|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) Part No. B14061-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) Part No. B14061-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
During inbound (client) processing, IDocs are transferred to the interface and stored in the R/3 System. The document data is generated in a second step, also in the course of a workflow.
Outbound processing in SAP involves event handling. An event in SAP is defined as an occurrence of a status change in an object. Events are created when the relevant status change occurs. The following topics describe how to enable inbound and outbound SAP processing.
SAP inbound processing requires the upstream system to transfer an IDoc to the IDoc interface through the R/3 System port. For this reason, you do not have to specify a port in the inbound partner profiles; the IDoc interface only must recognize the upstream system as a port. A port definition, which provides a unique ID for the upstream system, must be available for the port. The technical parameters of this port definition can (and usually are) overwritten by the upstream system.
The IDoc is "accepted", that is, saved in the database, if the upstream system is recognized. If your partner is defined with the corresponding message in your partner profiles, the IDoc is then processed further. This is done independently in a second step. This ensures that the external system can receive the data quickly and reliably (automatically).
You must perform the following steps to configure SAP for inbound IDoc processing:
Configure a logical system.
Configure a distribution model.
Define an inbound partner profile.
In any distributed environment, each participating system must have a unique ID to avoid confusion. In SAP, the name of the logical system is used as the unique ID. This name is assigned explicitly to one client in an SAP system.
Defining a Logical System
Execute the sale transaction.

Expand Sending and Receiving Systems.
Expand Logical Systems.
Select Define Logical System.
Click the IMG - Activity icon.
A message window opens indicating that the table is cross-client.
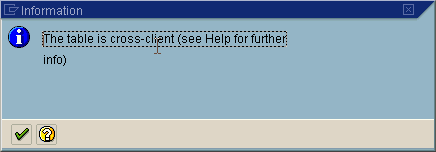
Click the check mark button to continue.
The Change View "Logical Systems": Overview window opens.
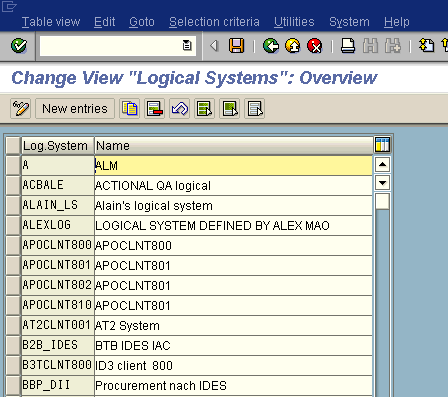
Click the New Entries button.
The New Entries: Overview of Added Entries window opens.
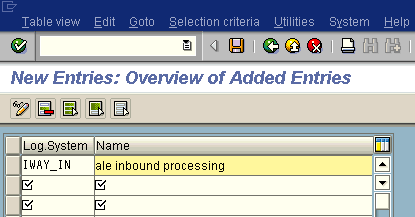
Type the Logical System, for example, ORACLETDS, in the Log.System column and type a description in the Name column.
Click Save.
The Prompt for Workbench request dialog box opens.
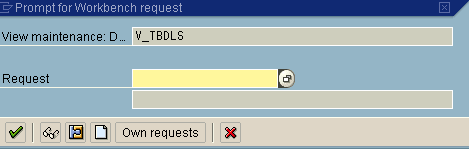
Click the Create Request icon.
The Create Request dialog box opens.
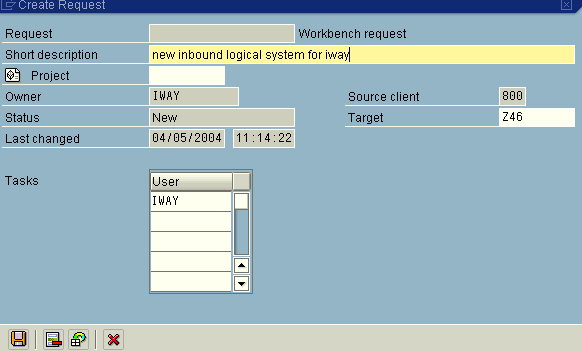
Type a name and description for your request and click Save.
