion Middleware 12c.
It is assumed that you understand the Oracle Database requirements when upgrading and ensure that the database hosting Oracle Fusion Middleware is supported and has sufficient space to perform an upgrade.
2.3.4 Verify that the JDK is certified for this release of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Before you can install any Oracle Fusion Middleware product using a generic installer, you must download and install a supported JDK on your system.
Make sure that the JDK is installed outside of the Oracle home. The Oracle Universal Installer validates that the designated Oracle home directory is empty, and the install does not progress until an empty directory is specified. If you install JDK under Oracle home, you may experience issues in future operations. Therefore, Oracle recommends that you use install the JDK in the /home/oracle/products/jdk directory. You can then use the java -jar command to run the installer JAR file.
For more information on the difference between generic and platform-specific installers, see Understanding the Difference Between Generic and Platform-Specific Distributions in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Download, Installation, and Configuration Readme Files.
To download the required JDK, use your browser to navigate to the following URL and download the Java SE JDK:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
2.4 Migrating from a 32-Bit to a 64-Bit Operating System
Most Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c components require a 64-Bit operating system. If you are running a 32-bit environment, then you must migrate your 32-bit environment to a 64-bit software environment before you upgrade.
Note:
When checking the certification, system requirements, and interoperability information, be sure to check specifically for any 32-bit or 64-bit system requirements. It is important for you to download software specifically designed for the 32-bit or 64-bit environment, explicitly.Make sure to validate the migration to ensure all your Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g software is working properly on the 64-bit machine, and only then perform the upgrade to Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c.
In these tasks, host refers to the 32-bit source machine and target refers to the new 64-bit target machine.
Note:
These steps assume that your database is located on a separate host and will not be moved.Caution:
These steps are provided as an example of the operating system upgrade process and may or may not include all of the procedures you must perform to update your specific operating system. Consult your operating system's upgrade documentation for more information.- Procure the Hardware that Supports your Upgrade's 64-bit Software Requirement
Make sure that you have supported target hardware in place before you begin the upgrade process. - Stop all processes, including the Administration Server, Managed Servers, and Node Manager
You must stop all processes, including the Administration Server, Managed Servers, and Node Manager, if they are started on the host. - Back up all Files from the 32-bit Host Machine
Make sure that you have created a complete backup of your entire 11g deployment before you begin the upgrade process. These files can be used if there is an issue during the migration and you have to restart the process. - Set up the Target 64-bit Machine with the 11g Host Name and IP Address
The host name and IP address of the target machine must be made identical to the host. This require you to change the IP address and name of the source machine or decommission the source machine to avoid conflicts in the network. - Restore the 11g Backup from 32-bit Host to 64-bit Host
Restore the files you backed up in Task 3 using the same directory structure that was used in 11g. The directory structure on the target machine must be identical to the structure of the host machine. - Install the 12c Product Distribution(s) on the Target Machine
Oracle recommends an Out-of-Place approach for upgrade. Therefore, you must install the 12c product distributions in a new Oracle home on the target machine. - Upgrade the Target 64-bit Environment Using the Standard Upgrade Procedure
After installing the product on the target machine, you must upgrade each component individually using an upgrade utility specified in the component-specific upgrade guide and complete any post-upgrade tasks.
2.4.1 Procure the Hardware that Supports your Upgrade's 64-bit Software Requirement
Make sure that you have supported target hardware in place before you begin the upgrade process.
2.4.2 Stop all processes, including the Administration Server, Managed Servers, and Node Manager
You must stop all processes, including the Administration Server, Managed Servers, and Node Manager, if they are started on the host.
For example, to stop the Administration Server, enter the following command:
DOMAIN_HOME/bin/stopWebLogic.sh username password [admin_url]2.4.3 Back up all Files from the 32-bit Host Machine
Make sure that you have created a complete backup of your entire 11g deployment before you begin the upgrade process. These files can be used if there is an issue during the migration and you have to restart the process.
