|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) Part No. B14061-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) Part No. B14061-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter describes Oracle Containers for J2EE (OC4J) deployment and integration with OracleAS Integration InterConnect.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
|
See Also: |
The following topic shows the basic commands for using CCI with packaged application adapters.
|
See Also: |
The following example shows the code structure for using CCI with packaged application adapters. The code sample is shown in five steps.
Step 1. Obtain the Connection Factory
The connection factory is obtained by JNDI lookup.
InitialContext context = new InitialContext(); ConnectionFactory cf = (ConnectionFactory)context.lookup(iwayJndi)
Step 2. Obtaining a Connection for the Adapter
IWAFConnectionSpec is an implementation of ConnectionSpec used for creating a design time or runtime service adapter connection. The ConnectionSpec has seven parameters. Connection Pooling is fully supported and established based on these parameters, except log level.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| adapterName | Name of the packaged application adapter. |
| config - | Adapter configuration name. NOT REQUIRED FOR IWAEAdapter. |
| language | Default is en. |
| country | Default is us. |
| userName | User name. If provided, it overwrites configuration. |
| password | Password. If provided, it overwrites configuration. |
| logLevel | It overwrites the level set by the ManagedConnectionFactory property. |
|
Note: Currently the OracleAS Adapter JCA supports only basic security mapping. The DEBUG log level provides detaild information on the mapping behavior. It functions as follows:
|
The iWAFConnectionSpec can be made to invoke an interaction with SAP by specifying the adapter name and configuration parameters in the ConnectionSpec. For example,
iWAFConnectionSpec cs = new IWAFConnectionSpec(); cs.setAdapterName(ADAPTER); cs.setConfig(TARGET); cs.setLogLevel(LOG_LEVEL); // Adapter layer log level Connection c = cf.getConnection(cs);// where cf is the connection factory
In this snippet, ADAPTER and TARGET refer to the adapter being invoked, in this case SAP, and the name of a target defined in Application Explorer. See "Complete Code Sample" for more information.
Step 3. Create interaction with interactionSpec for runtime
Interaction i = c.createInteraction(); IWAFInteractionSpec is = new IWAFInteractionSpec(); is.setFunctionName(IWAFInteractionSpec.PROCESS);
Two functions can be set: PROCESS and IWAE. PROCESS is used at runtime. IWAE is used when you are using the IAEAdapter at design time.
Step 4. Create Input Record and Execute Interaction
In this case, to complete the EIS invocation, an SAP RFC message is referenced. The schema is provided by Application Explorer.
A standard JCA Indexed Record is used in this example:
// Use JCA IndexRecord, named "input" for runtime processing.
IndexedRecord rIn = cf.getRecordFactory().createIndexedRecord("input");
rIn.add(msg_run);
IndexedRecord rOut = (IndexedRecord)i.execute(is, rIn);
System.out.println((String)rOut.get(0));
A special record is supported in this example:
//IWAFRecord rIn = new IWAFRecord("input");
//rIn.setRootXML(msg_run);
//IWAFRecord response = executeRunInteraction(c, rIn);
//IWAFRecord rOut = (IWAFRecord)i.execute(is, rIn);
//System.out.println(rOut.getRootXML());
msg_run
Is an instance XML document generated from the schema created by Application Explorer. For example, the following is a sample SAP request XML document.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <BAPI_CUSTOMER_GETDETAIL2> <COMPANYCODE></COMPANYCODE> <CUSTOMERNO>0000401026</CUSTOMERNO> </BAPI_CUSTOMER_GETDETAIL2>
Complete Code Sample
The following is a sample of the complete code:
import javax.resource.cci.*;
import com.ibi.afjca.cci.*;
import com.ibi.afjca.spi.*;
/**
* The purpose of this sample is to illustrate how to use the IWAF Universal
* JCA connector.