The logical system you configured, for example, ORACLETDS, is now added to the list.

A distribution model is used to describe the ALE message flow between logical systems. Business objects are distributed to connected recipients according to a unique distribution model that can contain rules of varying complexity depending on the type of business objects involved.
Defining a Distribution Model
To define a distribution model:
Execute the bd64 transaction.
The Display Distribution Model window opens.
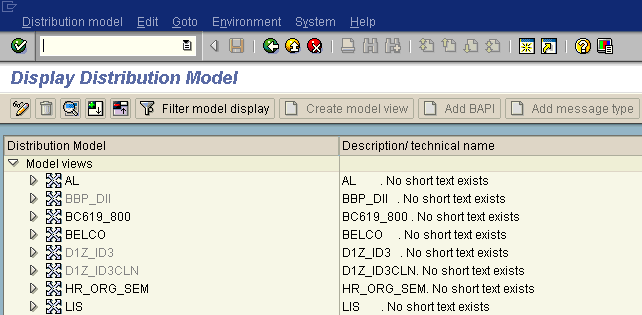
Click Distribution Model from the menu bar.
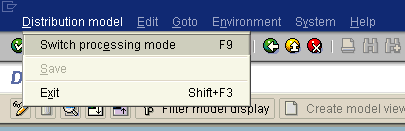
Select Switch processing mode.
The Display Distribution Model window is switched to Change Distribution Model.
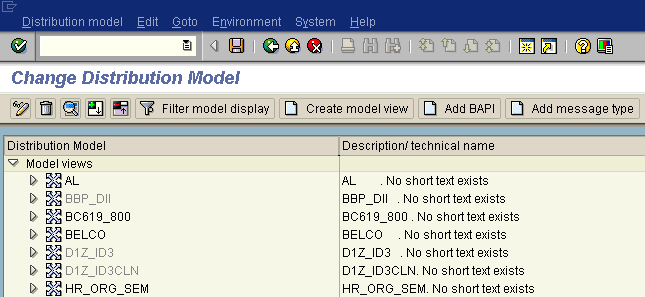
Click the Create model view button.
The Create Model View dialog box opens.
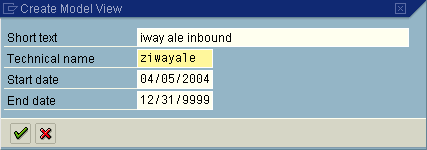
Type a model view name in the Short text field and a name in the Technical name field, which also serves as a description.
Click the check mark button to enter the information.
You are returned to the main Change Distribution Model window. The distribution model you configured is now added to the list.

Click the Add message type button.
The Add Message Type dialog box opens.
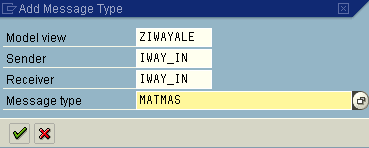
In the Sender and Receiver fields, enter the logical system you configured, for example, ORACLETDS.
You can click the icon to the right of each field to browse from a list of logical systems.
In the Message type field, enter the message type you want to use, for example, MATMAS.
You can click the icon to the right of each field to browse from a list of available message types.
Click the check mark button to enter the information.
You are returned to the main Change Distribution Model window.
Partner profiles are a prerequisite for data exchange. This involves defining who can exchange messages with the SAP system and using which port.
Defining a Partner Profile
To define a partner profile:
Execute the we20 transaction.

The Partner profiles window opens.