Note:
If the upgrade from 32-bit to 64-bit takes place on the same machine, there is a risk of corrupting the source environment if the upgrade fails.For more information on backing up your 11g files, see Backing Up Your Environment in Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
During the upgrade you must have access to the contents of the following:
-
11g Domain Home
-
11g
/nodemanagerdirectory located inMW_HOME/wlserver_10.3/common/
Some of the backup and recovery procedures described in Backing Up Your Environment in Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide are product-specific. Do not proceed with the upgrade until you have a complete backup.
2.4.4 Set up the Target 64-bit Machine with the 11g Host Name and IP Address
The host name and IP address of the target machine must be made identical to the host. This require you to change the IP address and name of the source machine or decommission the source machine to avoid conflicts in the network.
The process of changing an IP address and host name vary by operating system. Consult your operating system's administration documentation for more information.
2.4.5 Restore the 11g Backup from 32-bit Host to 64-bit Host
Restore the files you backed up in Task 3 using the same directory structure that was used in 11g. The directory structure on the target machine must be identical to the structure of the host machine.
For detailed information about restoring your 11g files to the 64-bit target machine, see Recovering Your Environment in Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
2.4.6 Install the 12c Product Distribution(s) on the Target Machine
Oracle recommends an Out-of-Place approach for upgrade. Therefore, you must install the 12c product distributions in a new Oracle home on the target machine.
For detailed instructions on how to obtain 12c distributions, identify an installation user, and understand the directory structure for installation and configuration, see Planning an Installation of Oracle Fusion Middleware. Refer to the component-specific installation guides for the component(s) you are installing.
2.4.7 Upgrade the Target 64-bit Environment Using the Standard Upgrade Procedure
After installing the product on the target machine, you must upgrade each component individually using an upgrade utility specified in the component-specific upgrade guide and complete any post-upgrade tasks.
For a complete upgrade procedure, see the component-specific upgrade guide for the component(s) you are upgrading.
Note:
The Node Manager upgrade procedure requires access to the original Node Manager files. Use the 11g Node Manger files that were backed up from the 32–bit source machine as part of Back up all Files from the 32-bit Host Machine.2.5 Purging Unused Data
Purging unused data before an upgrade can optimize the upgrade process. Automated purge scripts are available for some components and can run before an upgrade to purge unused and obsolete data.
For Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) Components
Purge the execution logs to avoid exporting and importing excessive data as part of work repository export/import in the next step. See Purging the Logs
For SOA Suite Components
Note:
If a large amount of data needs to be purged, consider partitioning tables or employing other data optimization strategies. Using scripts to remove large amounts of data may impact performance.See Developing a Purging and Partitioning Methodology and Developing a Database Growth Management Strategy
2.6 Creating the Required Schemas Before Upgrade
Before you upgrade, you may be required to create new schemas for your 12c deployment. To determine which additional schemas need to be created for 12c, compare the component schemas you have in your existing environment to the schemas required for your upgrade.
Refer to the component-specific upgrade guides in order to identify the schemas that are required for your components. The Upgrade Assistant identifies all of the schemas that are available for an upgrade, and includes all the schemas in the upgrade. It also allows you to select the schemas that should be upgraded. For more information about , see Identifying Schemas that Can be Upgraded with the Upgrade Assistant.
If you are upgrading from 11g, note the following:
-
In 12c, there is a new schema that must be created before you can upgrade from 11g. The new Service Table schema (prefix
_STB) stores basic schema configuration information that can be accessed and used by other Oracle Fusion Middleware components during the domain creation. For more information, see Understanding the Service Table Schema.Note:
If you have not created the Service Table schema, you might encounter the error message UPGAST-00328 : The schema version registry table does not exist on this database. If that happens is it necessary to create the service table schema in order to run Upgrade Assistant. -
An OPSS schema is also required for 12c if your 11g environment is not already using an OPSS schema.