*
* Author: Marcelo Borges
* Date: August, 2004
*/
public class IWAFJCASimple {
private static String HOME = "c:/iway/xfoc/components/iwafcont/dist";
private static String CONFIG = "base";
private static String LOG_LEVEL = "FATAL";
private static String ADAPTER = "SAP";
private static String TARGET = "SAP_connection";
// Input Message
private static String msg_run = "<SAP/>";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. Getting the Connection factory through JNDI lookup
// ---------------------------------------------------------
InitialContext context = new InitialContext();
ConnectionFactory cf = (ConnectionFactory)context.lookup(iwayJndi)
// 2. Getting a connection for a particular adapter target, in this case SAP
// ---------------------------------------------------------
IWAFConnectionSpec cs = new IWAFConnectionSpec();
cs.setAdapterName(ADAPTER);
cs.setConfig(TARGET);
cs.setLogLevel(LOG_LEVEL); // Adapter layer log level
Connection c = cf.getConnection(cs);// where cf is the connection factory
// 3. Create interaction with interactionSpec for RUNTIME
// ---------------------------------------------------------
Interaction i = c.createInteraction();
IWAFInteractionSpec is = new IWAFInteractionSpec();
is.setFunctionName("PROCESS");
// 4. Create input Record and execute interaction
// ---------------------------------------------------------
// 4.1 Using JCA standard Indexed Record
// Use JCA IndexRecord, named "input" for runtime processing.
IndexedRecord rIn = cf.getRecordFactory().createIndexedRecord("input");
rIn.add(msg_run);
IndexedRecord rOut = (IndexedRecord)i.execute(is, rIn);
System.out.println((String)rOut.get(0));
// 4.2 Our own Record is supported here
//IWAFRecord rIn = new IWAFRecord("input");
//rIn.setRootXML(msg_run);
//IWAFRecord response = executeRunInteraction(c, rIn);
//IWAFRecord rOut = (IWAFRecord)i.execute(is, rIn);
//System.out.println(rOut.getRootXML());
} // main()
}
Creating a Managed Connection Factory
The OC4J-ra.xml descriptor provides OC4J-specific deployment information for resource adapters. For example, the default jca_sample configuration in Application Explorer is represented in the OC4J-ra.xml file as follows:
<?xml version="1.0"?><!DOCTYPE oc4j-connector-factories PUBLIC "-//Oracle//DTD Oracle Connector > 9.04//EN" "http://xmlns.oracle.com/ias/dtds/oc4j-connector-factories-9_04.dtd" <oc4j-connector-factories> <connector-factory location="eis/OracleJCAAdapter/DefaultConnection" connector-name="IWAFJCA10"> <config-property name="IWayHome" value="../../adapters/application"/> <config-property name="IWayConfig" value="jca_sample"/> <config-property name="IWayRepoURL" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoUser" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoPassword" value=""/> <config-property name="logLevel" value="debug"/> </connector-factory> </oc4j-connector-factories>
The parameters are defined in the following table:
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| IWayHome | The base installation directory for the OracleAS packaged application adapter. |
| IWayConfig | The adapter configuration name as defined in Application Explorer. For example, the OracleAS Adapter for SAP has a preconfigured jca_sample configuration in the Application Explorer. |
| IWayRepoURL | The URL to use when opening a connection to the database. This is necessary only when using an Oracle database as the BSE repository. See"Configuring an Oracle Repository" in Chapter 2, "Adapter Configuration Using Application Explorer" for more information. |
| IWayRepoUser | User name to use when connecting to the database. This is necessary only when using an Oracle database as the BSE repository. See"Configuring an Oracle Repository" in Chapter 2, "Adapter Configuration Using Application Explorer" for more information. |
| IWayRepoPassword | Password. If provided, it overwrites configuration. This is necessary only when using an Oracle database as the BSE repository. See"Configuring an Oracle Repository" in Chapter 2, "Adapter Configuration Using Application Explorer" for more information. |
| loglevel | It overwrites the level set by the ManagedConnectionFactory property. |
Creating Multiple Managed Connection Factories