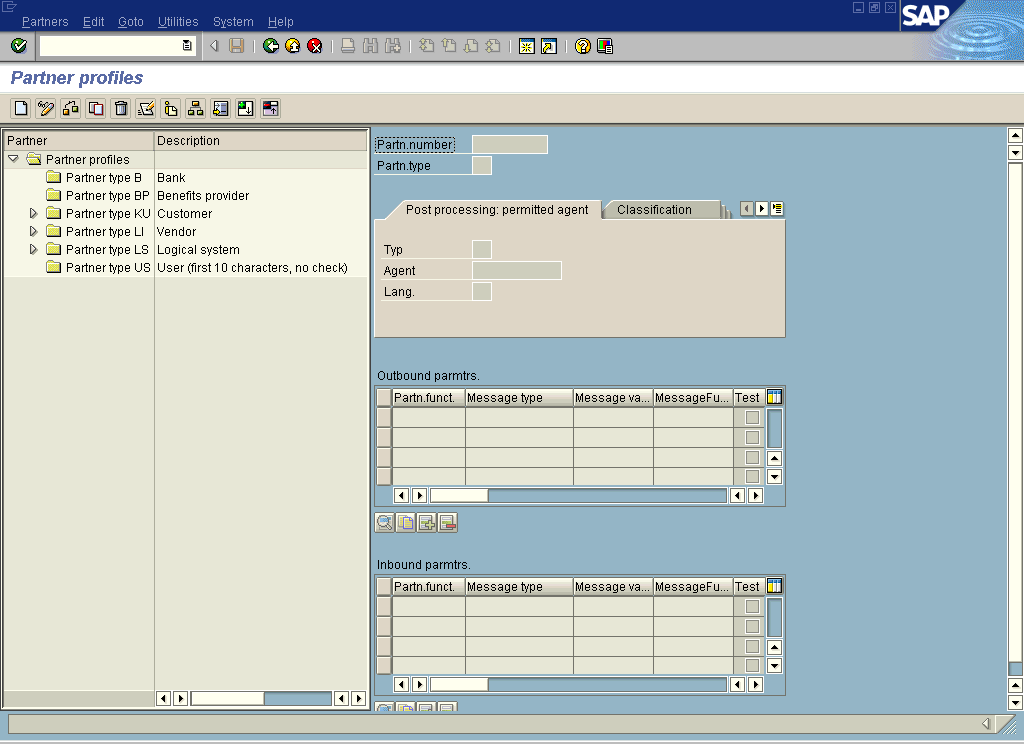
In the left pane, expand Partner type LS and select the logical system you configured from the list, for example, ORACLETDS.
In the right pane, the Partn.number field refers to the name of the logical system.
Click Save.
From the Inbound parameters table, click the Create inbound parameter icon.
The Partner profiles:Inbound parameters window opens.
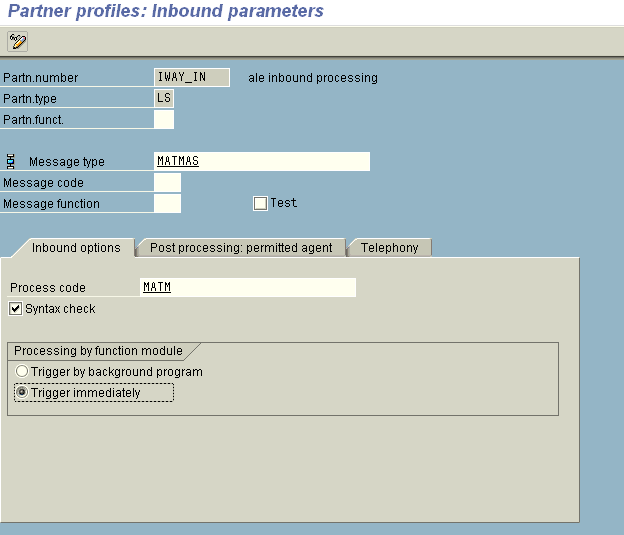
In the Message type field, enter the message type you want to use, for example, MATMAS.
You can click the icon to the right of each field to browse from a list of available message types.
The Inbound options tab is selected by default.
In the Process code field, enter the process code you want to use, for example, MATM.
You can click the icon to the right of each field to browse from a list of available process codes.
In the Processing by function module area, select one of the following options:
Trigger by background program.
In this case the adapter writes IDocs to the SAP database, which is processed immediately.
Trigger immediately.
In this case, the adapter waits for the SAP system to process IDocs. This can take anywhere from 1 to 15 minutes.