-
The audit schema includes two additional schemas which also need to be created before running 12c. When upgrading audit services (
_IAU), make sure that you select_IAU_APPENDand_IAU_VIEWERin addition to_IAU.
2.7 Reassociating File-based Policy Stores to Database-based Policy Stores (Required)
Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c uses database-based policy stores. A database-based policy store is recommended for a production environment. If you are using a file-based or OID-based policy store, you must reassociate the store to a database-based store prior to upgrade.
To reassociate file-based policy stores to database-based policy store, you must create an OPSS schema in the database and also create a data source in the WebLogic server.
If you are already using database-based policy store, then you do not have to perform these tasks.
- Creating 11g OPSS and IAU Schemas
To use a database repository for the Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) security store, you must create the required schema and seed some initial data using the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility (RCU). This setup is also required before reassociating the OPSS security store to a DB-based security store. - Reassociating the 11g Policy Store with the Database-Based Policy Store and OPSS Schema
The OPSS security store is the repository of system and application-specific policies, credentials, keys, and audit services. OPSS delegates the identity store service to the identity providers that are configured in the WebLogic server. Out-of-the-box, the OPSS security store is file-based. You must reassociate it to a database-based security store. - Validating that the Policy Store Reassociation is Successful
Reassociation modifies the domain configuration file:DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml. It deletes any configuration for the old store provider, inserts a configuration for the new store provider, and moves the policy and credential information from the source to the destination store. - Creating the 12c OPSS Schema for an OID-based Security Store
The only supported LDAP-based OPSS security store is Oracle Internet Directory (OID). An LDAP-based policy store is typically used in production environments. If you are using an OID-based security store in 11g, you must create the new 12c schemas using the Repository Creation Utility (RCU).
2.7.1 Creating 11g OPSS and IAU Schemas
To use a database repository for the Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) security store, you must create the required schema and seed some initial data using the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility (RCU). This setup is also required before reassociating the OPSS security store to a DB-based security store.
Create new 11g Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) and Audit Schemas (IAU) schemas in a supported Database using the 11g Repository Creation Utility.
For more information about creating 11g schemas, see Obtaining and Running Repository Creation Utility in the 11g version of the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide.
2.7.2 Reassociating the 11g Policy Store with the Database-Based Policy Store and OPSS Schema
The OPSS security store is the repository of system and application-specific policies, credentials, keys, and audit services. OPSS delegates the identity store service to the identity providers that are configured in the WebLogic server. Out-of-the-box, the OPSS security store is file-based. You must reassociate it to a database-based security store.
For complete information about reassociating the 11g OPSS schema with database-based repository, see Reassociating the OPSS Security Store.
2.7.3 Validating that the Policy Store Reassociation is Successful
Reassociation modifies the domain configuration file: DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml. It deletes any configuration for the old store provider, inserts a configuration for the new store provider, and moves the policy and credential information from the source to the destination store.
2.7.3.1 Validating the Policy Store Reassociation using the Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control
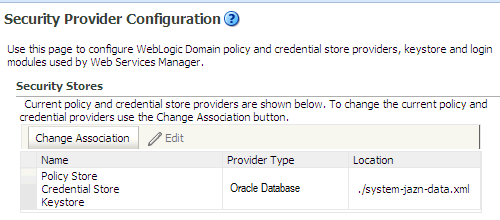
To verify that the policy store reassociation is successful:
2.7.3.2 Validating the Policy Store Reassociation by Viewing the jps-config.xml File
<jpsContext name="default" <serviceInstanceRef ref="credstore.db"/> <serviceInstanceRef ref="keystore.db"/> <serviceInstanceRef ref="policystore.db"/> <serviceInstanceRef ref="audit"/> <serviceInstanceRef ref="idstore.ldap"/> <serviceInstanceRef ref="trust"/> <serviceInstanceRef ref="pdp.service"/> </jpsContext> <serviceInstance provider="policystore.provider" name="policystore.db" <property value="DB_ORACLE" name="policystore.type"/> <propertySetRef ref="props.db.1"/> </serviceInstance> <propertySet name="props.db.1"> <property value="cn=soa_domain" name="oracle.security.jps.farm.name"/> <property value="cn=jpsroot" name="oracle.security.jps.ldap.root.name"/> <property value="jdbc/opss" name="datasource.jndi.name"/> </propertySet>
2.7.4 Creating the 12c OPSS Schema for an OID-based Security Store
The only supported LDAP-based OPSS security store is Oracle Internet Directory (OID). An LDAP-based policy store is typically used in production environments. If you are using an OID-based security store in 11g, you must create the new 12c schemas using the Repository Creation Utility (RCU).
