Optimal Rate Calculation
Without any restrictions, such as firm or partially firm repetitive schedules, the repetitive planning process always suggests a daily rate that equals the optimal rate.
The basic calculation of optimal rates involves three steps:
- Calculate average daily demand
- Set optimal rate = average daily demand
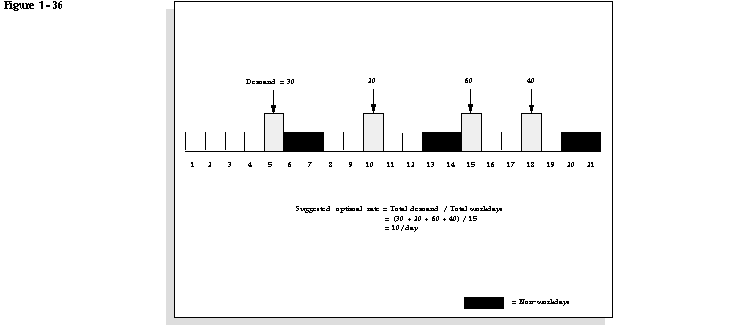
The repetitive planning process calculates optimal rates by summing net requirements for each repetitive assembly within each repetitive planning period. An average daily demand is calculated by dividing the total demand for the period by the total number of workdays within the same period. The repetitive planning process recommends an optimal rate that matches the average daily demand.
The following diagram illustrates how the repetitive planning process calculates optimal rates.