Click Save.
Event creation must be implemented by you or by SAP. An event is created from specific application programs (the event creator) and then published systemwide. Any number of receivers can respond to the event with their own response mechanisms. An event is usually defined as a component of an object type.
SAP pseudo events are events that are not processed by the SAP Event manager, but are called from an ABAP program or Remote Function call (using the Destination parameter).
The following topic lists and defines specific terminology related to SAP and SAP event handling.
Client and Server Programs
RFC programs for non-SAP systems can function as either the caller or the called program in an RFC communication. There are two types of RFC programs:
RFC Client
RFC Server
The RFC client is the instance that calls the RFC to execute the function that is provided by an RFC server. The functions that can be executed remotely are called RFC functions, and the functions provided by the RFC API are called RFC calls.
SAP Gateway
The SAP Gateway is a secure application server. No connections are accepted unless they have been preregistered previously from the SAP presentation Client. A server connection presents itself to the Gateway and exposes a Program Identifier. If the Program Identifier is found in the list of registered Program IDs, the Gateway server then offers a connection to the server, which "Accepts" a connection. This ProgramID is then linked with an RFC Destination within SAP, which enables SAP Function Modules and ALE documents (IDocs or BAPI IDocs) to be routed to the destination. The RFC Destination functions as a tag to mask the Program ID to SAP users.
An RFC server program can be registered with the SAP gateway and wait for incoming RFC call requests. An RFC server program registers itself under a Program ID at an SAP gateway and not for a specific SAP system.
In SAPGUI, the destination must be defined with transaction SM59, using connection type T and Register Mode. Moreover, this entry must contain information on the SAP gateway at which the RFC server program is registered.
Program IDs and Load Balancing
If the Gateway Server has a connection to a particular server instance and another server instance presents itself to the gateway, the gateway offers the connection and then begins functioning in Load Balancing mode. Using a proprietary algorithm, the Gateway sends different messages to each server depending on demand and total processing time. This may cause unpredictable results when messages are validated by schema and application.
When configuring multiple events in the Oracle Application Server using a single SAP program ID, SAP load balances the event data. For example, if multiple remote function calls or BAPIs use the same program ID (for example, ORACLETDS) and multiple SAP listeners are configured with this progamID, then SAP sends one request to one listener and the next to another listener, and so on.
There is a load balancing algorithm present in the SAP Gateway Server. This mechanism is proprietary to SAP application development and might work by comparing total throughput of the connection, the number of times in wait state, and so on. This means one connection might receive nine messages and a second connection might receive one message. If five of the nine messages are rejected for schema validation and the one message on the other connection is rejected for schema validation, you might suspect that you are missing SAP event handling messages.
Connection Pooling
A connection pool is a set of client connections to a specific destination. The pool may automatically create new connections to the specified remote system or return an already existing connection. It also provides methods to return a connection back to the pool when it is no longer needed.
A connection pool can check which connections are no longer in use and can be closed to save system resources. The time period after which the pool checks the connections as well as the time after which a connection will time out can be configured by the calling application.
A pool is always bound to one user ID and password, meaning that all connections taken from this pool will also use these credentials. An SAP connection is always bound to an SAP user ID and an SAP Client number.
If you log on with a pool size that is set to 1, no connection pool is created (1 userid – 1 process thread). If you log on with a pool size that is greater than 1, a pool is created with a size of n, which is the number you specified.
For more information about connection pooling, see the SAP JCO API documentation.
To enable your SAP system to issue the following calls or interfaces to the SAP event adapter, you must register your program ID under an RFC destination.
Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPI)
The RFC destination is a symbolic name (for example, ORACLETDS) that is used to direct events to a target system, masking the program ID. The Program ID is configured in both SAPGUI and the event adapter.
Registering Your Program ID
Select Tools, Administration, Network, and then RFC destination.
Execute the SM59 transaction.
The Display and maintain RFC destinations window opens.