You do not need to reassociate an OID-based security store before upgrade. While the Upgrade Assistant is running, select the OPSS schema. The Upgrade Assistant upgrades the OID-based security store automatically.
Note:
The 12c OPSS database schema is required so that you can reference the 12c schema during the reconfiguration of the domain. Your domain continues to use the OID-based security store after the upgrade is complete.
2.8 Upgrading Security Stores to the Latest Version
Upgrading to the latest version of the OPSS security store enable you to use enhanced features and fixes. OPSS security store is a part of Oracle Fusion Middleware product installation and therefore, you can use the Upgrade Assistant directly to upgrade the OPSS schema.
Before upgrading the OPSS security store, it is important to create a back up so that it can be recovered in case the upgrade fails. For details about backing up the security store, see Backing Up and Recovering the OPSS Security Store.
schema_name
SELECT VERSION, STATUS, UPGRADED
FROM SCHEMA_VERSION_REGISTRY
WHERE OWNER=’schema_name’;
where, schema_name is the name of the OPSS schema. For example, DEV_OPSS.
2.9 Creating a Non-SYSDBA User
Oracle recommends that you create a non-SYSDBA user to run the Upgrade Assistant. The user created using this procedure has the privileges required to complete the upgrade.
Note:
The v$xatrans$ table does not exist by default. You must run the XAVIEW.SQL script to create this table before creating the user. Moreover, grant on v$xatrans$ table is required only for Oracle Identity Manager. If you do not require Oracle Identity Manager for configuration or if you do not have the v$xatrans$ table, then remove the following line from the script:grant select on v$xatrans$ to FMW with grant option;
Note:
If you are upgrading an ORASDPM schema that was created using RCU 11g (11.1.1.1.4 or earlier), and you subsequently upgraded ORASDPM to 11g (11.1.1.6 or later), the FMW user will need to grant the CREATE TABLE privilege to user <prefix>_ORASDPM before upgrading to 12c (12.2.1).grant CREATE TABLE to <prefix>_ORASDPM;
Where <prefix> is the name given to the schema when it was created.
welcome1 is the password. Make sure that you specify your actual password when granting privileges.
