Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96540-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-01 |
|
Functions, 119 of 177
substr::=
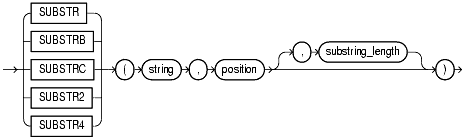
The "substring" functions return a portion of string, beginning at character position, substring_length characters long. SUBSTR calculates lengths using characters as defined by the input character set. SUBSTRB uses bytes instead of characters. SUBSTRC uses Unicode complete characters. SUBSTR2 uses UCS2 codepoints. SUBSTR4 uses UCS4 codepoints.
position is 0, then it is treated as 1.position is positive, then Oracle counts from the beginning of string to find the first character.position is negative, then Oracle counts backward from the end of string.substring_length is omitted, then Oracle returns all characters to the end of string. If substring_length is less than 1, then a null is returned.string can be any of the datatypes CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB. The return value is the same datatype as string. Floating-point numbers passed as arguments to SUBSTR are automatically converted to integers.
The following example returns several specified substrings of "ABCDEFG":
SELECT SUBSTR('ABCDEFG',3,4) "Substring" FROM DUAL; Substring --------- CDEF SELECT SUBSTR('ABCDEFG',-5,4) "Substring" FROM DUAL; Substring --------- CDEF
Assume a double-byte database character set:
SELECT SUBSTRB('ABCDEFG',5,4.2) "Substring with bytes" FROM DUAL; Substring with bytes -------------------- CD
|
 Copyright © 1996, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|