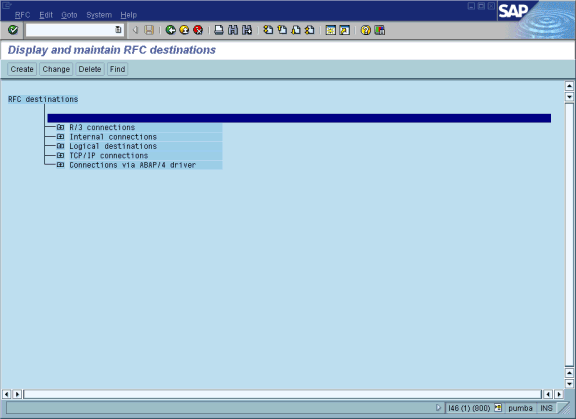
Select TCP/IP connections and click Create.
The RFC Destination window opens.
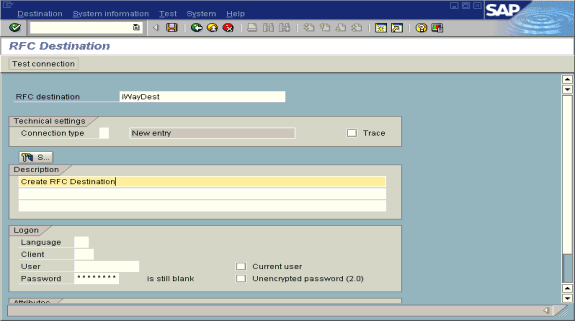
In the RFC destination field, type a name, for example, ORACLETDS.
The value you enter in this field is case sensitive.
In the Connection type field, enter T for destination type TCP/IP.
In the Description field, type a brief description.
Click Save from the tool bar or select Save from the Destination menu.
The RFC Destination ORACLETDS window opens.
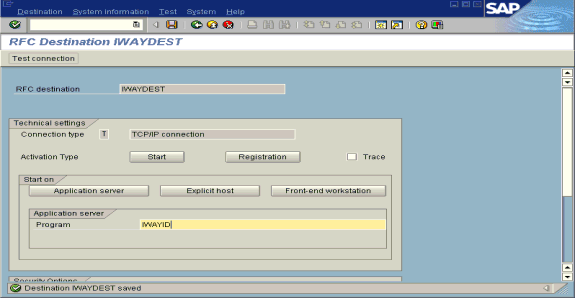
Click Save from the tool bar or select Save from the Destination menu.
Ensure your event adapter is running.
Verify that the SAP system and the OracleAS Adapter for SAP are communicating.
In the SAP Server, the SE37 transaction enables you to send an RFC (Remote Function Call) or a BAPI (Business Application Programming Interface) to any RFC destination. See "Registering Your Program ID" for more information on RFC destination.
Testing the SAP Event Adapter by Sending an RFC or a BAPI Manually
To test the SAP event adapter:
In the Function Builder, select a function module, for example, RFC_CUSTOMER_GET.
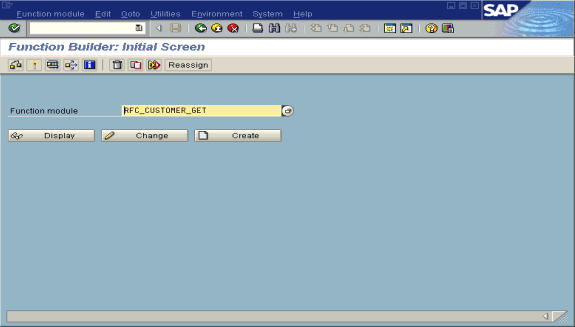
To choose single test, press F8 and click the Single Test icon or choose Function module, select Test and then Single Test.
Enter input data for the particular RFC modules, for example, AB*.
To execute, press F8.
The Test Function Module: Initial Screen window opens.