To establish Multiple Managed Connection Factories, you must edit the OC4J-ra.xml file to add the required information. The file can contain more than one <connector-factory> element. By adding more <connector-factory> elements, you can create Multiple Managed connection factories. For example, the default jca_sample configuration in Application Explorer is represented in the OC4J-ra.xml file as follows:
<?xml version="1.0"?><!DOCTYPE oc4j-connector-factories PUBLIC "-//Oracle//DTD Oracle Connector 9.04//EN" "http://xmlns.oracle.com/ias/dtds/oc4j-connector-factories-9_04.dtd"> <oc4j-connector-factories> <connector-factory location="eis/OracleJCAAdapter/DefaultConnection" connector-name="IWAFJCA10"> <config-property name="IWayHome" value="../../adapters/application"/> <config-property name="IWayConfig" value="jca_sample"/> <config-property name="IWayRepoURL" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoUser" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoPassword" value=""/> <config-property name="logLevel" value="debug"/> </connector-factory> </oc4j-connector-factories>
To create Multiple Managed Connection Factories, you must add new <connector-factory> nodes in the file. For example:
<?xml version="1.0"?><!DOCTYPE oc4j-connector-factories PUBLIC "-//Oracle//DTD Oracle Connector 9.04//EN" "http://xmlns.oracle.com/ias/dtds/oc4j-connector-factories-9_04.dtd"> <oc4j-connector-factories> <connector-factory location="eis/OracleJCAAdapter/DefaultConnection1" connector-name="IWAFJCA10"> <config-property name="IWayHome" value="../../adapters/application"/> <config-property name="IWayConfig" value="jca_sample"/> <config-property name="IWayRepoURL" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoUser" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoPassword" value=""/> <config-property name="logLevel" value="debug"/> </connector-factory> <connector-factory location="eis/OracleJCAAdapter/DefaultConnection2" connector-name="IWAFJCA10"> <config-property name="IWayHome" value="../../adapters/application"/> <config-property name="IWayConfig" value="jca_sample2"/> <config-property name="IWayRepoURL" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoUser" value=""/> <config-property name="IWayRepoPassword" value=""/> <config-property name="logLevel" value="debug"/> </connector-factory> </oc4j-connector-factories>
Oracle Application Server Adapter JCA Architecture
Figure 3-1 shows deployment of the Connector to the Oracle Application Server. In a runtime service scenario, an Enterprise Java Bean (EJB), Servlet, or Java program client makes CCI calls to JCA resource adapters. The adapters process the calls as requests and send them to the EIS. The EIS response is then sent back to the client.
|
See Also: "Deployment and Integration through OracleAS Web Services" in Oracle Application Server Adapter Concepts |
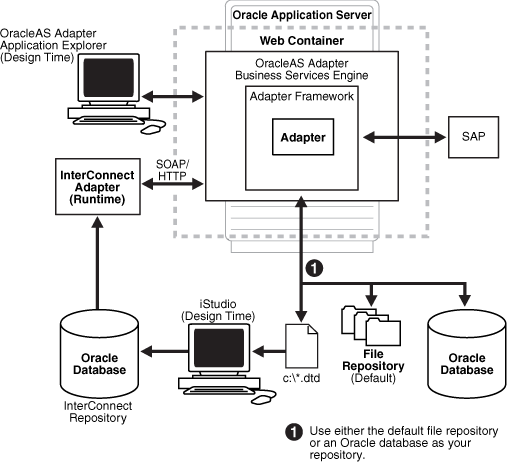
BSE Architecture as Deployed to Oracle Application Server
Figure 3-2 shows adapter framework deployment with BSE to OracleAS Integration InterConnect. In a runtime service scenario, the OracleAS Integration InterConnect EIS Adapter Plugin (EIS Adapter Plugin) receives DTD-compliant XML from the agent component of the EIS Adapter Plugin. The EIS Adapter Plugin strips runtime information from the XML, wraps the XML in a SOAP envelope, and sends the result to BSE, including the runtime information in the SOAP request. BSE receives the request, removes the envelope, retrieves Web service method metadata, including adapter and connection information from the repository, and makes the adapter request.
BSE receives the adapter response, wraps the response XML in a SOAP envelope, and returns it to the EIS Adapter Plugin. The EIS Adapter Plugin then strips the SOAP envelope, strips the namespace prefix, if present, and passes the DTD-compliant XML to the agent component of the EIS Adapter Plugin.
Figure 3-2 BSE Architecture as Deployed to Oracle Application Server
Upon installation of the Oracle Web Services Adapter, an adapter.ini file is created. The file consists of all the initialization parameters that the adapter reads at startup. You can configure the OracleAS Integration InterConnect EIS Adapter Plugin by modifying these parameters.
|
See Also: Oracle Application Server Adapters Installation Guide |