Release 1 (9.0.1)
Part Number A90136-02
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle9i Recovery Manager Reference Release 1 (9.0.1) Part Number A90136-02 |
|
RMAN Commands , 13 of 60
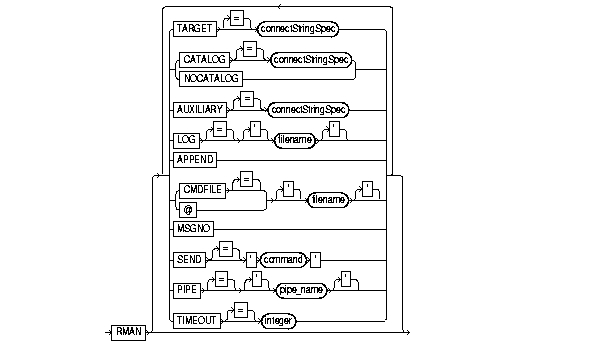
To start RMAN from the operating system command line. Use these arguments to:
If you start RMAN without specifying either CATALOG or NOCATALOG on the command line, then RMAN makes no connection to a repository. If you run a command that requires the repository, and if no CONNECT CATALOG command has been issued yet, then RMAN automatically connects in the default NOCATALOG mode. After that point, the CONNECT CATALOG command is not valid in the session.
Use these arguments at the operating system command line rather than at the RMAN prompt.
|
Specifies a connect string to the target database, for example, See Also: "connectStringSpec" |
||
|
Specifies a connect string to the database containing the recovery catalog, for example, See Also: "connectStringSpec" |
||
|
|
Indicates that you are using RMAN without a recovery catalog.
Note: If you do not specify either |
|
|
Specifies a connect string to an auxiliary database, for example, See Also: "connectStringSpec" |
||
|
|
Specifies the file where Recovery Manager will record RMAN output, that is, the commands that were processed and their results. If you do not specify this argument, then RMAN writes its message log file to standard output.
The |
|
|
|
Causes new output to be appended to the end of the message log file. If you do not specify this parameter, and if a file with the same name as the message log file already exists, then RMAN overwrites it. |
|
|
|
Runs a file containing a user-defined list of RMAN commands. If the first character of the filename is alphabetic, then you can omit the quotes around the filename.
The contents of the command file should be identical to commands entered at the RMAN prompt. For example, the following file contents will cause RMAN to connect to a target database and recovery catalog CONNECT TARGET; CONNECT CATALOG rman/rman@rcat; BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG; RMAN terminates after running the command file. |
|
|
|
Equivalent to |
|
|
|
Causes RMAN to print message numbers, that is, |
|
|
|
Sends a vendor-specific command string to all allocated channels. See Also: Your media management documentation to determine whether this feature is supported, and "SEND" |
|
|
|
Invokes the RMAN pipe interface. RMAN uses two public pipes: one for receiving commands and the other for sending output. The names of the pipes are derived from the value of the RMAN opens the following pipes in the target database:
All messages on both the input and output pipes are of type See Also: Oracle9i Recovery Manager User's Guide to learn how to pass commands to RMAN through a pipe |
|
|
|
Causes RMAN to exit automatically if it does not receive input from an input pipe within integer seconds. The See Also: Oracle9i Recovery Manager User's Guide to learn how to pass commands to RMAN through a pipe |
|
This example connects to the target database prod1 without a recovery catalog:
% rman TARGET SYS/sys_pwd@prod1 NOCATALOG
This example connects to the target database prod1 without specifying catalog options. Because CONNECT CATALOG is not run at the RMAN prompt, RMAN connects in default NOCATALOG mode when the first command requiring a repository connection is run:
% rman RMAN> CONNECT TARGET RMAN> BACKUP DATABASE;
This example connects to the target database prod1, the recovery catalog database rcat, and the auxiliary instance aux1:
% rman TARGET SYS/sys_pwd@prod1 CATALOG rman/rman@rcat AUXILIARY sys/aux_pwd@aux1
This example connects to the target database prod1 and the recovery catalog database rcat, and then runs the command file b_whole_10.rcv:
% rman TARGET SYS/sys_pwd@prod1 CATALOG rman/rman@rcat @'/oracle/dbs/b_whole_l0.rcv'
This example connects to the target database prod1 without a recovery catalog and then specifies that RMAN should append messages to the message log:
% rman TARGET / NOCATALOG LOG = $ORACLE_HOME/dbs/log/msglog.f APPEND
This example invokes the RMAN pipe newpipe with a 90 second timeout option:
% rman PIPE newpipe TARGET SYS/sys_pwd@prod1 TIMEOUT = 90
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|