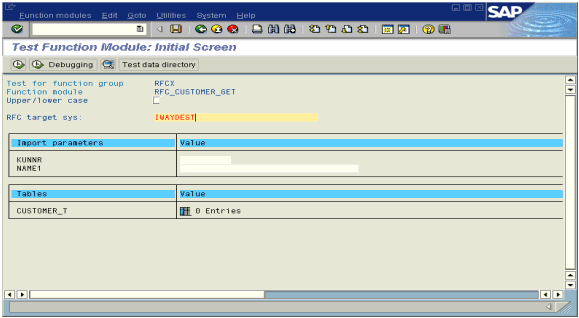
Enter data into the SAP GUI and click the Execute button.
The function name and input data are transferred through RFC to create an XML document on the Oracle Application Server with the parameters input in SAPGUI.
The SAP event adapter receives IDocs (Intermediate Documents) from SAP. To configure an SAP system to send IDocs to the SAP event adapter, use the ALE (Application Link Embedding) configuration to:
A port identifies where to send messages. This port can be used only if an RFC destination was created previously.
Defining a Port
To define a port:
In the ALE configuration, choose Tools, Business Communications, IDocs Basis, IDoc, and then Port Definition.
You can also execute the WE21 transaction.
The Creating a tRFC port window opens.
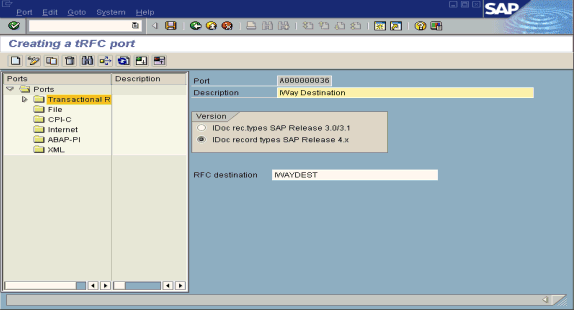
In the left pane under Ports, select Transactional RFC and click Create.
Select Generate port name.
The system generates the port name.
Enter the IDoc version you want to send through this port.
Click the destination you created, for example, ORACLETDS.
Save the session, making note of the system-generated RFC port.
One type of partner is a logical system. A logical system manages one or more RFC destinations.
Creating a Logical System
To create a logical system called ORACLETDS:
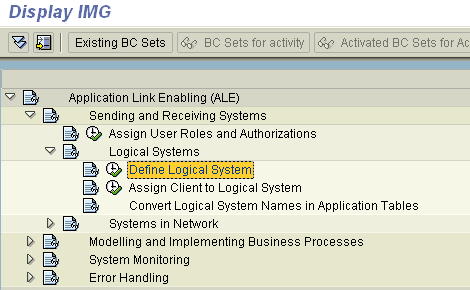
In the ALE configuration, enter the area menu selection SALE transaction.
Select SAP Reference IMG.
Expand the following nodes: Basis Components, Application Link Enabling (ALE), Sending and Receiving Systems, Logical Systems, and Define Logical System.
Click the check mark beside Define Logical System.
The Change View "Logical Systems": Overview window opens displaying a list of logical systems and their names.
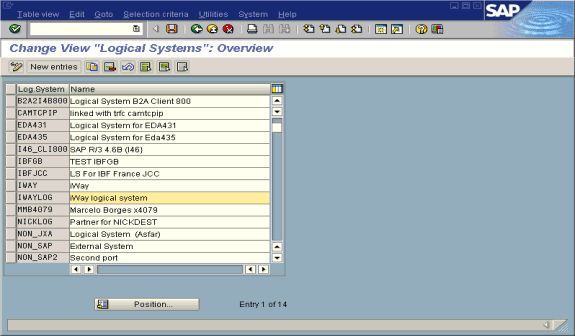
Click New entries.
The New Entries: Overview of Added Entries window opens with Log.System and Name columns for new log system.
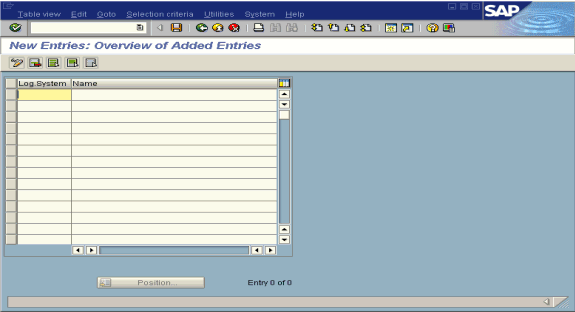
Type an entry for Log System, for example, ORACLETDS.
