What Are the System Requirements for Map Views?
Several components need to be configured so that map views can be added to dashboards.
To include map views on dashboards, the system must include the following components:
-
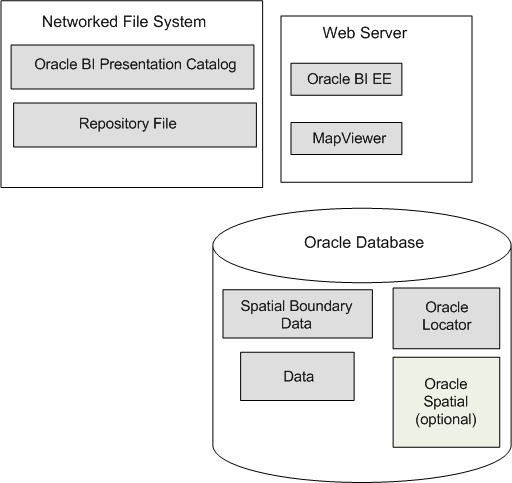
Oracle MapViewer, which is a J2EE service that serves as an engine for rendering maps using spatial data managed by Oracle Spatial. MapViewer is closely integrated with Oracle BI EE. MapViewer is installed as part of Oracle BI EE and deployed in the same domain as Oracle BI EE on the web application server.
MapViewer provides services and tools that hide the complexity of spatial data queries and cartographic rendering, while providing customizable options for more advanced users. MapViewer is designed to integrate with Location-Based services and applications.
-
Spatial boundary data. NAVTEQ is one provider of this data to Oracle customers, which can be downloaded from the Oracle Technology Network. This spatial data and any other spatial metadata, including themes and styles, must be stored in an Oracle Database to be accessed by Oracle MapViewer for display in map views.
-
Hosted maps. In Oracle BI EE, users can access hosted maps from the Oracle eLocation service. Terms and conditions of use are located at the following URL:
-
Oracle Database, version 10g or later, to store the spatial data.
Oracle Locator, which is a feature of Oracle Database (all editions) that provides core location functionality needed by most customer applications.
If you use an Oracle Database as the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) database, then you can use that same Oracle Database for spatial data also. See Installing and Configuring Oracle Business Intelligence for information.
-
(Optional) Oracle Spatial is an option for Oracle Database Enterprise Edition that provides advanced spatial features to support high-end geographic information systems (GIS) and location-based services (LBS) solutions. The Spatial option is required only if you plan to make use of maps or features that require advanced spatial capabilities that are not available with the Locator option. Additional Oracle Spatial features include raster and 3D data management, spatial web services, topology, network data modeling, resource description framework (RDF), and semantic web capabilities.
-
Metadata of the mapping between Oracle BI EE data and spatial data, which can be stored in a file system, in the Oracle BI Presentation Catalog.
The illustration shows the default architecture for map views when Oracle BI EE is installed. You can store the data either in an Oracle Database or in other databases that Oracle BI EE supports. See Configuring MapViewer to Support Map Views for a diagram of the preferred architecture for map views.
When these pieces are in place, you administer the map using the Oracle BI Presentation Services Administration page, as described in Administering Maps.