| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |
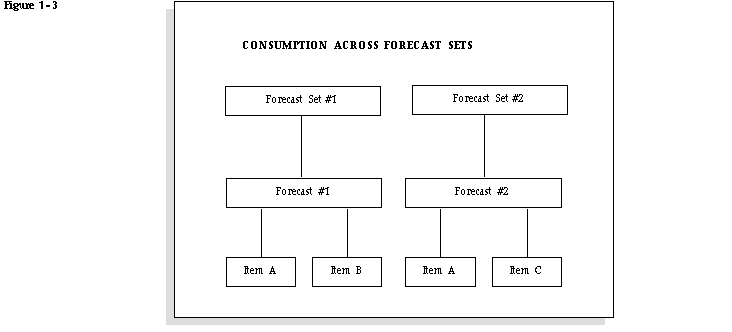
Forecast Set #1 contains Forecast #1 and Forecast Set #2 contains Forecast #2. The same item, Item A, belongs to both forecasts within each set.
When you create a sales order, both forecasts for Item A in Forecast Set #1 and Forecast Set #2 are consumed. This is because consumption occurs against each forecast set, and Item A exists in both forecast sets.
For example, if each forecast for Item A is quantity 100 and you place sales order demand for 20, the consumption process would decrement each forecast in each set from 100 to 80.
Note: In this example, Forecast Set #1 and Forecast Set #2 are most likely alternative scenarios -- two different sets for comparison purposes, so that consumption occurs for the same item in both sets. If you want to consume an item only once, define all forecasts for an item within a single set. See: Figure 1 - 1.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index | Navigation | Glossary | Library |