In the Name column, type a name (description) for the partner profile.
Click Save to save the session.
A partner profile is a definition of parameters for the electronic interchange of data with a trading partner using the IDoc interface.To communicate with a partner using the IDoc interface, you must create a partner profile.
Creating a Partner Profile
To create a partner profile:
In SAP GUI, choose Tools, Business Communication, IDoc Basis, and Partner profile.
You can also execute the WE21 transaction.
The Partner profiles: Outbound parameters window opens with fields for specifying details for the partner profile.
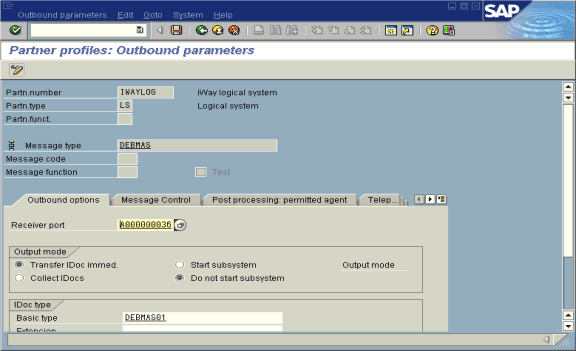
Select Partner type LS (Logical system).
Press F5 (Create).
For Type, enter USER.
For Agent, enter the current user ID, or you may select another agent type.
Under the outbound parameter table control, select Create outbound parameter.
Partn.type is LS, and the Message type is DEBMAS, which is the IDoc document type.
Leave Partn.funct blank.
Click the Outbound options tab.
Depending on your performance requirements, click Transfer IDoc Immed or Collect IDocs.
For the IDoc, type a message type, for example, DEBMAS.
Type a receiver port, for example, A000000036.
Click Save to save the session.
The Partner profiles summary window opens and displays information for the logical system that you created.
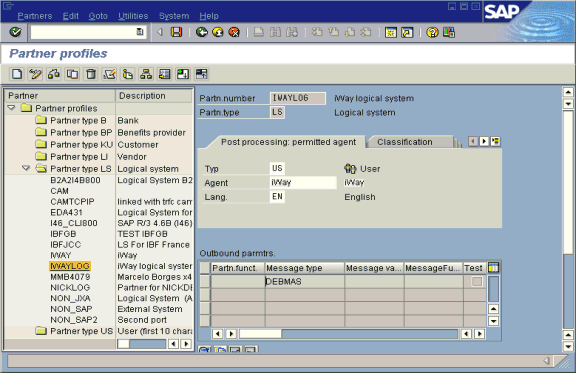
When using collected IDocs on any platform during inbound processing (service mode), if the DOCNUM field does not have a unique document number for each IDoc, the system creates an IDoc for each header record in the collected IDoc file and duplicates the data for each IDoc.
Make sure the DOCNUM field is included in the EDI_DC40 structure and that each IDoc has a unique sequence number within the collected IDoc file.
You must create a distribution model for the partner and message type you designated.
Creating a Distribution Model
To create a distribution model called ORAMOD:
In SAP GUI, choose Tools, AcceleratedSAP, Customizing, and then Project Management.
You can also execute the BD64 transaction.
The Display Distribution Model window opens.
Select Create model view.
If required, switch the processing mode to edit within Distribution Model/Switch Processing Mode.
Type a short text string and a technical name for your new model view.
Click Save.
The Distribution Model Changed window opens with a tree structure of the distribution model.
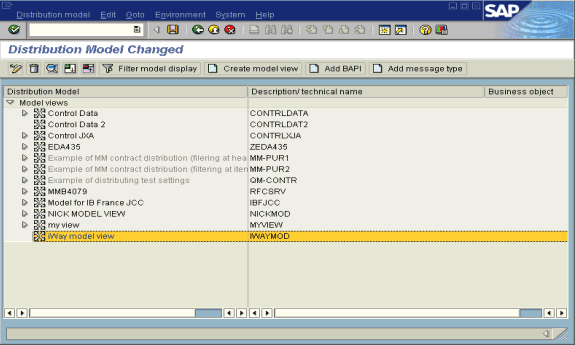
In the Distribution Model tree, select a new model view.
