| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1) Part Number B10759-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
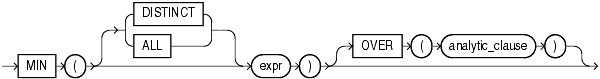
MIN returns minimum value of expr. You can use it as an aggregate or analytic function.
If you specify DISTINCT, then you can specify only the query_partition_clause of the analytic_clause. The order_by_clause and windowing_clause are not allowed.
|
See Also: "About SQL Expressions " for information on valid forms ofexpr, "Floating-Point Numbers " for information on binary-float comparison semantics, and "Aggregate Functions " |
The following statement returns the earliest hire date in the hr.employees table:
SELECT MIN(hire_date) "Earliest" FROM employees; Earliest --------- 17-JUN-87
The following example determines, for each employee, the employees who were hired on or before the same date as the employee. It then determines the subset of employees reporting to the same manager as the employee, and returns the lowest salary in that subset.
SELECT manager_id, last_name, hire_date, salary,
MIN(salary) OVER(PARTITION BY manager_id ORDER BY hire_date
RANGE UNBOUNDED PRECEDING) as p_cmin
FROM employees;
MANAGER_ID LAST_NAME HIRE_DATE SALARY P_CMIN
---------- ------------------------- --------- ---------- ----------
100 Kochhar 21-SEP-89 17000 17000
100 De Haan 13-JAN-93 17000 17000
100 Raphaely 07-DEC-94 11000 11000
100 Kaufling 01-MAY-95 7900 7900
100 Hartstein 17-FEB-96 13000 7900
100 Weiss 18-JUL-96 8000 7900
100 Russell 01-OCT-96 14000 7900
100 Partners 05-JAN-97 13500 7900
100 Errazuriz 10-MAR-97 12000 7900
. . .