create user FMW identified by welcome1; grant dba to FMW; grant execute on DBMS_LOB to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_OUTPUT to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_STATS to FMW with grant option; grant execute on sys.dbms_aqadm to FMW with grant option; grant execute on sys.dbms_aqin to FMW with grant option; grant execute on sys.dbms_aqjms to FMW with grant option; grant execute on sys.dbms_aq to FMW with grant option; grant execute on utl_file to FMW with grant option; grant execute on dbms_lock to FMW with grant option; grant select on sys.V_$INSTANCE to FMW with grant option; grant select on sys.GV_$INSTANCE to FMW with grant option; grant select on sys.V_$SESSION to FMW with grant option; grant select on sys.GV_$SESSION to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_scheduler_jobs to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_scheduler_job_run_details to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_scheduler_running_jobs to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_aq_agents to FMW with grant option; grant execute on sys.DBMS_SHARED_POOL to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_2pc_pending to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_pending_transactions to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_FLASHBACK to FMW with grant option; grant execute on dbms_crypto to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_REPUTIL to FMW with grant option; grant execute on dbms_job to FMW with grant option; grant select on pending_trans$ to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_scheduler_job_classes to fmw with grant option; grant select on SYS.DBA_DATA_FILES to FMW with grant option; grant select on SYS.V_$ASM_DISKGROUP to FMW with grant option; grant select on v$xatrans$ to FMW with grant option; grant execute on sys.dbms_system to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_SCHEDULER to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_data_files to FMW with grant option; grant execute on UTL_RAW to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_XMLDOM to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_UTILITY to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_SESSION to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_METADATA to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_XMLGEN to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_DATAPUMP to FMW with grant option; grant execute on DBMS_MVIEW to FMW with grant option; grant select on ALL_ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS to FMW with grant option; grant select on dba_queue_subscribers to FMW with grant option; grant execute on SYS.DBMS_ASSERT to FMW with grant option;
Note:
Oracle Database 11.2.0.3 Database Users ONLY: You must apply Oracle Patch 13036331 before you begin the upgrade. Go to My Oracle Support to download the patch.
If you do not apply this patch, then you will have to grant additional privileges for some schemas.
2.10 Using Enhanced Encryption (AES 256)
The Java platform defines a set of APIs spanning major security areas, including cryptography, public key infrastructure, authentication, secure communication, and access control. These APIs allow developers to easily integrate security mechanisms into their application code If you plan to use enhanced encryption (such as AES 256), Oracle recommends that you apply these policy files to the JDK before you upgrade.
Some of the security algorithms used in Fusion Middleware 12c require additional policy files for the JDK. For more information, see Java Cryptography Architecture Oracle Providers Documentation.
If you do not apply these policy files to the JDK before you begin the upgrade, the upgrade can fail and you need to restore the entire pre-upgrade environment and start the upgrade from the beginning.
2.11 Creating an Edition on the Server for Edition-Based Redefinition (Optional)
Edition-based redefinition enables you to upgrade an Oracle Database component of an application, such as PL/SQL objects, views, and synonyms, while it is in use, thereby minimizing or eliminating down time.
Note:
This task must be carried out only by the Oracle Database User, having DBA privileges.Before upgrading an Edition-Based Redefinition (EBR) enabled schema, you must connect to the database server and create an edition on the database server for 12c. The new edition for 12c must be a child of your existing 11g or 12c edition.
To create an edition on the database server, log in as an SYS user (or another Oracle user that has DBA privileges) and enter the following command:
create edition Oracle_FMW_12_2_1 as child of Oracle_FMW_11_1_1_7_0;
Where, Oracle_FMW_11_1_1_7_0 is an example of the edition name you specified in RCU 11.1.1.7 when the 11.1.1.7 schemas were created. Be sure to provide the actual name used when creating the edition.
If the edition is created successfully, you get the following message:
Edition created.
During the upgrade, you are prompted to launch the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your existing domain. Before running the Reconfiguration Wizard, you must specify the database default edition. Use the following SQL to manually setup the default edition name for the database, for example:
ALTER DATABASE DEFAULT EDITION = Oracle_FMW_12_2_1;
2.12 Maintaining Custom Domain Environment Settings
Every domain includes dynamically generated domain and server startup scripts, such as setDomainEnv. Oracle recommends that you do not modify these startup scripts, as any changes made to them are overwritten during subsequent domain upgrade and reconfiguration operations.
To maintain your custom domain-level environment settings, creating a separate file to store the custom domain information before you upgrade.