On the right, select Add message type.
The Add Message Type box opens displaying fields for specifying the sender and receiver of the message, as well as the message type.
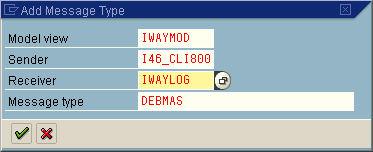
In the Sender field, provide the sender that points to the SAP system, which sends the IDoc, for example, I46_CLI800.
In this case, the sender is an SAP 4.6B system.
In the Receiver field, provide the logical system, for example, ORACLETDS.
In the Message type field, provide the type of IDoc, for example, DEBMAS.
Click the check mark.
Click Save.
The Change Distribution Model window opens displaying the new model view to use to send message type, DEBMAS, from the I46_CLI800 SAP system to the ORACLETDS logical system.
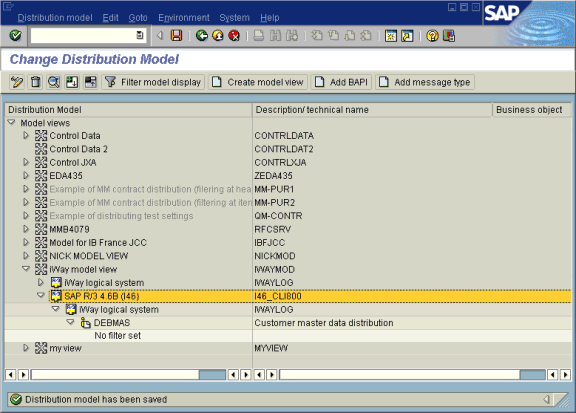
You are now ready to test the connection to the logical system.
In the SAP Server, the BD12 transaction enables you to send IDocs to any logical system, for example, to an event adapter.
Testing the SAP ALE Configuration
To test the SAP Application Link Embedding (ALE) configuration:
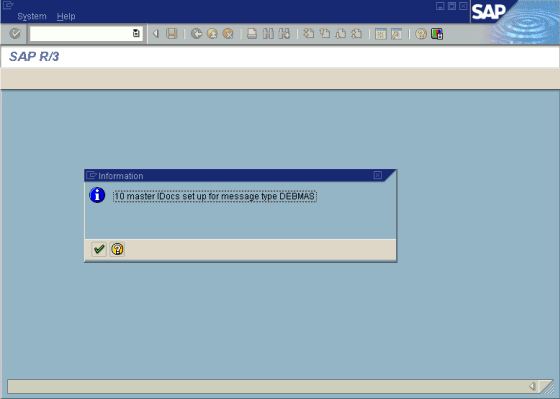
In the Send Customers window, type the IDoc message type, for example, DEBMAS in the Output type field.
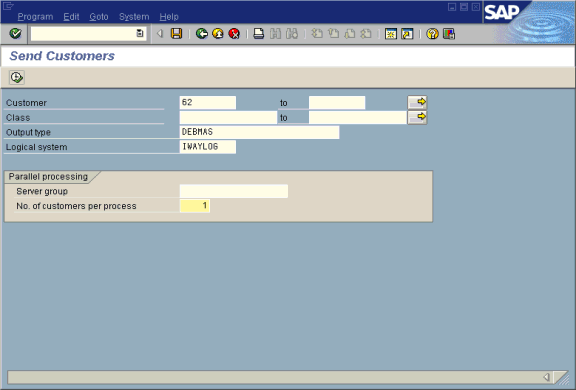
In the Logical system field, type the logical system, for example, ORACLETDS.
Click Run.
The SAP event adapter receives the IDoc in XML format. No response is expected from the event adapter.
A confirmation window displays.