Release 1 (9.0.1)
Part Number A90125-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 1 (9.0.1) Part Number A90125-01 |
|
SQL Statements:
DROP SEQUENCE to ROLLBACK, 7 of 20
Use the DROP TYPE statement to drop the specification and body of an object type, a varray, or nested table type.
|
See Also:
|
The object type, varray, or nested table type must be in your own schema or you must have the DROP ANY TYPE system privilege.
drop_type::=
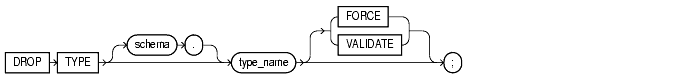
drop_type
Specify the schema containing the type. If you omit schema, Oracle assumes the type is in your own schema.
Specify the name of the object, varray, or nested table type to be dropped. You can drop only types with no type or table dependencies.
If type_name is a supertype, this statement will fail unless you also specify FORCE. If you specify FORCE, Oracle invalidates all subtypes depending on this supertype.
If type_name is a statistics type, this statement will fail unless you also specify FORCE. If you specify FORCE, Oracle first disassociates all objects that are associated with type_name, and then drops type_name.
If type_name is an object type that has been associated with a statistics type, Oracle first attempts to disassociate type_name from the statistics type and then drop type_name. However, if statistics have been collected using the statistics type, Oracle will be unable to disassociate type_name from the statistics type, and this statement will fail.
If type_name is an implementation type for an indextype, the indextype will be marked INVALID.
Unless you specify FORCE, you can drop only object types, nested tables, or varray types that are standalone schema objects with no dependencies. This is the default behavior.
Specify FORCE to drop the type even if it has dependent database objects. Oracle marks UNUSED all columns dependent on the type to be dropped, and those columns become inaccessible.
|
Caution: Oracle does not recommend that you specify |
If you specify VALIDATE when dropping a type, Oracle checks for stored instances of this type within substitutable columns of any of its supertypes. If no such instances are found, Oracle completes the drop operation.
This clause is meaningful only for subtypes. Oracle Corporation recommends the use of this option to safely drop subtypes that do not have any "explicit" type or table dependencies.
DROP TYPE Example
The following statement removes object type person_t (created in "Type Hierarchy Example"):
DROP TYPE person_t;
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|