For example, if you want to customize server startup parameters that apply to all servers in a domain, you can create a file called setUserOverrides.cmd (Windows) or setUserOverrides.sh (UNIX) and configure it to add custom libraries to the WebLogic Server classpath, specify additional java command line options for running the servers, or specify additional environment variables, for instance. Any custom settings you add to this file are preserved during domain upgrade operation and are carried over to the remote servers when using the pack and unpack commands.
setUserOverrides file:
# add custom libraries to the WebLogic Server system claspath
if [ "${POST_CLASSPATH}" != "" ] ; then
POST_CLASSPATH="${POST_CLASSPATH}${CLASSPATHSEP}${HOME}/foo/fooBar.jar"
export POST_CLASSPATH
else
POST_CLASSPATH="${HOME}/foo/fooBar.jar"
export POST_CLASSPATH
fi
# specify additional java command line options for servers
JAVA_OPTIONS="${JAVA_OPTIONS} -Dcustom.property.key=custom.value"
If the setUserOverrides file exists during a server startup, the file is included in the startup sequence and any overrides contained within this file take effect. You must store the setUserOverrides file in the domain_home/bin directory.
Note:
If you are unable to create the setUserOverrides script before an upgrade, you need to reapply your settings as described in Re-apply Customizations to Startup Scripts.
2.13 Downloading and Installing the 12c Oracle Fusion Middleware Product Distributions
Oracle Fusion Middleware product distributions are available for download on Oracle Technology Network (OTN) and Oracle Software Delivery Cloud.
For more information on which site you should visit to obtain your distribution, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Download, Installation, and Configuration Readme Files page.
After you have downloaded all the necessary software, you can proceed to install and configure your software.
To get started with your installations, refer to the Install, Patch, and Upgrade common tasks page in the Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c (12.2.1) Documentation Library on OTN.
Note:
You must install the Fusion Middleware Infrastructure distribution before installing the component-specific distributions.2.14 Using the Upgrade Assistant to Run a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
The Upgrade Assistant can be run in the -readiness mode to perform a read-only, pre-upgrade check on your domain. If issues are detected, you can correct them before starting the actual upgrade.
-readiness mode:The screens you see will vary depending on the upgrade options you select. The sections below describe the upgrade options and the information you will need to provide.
2.15 Locating the Component-Specific Upgrade Documentation
The component specific upgrade documentation provides upgrade procedure and information for every individual component including Oracle WebLogic Server, Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure, Oracle HTTP Server, Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management, Oracle Webcenter, User Messaging Service, and Oracle Data Integrator.
The following table helps you determine which upgrade-specific tasks you will need to complete for your 12c upgrade:
Table 2-2 Component-Specific Upgrade Documentation
| Product Area | If you are upgrading... | Use this upgrade document... |
|---|---|---|
|
Oracle WebLogic Server - Standalone |
An Oracle WebLogic Server that is not being managed by or registered to an existing Fusion Middleware 11g domain. |
|
|
Custom Oracle Application Developer Framework Applications with Oracle WebLogic Server (referred to as Infrastructure in 12c) |
A managed 11g WebLogic Server domain that has been deployed with a set of custom Oracle Application Developer Framework applications. |
|
|
Oracle HTTP Server - Managed or Standalone |
An Oracle HTTP Server that is configured to work with a WebLogic domain for management functions is a managed server. An Oracle HTTP Server that is not managed by or registered to an Oracle WebLogic domain is a standalone server. |
|
|
Oracle SOA Suite and BPM |
SOA Suite components including: Business Process Management (BPM), Oracle Service Bus (OSB), Enterprise Security Services (ESS), Managed File Transfer (MFT), Business Activity Monitoring (BAM), and workflow instance data. |
|
|
User Messaging Service |
User Messaging Service. |
|
|
Oracle Data Integrator |
Data Integrator. |
|
| Oracle WebCenter | WebCenter suite components including Content, Portal and Sites. | Upgrading Oracle WebCenter |
| Oracle Business Intelligence | Oracle Business Intelligence including BI Enterprise Edition, BI Publisher, and Essbase. | Upgrading Oracle Business Intelligence |
| Oracle Forms | Oracle Forms. | Upgrading Oracle Forms |